Giải các phương trình: x( x 2 -6 ) – x - 2 2 = x + 1 3

Những câu hỏi liên quan
3.15 giải các phương trình sau :
a) ( x - 6 ) ( 2x - 5 ) ( 3x + 9 ) = 0
b) 2x( x - 3 ) + 5( x - 3 ) = 0
c) ( x^2 - 4 ) - ( x - 2 ) ( 3 - 2x ) =0
3.16 tìm m để phương trình sau có nghiệm :
x=-7 ( 2m - 5 )x - 2m^2 + 8
3.17 giải các phương trình sau :
a) ( 2x - 1 )^2 - ( 2x + 1 ) = 0
\(a,\left(x-6\right)\left(2x-5\right)\left(3x+9\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-6=0\Leftrightarrow x=6\\2x-5=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\3x+9=0\Leftrightarrow x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,2x\left(x-3\right)+5\left(x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+5\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\Leftrightarrow x=3\\2x+5=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(c,x^2-4-\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)-\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2-3+2x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x=-7\left(2m-5\right)x-2m^2+8\Leftrightarrow x+7\left(2m-5\right)=8-2m^2\Leftrightarrow x\left(14m-34\right)=8-2m^2\)
\(ycđb\Leftrightarrow14m-34\ne0\Leftrightarrow m\ne\dfrac{34}{14}\)\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{8-2m^2}{14m-34}\)
\(3.17\Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x+1-2x-1=0\Leftrightarrow4x^2-6x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(4x-6\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
3.15:
a, \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-6=0\\2x-5=0\\3x+9=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\x=-\dfrac{9}{3}=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b, \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(2x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\2x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c, \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)-\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2-3+2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\3x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
3.16
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2m-5\right).-7-2m^2+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-14m+35-2m^2+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-14m-2m^2+43=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2\left(7m+m^2\right)=-43\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\left(7-m\right)=\dfrac{43}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{m\left(7-m\right)}{1}-\dfrac{43}{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{14m-2m^2}{2}-\dfrac{43}{2}=0\)
pt vô nghiệm
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình:
Giải các phương trình:
\(x^2-2x+3=\frac{6}{x^2-2x+4}\)
Đặt \(y=x^2-2x+3=\left(x-1\right)^2+2\ge2\), ta có:
\(x^2-2x+3=\frac{6}{x^2-2x+4}\Leftrightarrow y=\frac{6}{y+1}\Leftrightarrow y\left(y+1\right)=6\Leftrightarrow y^2+y-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(y+3\right)\left(y-2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y=2\\y=-3\end{cases}\Rightarrow y=2\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=1}\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{1\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
bài 1 giải các phương trình sau:h,left(dfrac{3}{4}x-1right)left(dfrac{5}{3}x+2right)0bài 2 giải các phương trình sau:b,3x-152x(x-5) m,(1-x)(5x+3)(3x-7)(x-1)d,x(x+6)-7x-420 p,left(2x-1right)^2-40f,x^3+2x^2-left(x-2right)0 r,left(2x-1right)^249h,(3x-1)(6x+1)(x+7)(3x-1) t,left(5x-3right)^2-left(4x-7right)^20j,left(2x-5right)^2-left(x+2right)^20 u,x^2-10x+160w,x...
Đọc tiếp
bài 1 giải các phương trình sau:
h,\(\left(\dfrac{3}{4}x-1\right)\left(\dfrac{5}{3}x+2\right)=0\)
bài 2 giải các phương trình sau:
b,3x-15=2x(x-5) m,(1-x)(5x+3)=(3x-7)(x-1)
d,x(x+6)-7x-42=0 p,\(\left(2x-1\right)^2-4=0\)
f,\(x^3+2x^2-\left(x-2\right)=0\) r,\(\left(2x-1\right)^2=49\)
h,(3x-1)(6x+1)=(x+7)(3x-1) t,\(\left(5x-3\right)^2-\left(4x-7\right)^2=0\)
j,\(\left(2x-5\right)^2-\left(x+2\right)^2=0\) u,\(x^2-10x+16=0\)
w,\(x^2-x-12=0\)
Bài `1:`
`h)(3/4x-1)(5/3x+2)=0`
`=>[(3/4x-1=0),(5/3x+2=0):}=>[(x=4/3),(x=-6/5):}`
______________
Bài `2:`
`b)3x-15=2x(x-5)`
`<=>3(x-5)-2x(x-5)=0`
`<=>(x-5)(3-2x)=0<=>[(x=5),(x=3/2):}`
`d)x(x+6)-7x-42=0`
`<=>x(x+6)-7(x+6)=0`
`<=>(x+6)(x-7)=0<=>[(x=-6),(x=7):}`
`f)x^3-2x^2-(x-2)=0`
`<=>x^2(x-2)-(x-2)=0`
`<=>(x-2)(x^2-1)=0<=>[(x=2),(x^2=1<=>x=+-2):}`
`h)(3x-1)(6x+1)=(x+7)(3x-1)`
`<=>18x^2+3x-6x-1=3x^2-x+21x-7`
`<=>15x^2-23x+6=0<=>15x^2-5x-18x+6=0`
`<=>(3x-1)(5x-1)=0<=>[(x=1/3),(x=1/5):}`
`j)(2x-5)^2-(x+2)^2=0`
`<=>(2x-5-x-2)(2x-5+x+2)=0`
`<=>(x-7)(3x-3)=0<=>[(x=7),(x=1):}`
`w)x^2-x-12=0`
`<=>x^2-4x+3x-12=0`
`<=>(x-4)(x+3)=0<=>[(x=4),(x=-3):}`
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
`m)(1-x)(5x+3)=(3x-7)(x-1)`
`<=>(1-x)(5x+3)+(1-x)(3x-7)=0`
`<=>(1-x)(5x+3+3x-7)=0`
`<=>(1-x)(8x-4)=0<=>[(x=1),(x=1/2):}`
`p)(2x-1)^2-4=0`
`<=>(2x-1-2)(2x-1+2)=0`
`<=>(2x-3)(2x+1)=0<=>[(x=3/2),(x=-1/2):}`
`r)(2x-1)^2=49`
`<=>(2x-1-7)(2x-1+7)=0`
`<=>(2x-8)(2x+6)=0<=>[(x=4),(x=-3):}`
`t)(5x-3)^2-(4x-7)^2=0`
`<=>(5x-3-4x+7)(5x-3+4x-7)=0`
`<=>(x+4)(9x-10)=0<=>[(x=-4),(x=10/9):}`
`u)x^2-10x+16=0`
`<=>x^2-8x-2x+16=0`
`<=>(x-2)(x-8)=0<=>[(x=2),(x=8):}`
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau: \(\dfrac{x}{x^2+5x+6}=\dfrac{2}{x^2+3x+2}\)
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne-2;-3;-1\)
PT \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}-\dfrac{2}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2+x-2x-6}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-3x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+2\right)-3\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-2\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x=3\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (1)
ĐKXĐ của phương trình là: \(x\ne-2;x\ne-3;x\ne-1\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{x}{x^2+5x+6}=\dfrac{x}{x^2+3x+2}\)
<=> \(\dfrac{x}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{x}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
<=> \(\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{x\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
<=> \(\dfrac{x^2+x-x^2-3x}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x+1\right)}=0\)
<=> \(-2x=0\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
Ta thấy x=0 thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ
Vậy tập nghiệm của pt là S={0}
Đúng 1
Bình luận (2)
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) 3x + 6 = x +10
b) x(x + 1) - 2 (x + 1) = 0
\(a,\\ \Leftrightarrow3x-x=10-6\\ \Leftrightarrow2x=4\\ \Leftrightarrow x=2\\ b,\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (1)
\(a,\Leftrightarrow3x-x=10-6\\ \Leftrightarrow2x=4\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{4}{2}=2\)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = \(\left\{2\right\}\)
\(b,\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x+1=0\) hoặc \(\Leftrightarrow x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-1\) \(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = \(\left\{-1;2\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a)3x + 6 = x +10
⟺3x-x=10-6
⟺2x=4 ⟺x=2
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S={2}
b) x(x + 1) - 2 (x + 1) = 0
⟺(x+1)(x-2)=0
⟺x+1=0 ⟺x=-1
x-2=0 ⟺x=2
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S={2;-1}
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:
2
(
x
+
5
)
3
+
x
+
12
2
-
5
(
x
-
2
)
6
x
3
+
11
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình sau: 2 ( x + 5 ) 3 + x + 12 2 - 5 ( x - 2 ) 6 = x 3 + 11
Ta có:
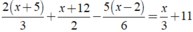
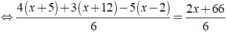
⇔ 4x + 20 + 3x + 36 - 5x + 10 = 2x + 66
⇔ 0x = 0
⇒ Phương trình đã cho vô số nghiệm.
Vậy phương trình đã cho vô số nghiệm.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau
1/ \(\sqrt{-x^2+2x+4}=x-2\)
2/ \(\left|x^2-5x+9\right|=6-x\)
cho phương trình ẩn x: \(x^2-\left(2m+1\right)x+m^2+5m=0\)
a, giải phương trình với m = -2
b, tìm m để phương trình có hai nghiệm sao cho tích các nghiệm bằng 6
a, \(x^2-\left(2m+1\right)x+m^2+5m=0\)
Với m=2
\(x^2-\left[2.\left(-2\right)+1\right]x+\left(-2\right)^2+5.\left(-2\right)=0\)
\(x^2+3x-6=0\)
\(\Delta=3^2-4.1.\left(-6\right)\)
\(=9+24\)
\(=33>0\Rightarrow\sqrt{\Delta}=\sqrt{33}\)
\(\Rightarrow\)Phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt:
\(x_1=\dfrac{-3+\sqrt{33}}{2}\)
\(x_2=\dfrac{-3-\sqrt{33}}{2}\)
Vậy khi m=-2 thì phương trình có nghiệm là \(x_1=\dfrac{-3+\sqrt{33}}{2};x_2=\dfrac{-3-\sqrt{33}}{2}\)
b,Ta có \(\Delta=\left[-\left(2m+1\right)\right]^2-4\left(m^2+5m\right)\)
\(=4m^2+4m+1-4m^2-20m\)
\(=1-16m\)
Phương trình có 2 nghiệm\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1-16m\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\le\dfrac{1}{16}\)
Khi đó hệ thức viet ta có tích các nghiệm là\(m^2+5m\)
Mà tích các nghiệm bằng 6, do đó \(m^2+5m=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2+5m-6=0\)
Ta thấy \(a+b+c=1+5+\left(-6\right)=0\) nên \(m_1=1;m_2=-6\)
Đối chiếu với điều kiện \(m\le\dfrac{1}{16}\) thì \(m=-6\) là giá trị cần tìm
-Chúc bạn học tốt-
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau: \(7x+6\sqrt{x+5}=x^2+30\)
\(7x+6\sqrt{x+5}=x^2+30\left(đk:x\ge-5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6\sqrt{x+5}=x^2-7x+30\)
Ta thấy 2 vế đều dương nên bình phương lên ta được:
\(36x+180=x^4+49x^2+900-14x^3+60x^2-420x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4-14x^3+109x^2-456x+720=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3\left(x-4\right)-10x^2\left(x-4\right)+69x\left(x-4\right)-180\left(x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x^3-10x^2+69x-180\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left[x^2\left(x-4\right)-6x\left(x-4\right)+45\left(x-4\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)^2\left(x^2-6x+45\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=4\left(tm\right)\) (do \(x^2-6x+45=\left(x^2-6x+9\right)+36=\left(x-3\right)^2+36\ge36>0\))
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) \(\sqrt {2 - x} + 2x = 3\)
b) \(\sqrt { - {x^2} + 7x - 6} + x = 4\)
a) \(\sqrt {2 - x} + 2x = 3\)\( \Leftrightarrow \sqrt {2 - x} = 3 - 2x\) (1)
Ta có: \(3 - 2x \ge 0 \Leftrightarrow x \le \frac{3}{2}\)
Bình phương hai vế của (1) ta được:
\(\begin{array}{l}2 - x = {\left( {3 - 2x} \right)^2}\\ \Rightarrow 2 - x = 9 - 12x + 4{x^2}\\ \Leftrightarrow 4{x^2} - 11x + 7 = 0\\ \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l}x = 1\left( {TM} \right)\\x = \frac{7}{4}\left( {KTM} \right)\end{array} \right.\end{array}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là \(S = \left\{ 1 \right\}\)
b) \(\sqrt { - {x^2} + 7x - 6} + x = 4\)\( \Leftrightarrow \sqrt { - {x^2} + 7x - 6} = 4 - x\) (2)
Ta có: \(4 - x \ge 0 \Leftrightarrow x \le 4\)
Bình phương hai vế của (2) ta được:
\(\begin{array}{l} - {x^2} + 7x - 6 = {\left( {4 - x} \right)^2}\\ \Leftrightarrow - {x^2} + 7x - 6 = 16 - 8x + {x^2}\\ \Leftrightarrow 2{x^2} - 15x + 22 = 0\\ \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l}x = 2\left( {TM} \right)\\x = \frac{{11}}{2}\left( {KTM} \right)\end{array} \right.\end{array}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là \(S = \left\{ 2 \right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)




























