Giải phương trình
|-(m+3)2|= 4|m-2|
Cho phương trình mx2-2(m-1)x+m-4=0
a, Giải phương trình khi m=1
b, Tìm m để phương trình có 2 nghiệm x1;x2 và x1+2x2=3
Lời giải:
a. Khi $m=1$ thì pt trở thành:
$x^2-3=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2=3\Leftrightarrow x=\pm \sqrt{3}$
b.
Để pt có 2 nghiệm $x_1,x_2$ thì:
\(\left\{\begin{matrix}
m\neq 0\\
\Delta'=(m-1)^2-m(m-4)=2m+1\geq 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix}
m\neq 0\\
m\geq \frac{-1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Áp dụng định lý Viet, với $x_1,x_2$ là nghiệm của pt thì:
$x_1+x_2=\frac{2(m-1)}{m}$
$x_1x_2=\frac{m-4}{m}$
Khi đó:
$x_1+2x_2=3$
$\Leftrightarrow x_2=3-(x_1+x_2)=3-\frac{2(m-1)}{m}=\frac{m+2}{m}$
$x_1=\frac{2(m-1)}{m}-x_2=\frac{m-4}{m}$
$\frac{m-4}{m}=x_1x_2=\frac{m-4}{m}.\frac{m+2}{m}$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{m-4}{m}(\frac{m+2}{m}-1)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{m-4}{m}.\frac{2}{m}=0$
$\Leftrightarrow m=4$ (tm)
Câu 3 : (2 điểm ) Cho phương trình ẩn x : x2 – 5x + m – 2 = 0 (1) Tìm m để phương trình (1) có 1 nghiệm duy nhất Giải phương trình (1) khi m = 4
ý 1: Để pt (1) có 1 nghiệm duy nhất thì \(\Delta=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(-5\right)^2-4m+8=-4m+33\)
\(\Rightarrow33-4m=0\Rightarrow m=\dfrac{33}{4}\)
ý 2: Khi \(m=4\Rightarrow x^2-5x+2=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(-5\right)^2-8=17\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{17}}{2}\\x=\dfrac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{17}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy...
x^2 - 2(m-2)x + m^2 - 3m + 5=0.
Giải phương trình với m=3
b) Tìm giá trị của m để phương trình có nghiệm No =-4
c) Tìm m để phương trình có nghiệm kép
Cho phương trình: \(x^2\) - 2 ( m -1 ) x - m -3 = 0 (1)
a) Giải phương trình với m = -3
b) Tìm m để phương trình (1) có hai nghiệm phân biệt x1 và x2 thỏa mãn: \(\left(x_1-x_2\right)^2\) = 4\(m^2\) - 5 x1 + x2
a, Thay \(m=-3\) vào \(\left(1\right)\)
\(x^2-2.\left(m-1\right)x-m-3=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-2.\left(-3-1\right)x+3-3=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2+8x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x+8\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-8\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy với \(m=-3\) thì \(x=0;x=-8\)
b,
\(\Delta'=\left[-\left(m-1\right)\right]^2-1.\left(-m-3\right)\\ =m^2-2m+1+m+3\\ =m^2-m+4\)
phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt
\(\Delta'>0\\ m^2-m+4>0\\ \Rightarrow m^2-2.\dfrac{1}{2}m+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{7}{2}>0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(m-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{7}{2}>0\left(lđ\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\forall m\)
Áp dụng hệ thức Vi ét :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m-1\right)\\x_1x_2=-m-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(x_1-x_2\right)^2=4m^2-5\left(x_1+x_2\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow x_1^2+2x_1.x_2+x^2_2-4x_1x_2=4m^2-5\left(x_1+x_2\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2=4m^2-5\left(x_1+x_2\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2.\left(m-1\right)\right)^2-4.\left(-m-3\right)=4m^2-5.\left(-m-3\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow4m^2-8m+4+4m+12-4m^2-5m-15=0\\ \Leftrightarrow-9m+1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m=\dfrac{1}{9}\)
Vậy \(m=\dfrac{1}{9}\)
a.
Thế m = -3 vào phương trình (1) ta được:
\(x^2-2\left(-3-1\right)x-\left(-3\right)-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x^2+8x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+8\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow x_1=0,x_2=-8\)
b.
Để phương trình (1) có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì:
\(\Delta>0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[-2\left(m-1\right)\right]^2-4.1.\left(-m-3\right)>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4.\left(m^2-2m+1\right)+4m+12>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-8m+4+4m+12>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-4m+16>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2m\right)^2-4m+1+15>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2m-1\right)^2+15>0\)
Vì \(\left(2m-1\right)^2\) luôn lớn hơn hoặc bằng 0 với mọi m nên phương trình (1) có nghiệm với mọi m.
Theo viét:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2m-2\\x_1x_2=-m-3\end{matrix}\right.\) (I)
có:
\(\left(x_1-x_2\right)^2=4m^2-5x_1+x_2\)
<=> \(x_1^2-2x_1x_2+x_2^2-4m^2+5x_1-x_2=0\)
<=> \(x_1^2-2x_1x_2+x_2^2+2x_1x_2-2x_1x_2-4m^2+5x_1-x_2=0\)
<=> \(\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2-4m^2+5x_1-x_2=0\)
<=> \(\left(2m-2\right)^2-4.\left(-m-3\right)-4m^2+5x_1-x_2=0\)
<=> \(4m^2-8m+4+4m+12-4m^2+5x_1-x_2=0\)
<=> \(-4m+16+5x_1-x_2=0\)
<=> \(5x_1-x_2=4m-16\) (II)
Từ (I) và (II) ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5x_1-x_2=4m-16\left(2\right)\\x_1+x_2=2m-2\left(3\right)\\x_1x_2=-m-3\left(4\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Từ (2) ta có:
\(x_1=\dfrac{4m-16+x_2}{5}=\dfrac{4}{5}m-3,2+\dfrac{1}{5}x_2\) (x)
Thế (x) vào (3) được:
\(\dfrac{4}{5}m-3,2+\dfrac{1}{5}x_2+x_2=2m-2\)
<=> \(\dfrac{4}{5}m-3,2+\dfrac{1}{5}x_2+x_2-2m+2=0\)
<=> \(-1,2m-1,2+1,2x_2=0\)
<=> \(x_2=1,2m+1,2\) (xx)
Thế (xx) vào (3) được:
\(x_1+1,2m+1,2=2m-2\)
<=> \(x_1+1,2m+1,2-2m+2=0\)
<=> \(x_1-0,8m+3,2=0\)
<=> \(x_1=-3,2+0,8m\) (xxx)
Thế (xx) và (xxx) vào (4) được:
\(\left(-3,2+0,8m\right)\left(1,2m+1,2\right)=-m-3\)
<=> \(-3,84m-3,84+0,96m^2+0,96m+m+3=0\)
<=> \(0,96m^2-1,88m-0,84=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(-1,88\right)^2-4.0,96.\left(-0,84\right)=6,76\)
\(m_1=\dfrac{1,88+\sqrt{6,76}}{2.0,96}=\dfrac{7}{3}\left(nhận\right)\)
\(m_2=\dfrac{1,88-\sqrt{6,76}}{2.0,96}=-\dfrac{3}{8}\left(nhận\right)\)
T.Lam
a) \(2\left(x^2-2x\right)+\sqrt{x^2-2x-3}-9=0\)
b) \(3\sqrt{2+x}-6\sqrt{2-x}+4\sqrt{4-x^2}=10-3x\)
c) Cho phương trình: \(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{9-x}=\sqrt{-x^2+9x+m}\)
+) Giải phương trình khi m=9
+) Tìm m để phương trình có nghiệm
a, ĐK: \(x\le-1,x\ge3\)
\(pt\Leftrightarrow2\left(x^2-2x-3\right)+\sqrt{x^2-2x-3}-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2\sqrt{x^2-2x-3}+3\right).\left(\sqrt{x^2-2x-3}-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x^2-2x-3}=-\dfrac{3}{2}\left(l\right)\\\sqrt{x^2-2x-3}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-3=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\pm\sqrt{5}\left(tm\right)\)
b, ĐK: \(-2\le x\le2\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{2+x}-2\sqrt{2-x}=t\Rightarrow t^2=10-3x-4\sqrt{4-x^2}\)
Khi đó phương trình tương đương:
\(3t-t^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=0\\t=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2+x}-2\sqrt{2-x}=0\\\sqrt{2+x}-2\sqrt{2-x}=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2+x=8-4x\\2+x=17-4x+12\sqrt{2-x}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{6}{5}\left(tm\right)\\5x-15=12\sqrt{2-x}\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vì \(-2\le x\le2\Rightarrow5x-15< 0\Rightarrow\left(1\right)\) vô nghiệm
Vậy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm \(x=\dfrac{6}{5}\)
c, ĐK: \(0\le x\le9\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{9x-x^2}=t\left(0\le t\le\dfrac{9}{2}\right)\)
\(pt\Leftrightarrow9+2\sqrt{9x-x^2}=-x^2+9x+m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(-x^2+9x\right)+2\sqrt{9x-x^2}+9=m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-t^2+2t+9=m\)
Khi \(m=9,pt\Leftrightarrow-t^2+2t=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=0\\t=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}9x-x^2=0\\9x-x^2=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(tm\right)\\x=9\left(tm\right)\\x=\dfrac{9\pm\sqrt{65}}{2}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Phương trình đã cho có nghiệm khi phương trình \(m=f\left(t\right)=-t^2+2t+9\) có nghiệm
\(\Leftrightarrow minf\left(t\right)\le m\le maxf\left(t\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{9}{4}\le m\le10\)
1) Trong mặt phẳng tọa độ Oxy cho 3 đường thắng (4,): y =x + 2, (4, ): y = 2x+1, (4,): y =(m² + 2)x-2m +1 Tim m để ba đường thắng trên đồng quy.
2) Cho phương trình: x-2(2m +3)x+ 4n+ 3=0 a) Giải phương trinh khi m-3 b) Tim m để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biết Khi đó, Xét đấu của hai nghiệm
Bài 1: Giải và biện luận các phương trình sau:
a) m(m-x)= 3(x+3)-6m
b) mx-3m=2x-3
c) (m^2 -9)x=m^2 +3m
Bài 2: Giải và biện luận các phương trình sau:
a) m(m-1)=2(2x+1)
b) (m^2 - 9)x=m^2 +3m
c) m(m-1)= 2(4-x)
d) (m^2 -3m+2)x= m-2
Các cậu giúp tớ với ạ, không cần làm hết đâu ạ, mng biết câu nào thì làm hộ tớ với nhé, plss!
Vì hai bài giống nhau nên anh sẽ làm mẫu bài 1 nhé.
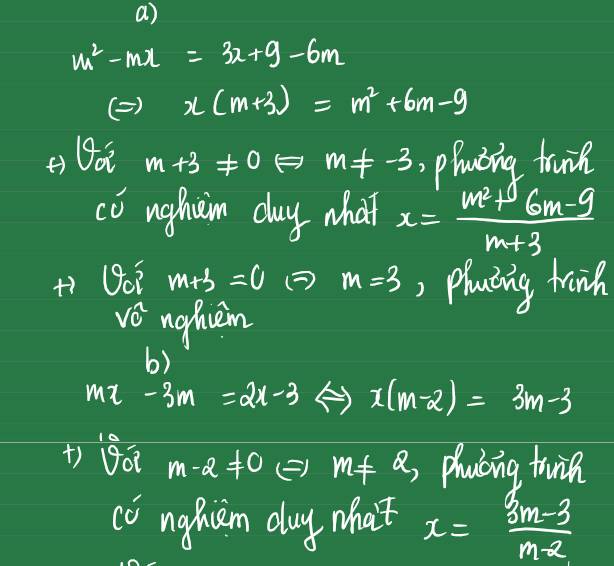
cho phương trình sau: x² - 2(m+1) -m - 1=0 a, Giải phương trình trên khi m=2 b, không giải phương trình tính giá trị biểu thức c,tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của phương trình tại m=4
a: Khi m=2 thì pt sẽ là x^2-6x-3=0
=>\(x=3\pm2\sqrt{3}\)