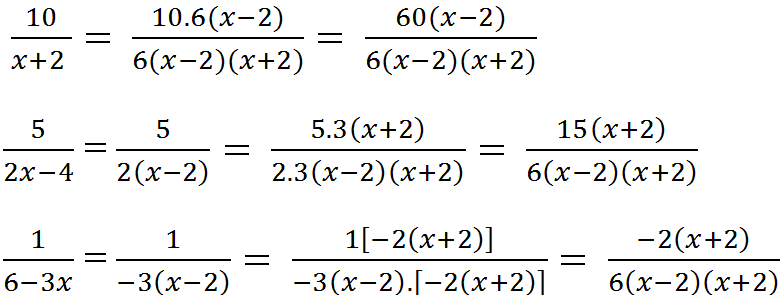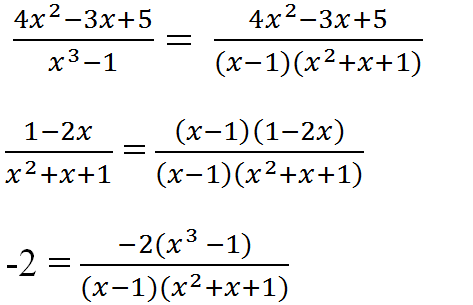Tìm x để phân thức \(Q=\dfrac{x^2+2x+1}{3x^2+2x-5}\) nhận gt dương

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Tìm x để biểu thức sau có gt dương:
\(A=x^2-3x\)
Tìm x để các biểu thức sau có gía trị âm:
\(D=x^2+\dfrac{5}{2}x\\ E=\dfrac{x-3}{x-2}\\ G=\left(2x-1\right)\left(3-2x\right)\)
a: A>0
=>\(x^2-3x>0\)
=>x(x-3)>0
TH1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\x-3>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\x>3\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>x>3
TH2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 0\\x-3< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 0\\x< 3\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>x<0
d: Để D<0 thì \(x^2+\dfrac{5}{2}x< 0\)
=>\(x\left(x+\dfrac{5}{2}\right)< 0\)
TH1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\x+\dfrac{5}{2}< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\x< -\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>Loại
Th2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 0\\x+\dfrac{5}{2}>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 0\\x>-\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(-\dfrac{5}{2}< x< 0\)
e: ĐKXĐ: x<>2
Để E<0 thì \(\dfrac{x-3}{x-2}< 0\)
TH1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3>=0\\x-2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=3\\x< 2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>Loại
TH2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3< =0\\x-2>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =3\\x>2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>2<x<=3
g: Để G<0 thì \(\left(2x-1\right)\left(3-2x\right)< 0\)
=>\(\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x-3\right)>0\)
TH1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-1>0\\2x-3>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>\dfrac{1}{2}\\x>\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(x>\dfrac{3}{2}\)
TH2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-1< 0\\2x-3< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< \dfrac{1}{2}\\x< \dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(x< \dfrac{1}{2}\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
Quy đồng mẫu thức các phân thức sau (có thể áp dụng quy tắc đổi dấu với một phân thức để tìm mẫu thức chung thuận tiện hơn)
a) \(\dfrac{4x^2-3x+5}{x^3-1},\dfrac{1-2x}{x^2+x+1},-2\)
b) \(\dfrac{10}{x+2},\dfrac{5}{2x-4},\dfrac{1}{6-3x}\)
a) Tìm MTC: x3 – 1 = (x – 1)(x2 + x + 1)
Nên MTC = (x – 1)(x2 + x + 1)
Nhân tử phụ:
(x3 – 1) : (x3 – 1) = 1
(x – 1)(x2 + x + 1) : (x2 + x + 1) = x – 1
(x – 1)(x2+ x + 1) : 1 = (x – 1)(x2 + x + 1)
Qui đồng:
b) Tìm MTC: x + 2
2x – 4 = 2(x – 2)
6 – 3x = 3(2 – x)
MTC = 6(x – 2)(x + 2)
Nhân tử phụ:
6(x – 2)(x + 2) : (x + 2) = 6(x – 2)
6(x – 2)(x + 2) : 2(x – 2) = 3(x + 2)
6(x – 2)(x + 2) : -3(x – 2) = -2(x + 2)
Qui đồng:
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
b1: cho phân thức:
P= (x+1/ x-1 + 2/ x^2-1 - x/ x+1 ) * x-1/ x+2
a, tìm ĐKXĐ
b, rút gọn
c, tính giá trị của P biết x^2 - 3x = 0
d, tìm x nguyên để P nhận giá trị nguyên
b2: cho phân thức:
Q= x^2+2x/2x+10 + x-5/x + 50-5x/2x(x+5)
a, tìm ĐKXĐ
b, tìm x để Q=0; Q=1/4
c,tìm x để Q>0; Q<0
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\pm1;-2\)
\(P=\left(\frac{x+1}{x-1}+\frac{2}{x^2-1}-\frac{x}{x+1}\right).\frac{x-1}{x+2}\)
\(=\left(\frac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right).\left(x+1\right)}+\frac{2}{\left(x-1\right).\left(x+1\right)}-\frac{x\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right).\left(x+1\right)}\right).\frac{x-1}{x+2}\)
\(=\left(\frac{x^2+2x+1}{\left(x-1\right).\left(x+1\right)}+\frac{2}{\left(x-1\right).\left(x+1\right)}-\frac{x^2-x}{\left(x-1\right).\left(x+1\right)}\right).\frac{x-1}{x+2}\)
\(=\left(\frac{x^2+2x+1+2-x^2+x}{\left(x-1\right).\left(x+1\right)}\right).\frac{x-1}{x+2}\)
\(=\frac{3x+3}{\left(x-1\right).\left(x+1\right)}.\frac{x-1}{x+2}=\frac{3.\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right).\left(x+1\right)}.\frac{x-1}{x+2}=\frac{3}{x+2}\)
c. \(x^2-3x=0\Leftrightarrow x.\left(x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=3\end{cases}}\)
Nếu x=0 thì: \(P=\frac{3}{x+2}=\frac{3}{0+2}=\frac{3}{2}\)
Nếu x=3 thì: \(P=\frac{3}{x+2}=\frac{3}{3+2}=\frac{3}{5}\)
d. Ta có: \(P=\frac{3}{x+2}\inℤ\)
Vì \(x\inℤ\Rightarrow x+2\inℤ\Rightarrow x+2\inƯ\left\{3\right\}\Rightarrow x+2\in\left\{\pm1;\pm3\right\}\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-3;-1;1;-5\right\}\)
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ \(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{-3;-5\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm điều kiện của x để phân thức sau xác định:
1) \(\dfrac{5-x}{x^2-3x}\)
2) \(\dfrac{3x}{2x+3}\)
1) \(\dfrac{5-x}{x^2-3x}=\dfrac{5-x}{x\left(x-3\right)}\left(đk:x\ne0,x\ne3\right)\)
2) \(\dfrac{3x}{2x+3}\left(đk:x\ne-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (1)
Cho biểu thức \(P=\dfrac{x^2+2x}{2x+10}+\dfrac{x-5}{x}+\dfrac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
a, Tìm điều kiện của x để giá trị của phân thức xác định
b, Tìm x để P = 0
c, Tìm x để \(P=-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
d, Tìm x để P > 0 ; P < 0
a) P xác định \(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x+5\ne0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x\ne-5\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy P xác định \(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x\ne-5\end{cases}}\)
b) \(P=\frac{x^2+2x}{2x+10}+\frac{x-5}{x}+\frac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x\left(x+2\right)}{2\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{x-5}{x}+\frac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x^2\left(x+2\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)2}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x^3+2x^2+2x^2-50+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
Có: \(P=0\)
\(\Rightarrow P=\frac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2+4x-5\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x^2+4x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-x\right)+\left(5x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)+5\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-1=0\\x+5=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=-5\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(P=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=-5\end{cases}}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1) Chúng minh: \(3x^2-2x+2\)luôn dương với mọi giá trị của x
2)Cho phân thức A = \(\frac{x^2+2x+1}{x^2-1}\).Tìm giá tri nguyên của x để A nhận giá trị nguyên
1)=2x^2+(x-1)^2+1
Tổng 2 số không âm và 1 luôn dương
2)
Tồn tại A=> x khác +-1
A=(x+1)/(x-1)=1+2/(x-1)
x-1={-2,-1,1,2}
x={-1,0,2,3}
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
thực hiện phép tính: a) dfrac{3x+5}{2x}-dfrac{5}{2x} B) dfrac{2x}{x+3}:dfrac{x}{x^2-9}...
Đọc tiếp
thực hiện phép tính: a) \(\dfrac{3x+5}{2x}-\dfrac{5}{2x}\) B) \(\dfrac{2x}{x+3}:\dfrac{x}{x^2-9}\) b) tìm GT của a để đa thức x3+2x2+x+a chia hết cho đa thức x2+1
Bài 1:
a: \(=\dfrac{3x+5-5}{2x}=\dfrac{3x}{2x}=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
b: \(=\dfrac{2x}{x+3}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}{x}=2\left(x-3\right)\)
Bài 2:
=>x^3+x+2x^2+2+a-2 chia hết cho x^2+1
=>a-2=0
=>a=2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm điều kiện của x để phân thức sau xác định:
a)\(\dfrac{3x^2+6x+12}{x^3-8}\)
b)\(\dfrac{x^2+2x+5}{2x^2+5x+3}\)
c)\(\dfrac{5x+1}{x^2-4}\)
`a,x^3-8 ne 0`
`=>x^3 ne 8`
`=>x ne 2`
`b,2x^2+5x+3 ne 0`
`=>2x^2+2x+3x+3 ne 0`
`=>2x(x+1)+3(x+1) ne 0`
`=>(x+1)(2x+3) ne 0`
`=>x ne -1,-3/2`
`c,x^2-4 ne 0`
`=>x^2 ne 4`
`=>x ne 2,-2`
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
a) ĐK:
\(x^3-8\ne0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\ne2\)
b) ĐK:
\(2x^2+5x+3\ne0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ne-1\\x\ne-\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) ĐK:
\(x^2-4\ne0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\ne\pm2\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne2\)
b) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-\dfrac{3}{2};-1\right\}\)
c) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{2;-2\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
tìm điều kiện để các phân thức sau có nghĩa và tìm mẫu chung của chúng:
a,\(\dfrac{5}{2x-4};\dfrac{4}{3x-9};\dfrac{7}{50-25x}\)
b,\(\dfrac{3}{2x+6};\dfrac{x-2}{x^2+6x+9}\)
c,\(\dfrac{x^4+1}{x^2-1};x^2+1\)