3x2-6x-2x+4
Chọn đa thức mà em cho là kết quả đúng:
| (2x3 – 2x + 1) – (3x2 + 4x – 1) = ? | 2x3 + 3x2 – 6x + 2 |
| 2x3 – 3x2 – 6x + 2 | |
| 2x3 – 3x2 + 6x + 2 | |
| 2x3 – 3x2 – 6x – 2 |
Đặt và thực hiện phép tính ta có :
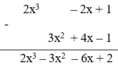
Vậy chọn đa thức thứ hai.
Tập nghiệm của phương trình 3 x 2 + 6 x + 16 + x 2 + 2 x = 2 x 2 + 2 x + 4 là:
A. 0 ; − 2
B. 0
C. − 2
D. ∅
Điều kiện: 3 x 2 + 6 x + 16 ≥ 0 x 2 + 2 x ≥ 0 x 2 + 2 x + 4 ≥ 0 ⇔ x ≤ − 2 x ≥ 0
Đặt t = x 2 + 2 x ( t ≥ 0 ) ⇔ t 2 = x 2 + 2 x
Phương trình trở thành: 3 t 2 + 16 + t = 2 t 2 + 4
⇔ 3 t 2 + 16 + t 2 + 2 t 3 t 2 + 16 = 4 t 2 + 16 ⇔ 2 t 3 t 2 + 16 = 0 ⇔ t = 0
Với t = 0 ⇔ x 2 + 2 x = 0 ⇔ x = 0 x = − 2
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là: S = 0 ; − 2
Đáp án cần chọn là: A
1) 3 - 2x + 4 + 6x = x + 7 + 3x
2) -6(1,5 - 2x) = 3(-15 + 2x)
3) 3(2x - 5) + 5(x -1) = 4(x + 1)
1/ 3-2x+4+6x=x+7+3x
⇔-2x+6x-x-3x=0
⇔0x=0 (Vô số nghiệm)
2/-6(1,5-2x)=3(-15+2x)
⇔-9+12x=-45+6x
⇔6x+36=0
⇔6(x+6)=0
⇔x+6=0
⇔x=-6
Vậy S ϵ {-6}
3/ 3(2x-5)+5(x-1)=4(x+1)
⇔6x-15+5x-5=4x+4
⇔7x=24
⇔x=\(\dfrac{24}{7}\)
Vậy S ϵ {\(\dfrac{24}{7}\)}
1) Ta có: \(3-2x+4+6x=x+7+3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+7=4x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+7-4x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x=0\)(luôn đúng)
Vậy: S={x|\(x\in R\)}
2) Ta có: \(-6\cdot\left(1.5-2x\right)=3\left(-15+2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9+12x=-45+6x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-9+45-6x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x+36=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x=-36\)
hay x=-6
Vậy: S={-6}
3) Ta có: \(3\left(2x-5\right)+5\left(x-1\right)=4\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x-15+5x-5=4x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow11x-20-4x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow7x-24=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow7x=24\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{24}{7}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{24}{7}\right\}\)
1) 3 - 2x + 4 + 6x = x + 7 + 3x
⇔-2x + 6x - x - 3x = 7 - 3 - 4
⇔0x = 0
⇔x ∈ R
Vậy ...
2) -6(1,5 - 2x) = 3(-15 + 2x)
⇔-9 + 12x = -45 + 6x
⇔6x = -36
⇔x = -6
Vậy ...
Câu 1: Giải hệ phương trình
a) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+3y=-5\\6x-5y=27\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) 3x2 + 4x = 0
c) x4 - 3x2 - 4 = 0
a) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+3y=-5\\6x-5y=27\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6x+9y=-15\\6x-5y=27\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}14y=-42\\2x+3y=-5\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-3\\2x+3.\left(-3\right)=-5\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-3\\2x-9=-5\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-3\\2x=4\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-3\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm là: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-3\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(3x^2+4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\3x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-\dfrac{4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là: \(S=\left\{0;-\dfrac{4}{3}\right\}\)
c) Đặt: \(x^2=t\left(t\ge0\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Ta có phương trình mới:
\(t^2-3t-4=0\)
Ta có: a - b + c = 1 + 3 - 4 = 0
\(\Rightarrow t_1=-1\left(loại\right);t_2=4\left(TM\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\pm2\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là: S = {2; -2}
a, \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+3y=-5\\6x-5y=27\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6x+9y=-15\left(1\right)\\6x-5y=27\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Lấy (1) - (2) ta được : \(14y=-15-27=-42\Leftrightarrow y=-3\)
\(\Rightarrow6x-27=-15\Leftrightarrow6x=12\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Vậy \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(2;-3\right)\)
b, \(3x^2+4x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x+4\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=0;x=-\dfrac{4}{3}\)
c, \(x^4-3x^2-4=0\Leftrightarrow x^4+x^2-4x^2-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x^2-4\right)+x^2-4=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\pm2;x^2+1>0\)
Vậy nghiệm của phương trình là x = -2 ; x = 2
1.(x2+3).(x4-3x2+9)
2.(2x+1).(4x2-2x+1)
3.(x2+2).(x4-2x2+4)
4.(3x+2).(9x2-6x+4)
\(1,=x^6+27\\ 2,=8x^3+1\\ 3,=x^6+8\\ 4,=27x^3+8\)
1. (x2 + 3)(x4 - 3x2 + 9)
= x6 + 27
2. (2x + 1)(4x2 - 2x + 1)
= 8x3 + 1
3. (x2 + 2)(x4 - 2x2 + 4)
= x6 + 8
4. (3x + 2)(9x2 - 6x + 4)
= 27x3 + 8
1: \(\left(x^2+3\right)\left(x^4-3x^2+9\right)=x^6+27\)
2: \(\left(2x+1\right)\left(4x^2-2x+1\right)=8x^3+1\)
3: \(\left(x^2+2\right)\left(x^4-2x^2+4\right)=x^6+8\)
4: \(\left(3x+2\right)\left(9x^2-6x+4\right)=27x^3+8\)
Cho A = x 2 + 1 3 x : x 2 + 1 x − 1 : x 3 − 1 x 2 + x : x 2 + 2 x + 1 x 2 + x + 1 và B = x + 3 x 2 − 1 : x + 4 x 2 + 6 x − x + 3 x 2 − 1 : x + 4 x − 4 . Khi x = 101, hãy so sánh A và B.
A. B < A
B. B > A
C.B = A
D. B ≤ A
a) 6x3:(-3x2)
b) (-9x2):6x
c) (-16x4):(-12x3)
d) (8x3+4x2-6x):2x
a) 6x³ : (-3x²) = [6 : (-3)] . (x³ : x²)
= -2x
b) (-9x²) : 6x
= (-9 : 6) . (x² : x)
= -3/2 x
c) (-16x⁴) : (-12x³)
= [-16 : (-12)] . (x⁴ : x³)
= 4/3 x
d) (8x³ + 4x² - 6x) : 2x
= 8x³ : 2x + 4x² : 2x - 6x : 2x
= 4x² + 2x - 3
Giải phương trình bằng cách đưa về phương trình tích :
3x2 + 2x - 1 = 0
x2 - 5x + 6 = 0
3x2 + 7x + 2 = 0
x2 - 4x + 1 = 0
2x2 - 6x + 1 = 0
3x2 + 4x - 4 = 0
3x2 + 2x - 1 = 0
=> 3x2 + 3x - x - 1 = 0
=> 3x(x + 1) - (x + 1) = 0
=> (3x - 1)(x + 1) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}3x-1=0\\x+1=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{3}\\x=-1\end{cases}}\)
x2 - 5x + 6 = 0
=> x2 - 2x - 3x + 6 = 0
=> x(x - 2) - 3(x - 2) = 0
=> (x - 3)(x - 2) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-3=0\\x-2=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=3\\x=2\end{cases}}\)
3x2 + 7x + 2 = 0
=> 3x2 + 6x + x + 2 = 0
=> 3x(x + 2) + (x + 2) = 0
=> (3x + 1)(x + 2) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}3x+1=0\\x+2=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{1}{3}\\x=-2\end{cases}}\)
1, \(3x^2+2x-1=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2+3x-x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+1\right)-\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+1=0\\3x-1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-1\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}}\)
2, \(x^2-5x+6=0\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-3x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)-3\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-2=0\\x-3=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=3\end{cases}}}\)
3, \(3x^2+7x+2=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2+6x+x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+2\right)+\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+2=0\\3x+1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-2\\x=-\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}}\)
\(x^2-4x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-4x+4\right)=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\sqrt{3}+2;x=2-\sqrt{3}\)
\(2x^2-6x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-12x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-3\right)^2=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{\sqrt{7}+3}{2};x=\frac{3-\sqrt{7}}{2}\)
\(3x^2+4x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-2x+6x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(3x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-2;x=\frac{2}{3}\)
Tìm x, biết:
a) 2(5x-8)-3(4x-5) = 4(3x-4) + 11;
b) 2 x ( 6 x - 2 x 2 ) + 3 x 2 ( x - 4 ) = 8;
c) 2 ( x 3 - 1 ) - 2 x 2 ( x + 2 x 4 ) + ( 4 x 5 + 4 ) x = 6;
d)(2x)2(4x-2)-(x3 -8x2) = 15.
a) x = 2 7 b) x = 2.
c) x = 2 d) x = 1.
Tìm x, biết:
a)(x+3)3-x(3x+1)2+(2x+1)(4x2-2x+1)-3x2=54
b)(x-3)3-(x-3)(x2+6x+9)+6(x+1)2+3x2=-33
\(a,\Rightarrow x^3+9x^2+27x+27-9x^3-6x^2-x+8x^3+1-3x^2=54\\ \Rightarrow26x=26\Rightarrow x=1\\ b,\Rightarrow x^3-9x^2+27x-27-x^3+27+6x^2+12x+6+3x^2=-33\\ \Rightarrow39x=-39\Rightarrow x=-1\)