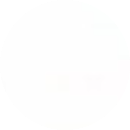
\(\dfrac{-6}{x}=\dfrac{30}{60}\)
Tìm x

Những câu hỏi liên quan
4/ Tìm sso nguyên x, biết :
a/ \(\dfrac{x}{10}\) = \(\dfrac{-11}{5}\) ; b/ \(\dfrac{-6}{x}\) = \(\dfrac{30}{60}\)
a: =>x/10=-22/10
hay x=-22
b: =>-6/x=6/12
=>x=-12
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(a,\dfrac{x}{10}=\dfrac{-11}{5}\Rightarrow x.5=10.\left(-11\right)=-110\\ \Rightarrow-22\\ b,\dfrac{-6}{x}=\dfrac{30}{60}\Rightarrow-6.60=x.30=-120\\ \Rightarrow x=-4\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(\dfrac{-6}{x}=\dfrac{30}{60}\)
Tìm số nguyên x , biết
-6/x = 30/60
- cách 1: rút gọc phân số vế phải
=> 30/60= -6/-12
=>x= -12
vậy x = -12
- cách 2 : tính theo công thức a/b=c/d
x= 60 . (-6) /30= -12
vậy..
Đúng 0
Bình luận (4)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Tìm số nguyên x, biết: \(\dfrac{-6}{x}=\dfrac{30}{60}\).
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{-6}{x}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-12\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
15: nếu \(\dfrac{x}{-15}\)=\(\dfrac{-60}{x}\) thì kết quả x bằng:
A) x=30 B) x=30 hoặc x=-1 C) x=3= hoặc x=-30 D) x=\(\dfrac{60}{15}\)
\(x^2=900\Leftrightarrow x^2=30^2\Rightarrow x=30\)
Chọn A
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
bài 45: Tìm x, biết:
a) x=\(\dfrac{-1}{2}+\dfrac{3}{4}\); b) \(\dfrac{x}{5}=\dfrac{5}{6}+\dfrac{-19}{30}\)
a, x= \(\dfrac{1}{4}\)
b, x= \(\dfrac{1}{5}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
x=-2/4+3/4 x=1/4
6x/30=25/30+-19/30 6x/30=6/30 6x=6 x=1
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
giải phương trình ; \(\dfrac{x-130}{20}\)+\(\dfrac{x-100}{25}\)+\(\dfrac{x-60}{30}\)+\(\dfrac{x-10}{35}\)=10
\(\dfrac{x-130}{20}\)+\(\dfrac{x-100}{25}\)+\(\dfrac{x-60}{30}\)+\(\dfrac{x-10}{35}\)=10
⇔\(\dfrac{2625\left(x-130\right)}{52500}\)+\(\dfrac{2100\left(x-100\right)}{52500}\)+\(\dfrac{1750\left(x-60\right)}{52500}\)+\(\dfrac{1500\left(x-10\right)}{52500}\)=\(\dfrac{525000}{52500}\)
⇔2625\(x\)-341250+2100\(x\)-210000+1750\(x\)-105000+1500\(x\)-15000=525000
⇔ 7975\(x\) = 1196250
⇔ \(x\) = \(\dfrac{1196250}{7975}\)
⇔\(x \) = 150
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình sau:
\(\dfrac{x+25}{75}+\dfrac{x+30}{70}=\dfrac{x+35}{65}+\dfrac{x+40}{60}\)
Lời giải:
PT $\Leftrightarrow \frac{x+25}{75}+1+\frac{x+30}{70}+1=\frac{x+35}{65}+1+\frac{x+40}{60}+1$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{x+100}{75}+\frac{x+100}{70}=\frac{x+100}{65}+\frac{x+100}{60}$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+100)(\frac{1}{75}+\frac{1}{70}-\frac{1}{65}-\frac{1}{60})=0$
Dễ thấy $\frac{1}{75}+\frac{1}{70}-\frac{1}{65}-\frac{1}{60}<0$
$\Rightarrow x+100=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=-100$ (tm)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x, biết \(\dfrac{1}{4}.\dfrac{2}{6}.\dfrac{3}{8}.\dfrac{4}{10}.\dfrac{5}{12}...\dfrac{30}{62}.\dfrac{31}{64}=2^x\)
=>\(1\cdot\dfrac{2}{4}\cdot\dfrac{3}{6}\cdot...\cdot\dfrac{31}{62}\cdot\dfrac{1}{64}=2^x\)
=>\(2^x=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot...\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\dfrac{1}{64}=\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^{30}\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^6=\dfrac{1}{2^{36}}\)
=>x=-36
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình
\(\dfrac{100}{x}\)-\(\dfrac{100}{x+10}\)=\(\dfrac{30}{60}\)
\(\dfrac{100}{x}-\dfrac{100}{x+10}=\dfrac{30}{60}=0,5\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne0;x\ne-10\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{100\left(x+10\right)-100x}{x\left(x+10\right)}=\dfrac{0,5x\left(x+10\right)}{x\left(x+10\right)}\\ \Leftrightarrow100x-100x+1000=0,5x^2+5x\\ \Leftrightarrow0,5x^2+5x-1000=0\\ \Leftrightarrow0,5x^2-20x+25x-1000=0\\ \Leftrightarrow0,5x.\left(x-40\right)+25.\left(x-40\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(0,5x+25\right)\left(x-40\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}0,5x+25=0\\x-40=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-50\\x=40\end{matrix}\right.\\ Vậy:S=\left\{-50;40\right\}\)
Đúng 5
Bình luận (0)