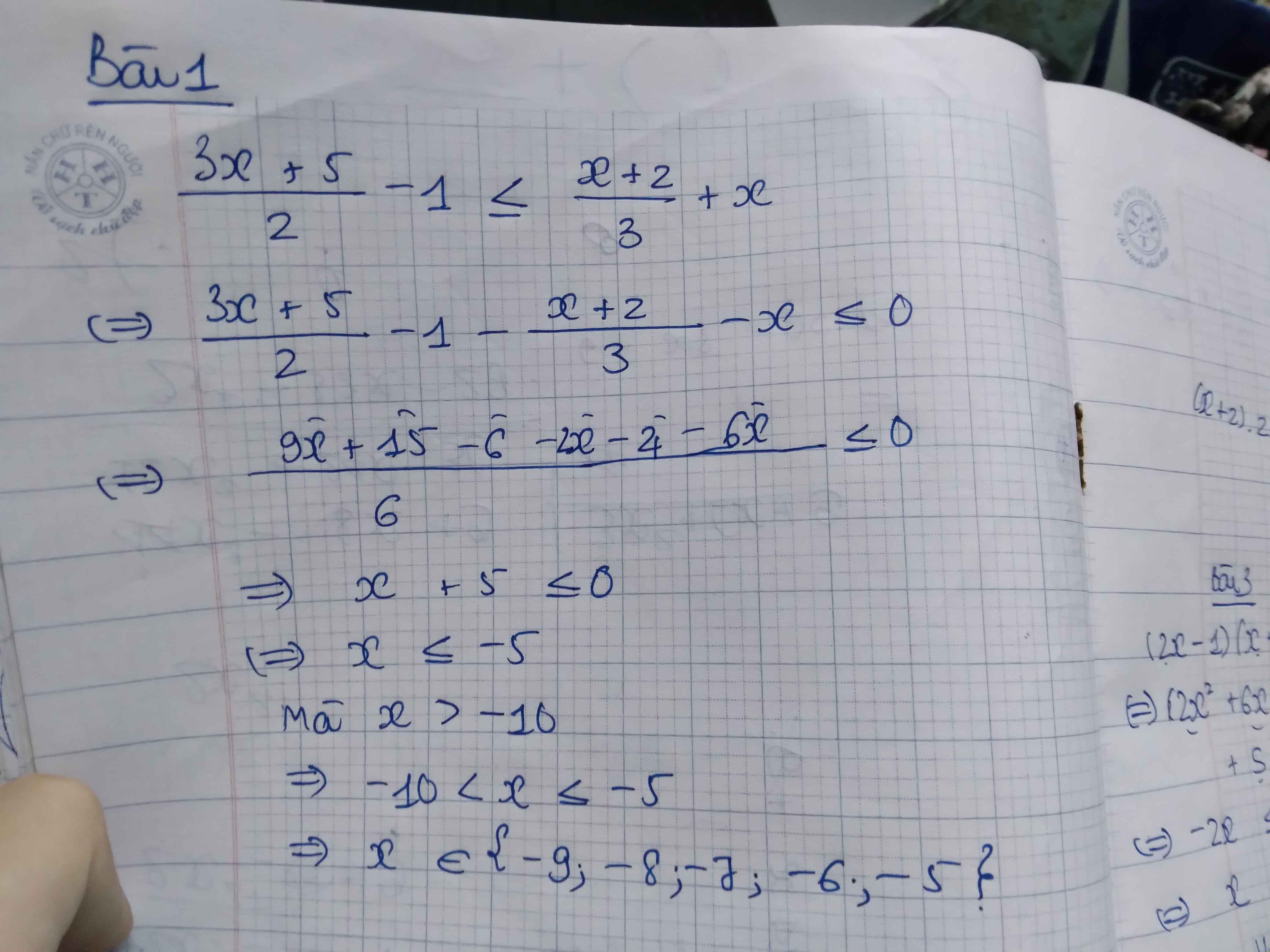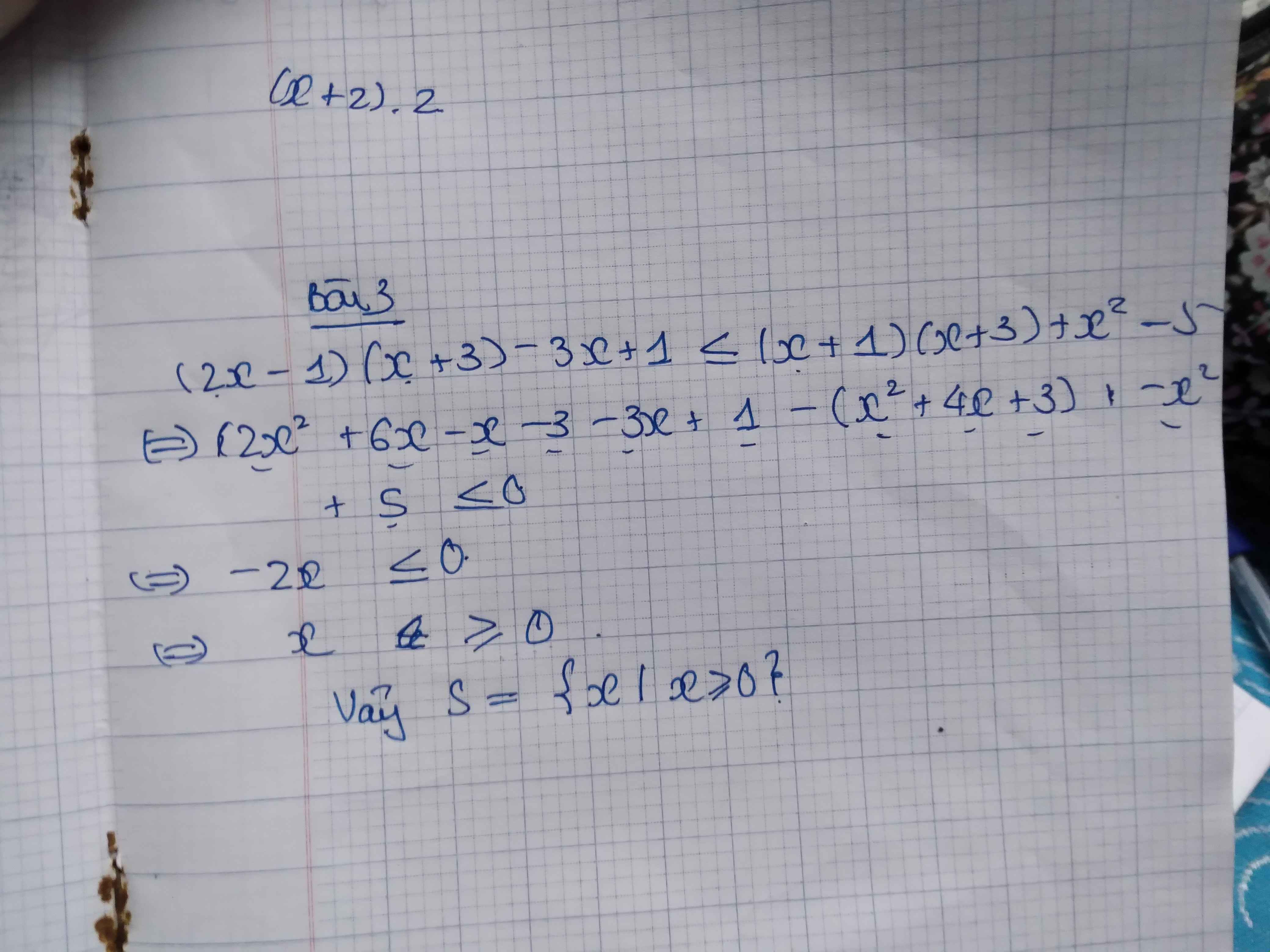\(\left(2x-3\right)^2\le\left(5-x\right)^2\)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Áp dụng BĐT Cô-si để tìm Maxa. yleft(x+3right)left(5-xright),left(-3le xle5right) b. yxleft(6-xright)left(0le xle6right) c. yleft(x+3right)left(5-2xright)left(-3le xlefrac{5}{2}right) d. yleft(2x+5right)left(5-2xright)left(-frac{5}{2}le xle5right) e. yleft(6x+3right)left(5-2xright)left(-frac{1}{2}le xlefrac{5}{2}right) f. yfrac{x}{x^2+2},xge0 g. yfrac{x^2}{left(x^2+2right)^3}
Đọc tiếp
Áp dụng BĐT Cô-si để tìm Max
a. \(y=\left(x+3\right)\left(5-x\right),\left(-3\le x\le5\right)\)
b. \(y=x\left(6-x\right)\left(0\le x\le6\right)\)
c. \(y=\left(x+3\right)\left(5-2x\right)\left(-3\le x\le\frac{5}{2}\right)\)
d. \(y=\left(2x+5\right)\left(5-2x\right)\left(-\frac{5}{2}\le x\le5\right)\)
e. \(y=\left(6x+3\right)\left(5-2x\right)\left(-\frac{1}{2}\le x\le\frac{5}{2}\right)\)
f. \(y=\frac{x}{x^2+2},x\ge0\)
g. \(y=\frac{x^2}{\left(x^2+2\right)^3}\)
Từ bđt Cauchy : \(a+b\ge2\sqrt{ab}\) ta suy ra được \(ab\le\frac{\left(a+b\right)^2}{4}\)
Áp dụng vào bài toán của bạn :
a/ \(y=\left(x+3\right)\left(5-x\right)\le\frac{\left(x+3+5-x\right)^2}{4}=...............\)
b/ Tương tự
c/ \(y=\left(x+3\right)\left(5-2x\right)=\frac{1}{2}.\left(2x+6\right)\left(5-2x\right)\le\frac{1}{2}.\frac{\left(2x+6+5-2x\right)^2}{4}=.............\)
d/ Tương tự
e/ \(y=\left(6x+3\right)\left(5-2x\right)=3\left(2x+1\right)\left(5-2x\right)\le3.\frac{\left(2x+1+5-2x\right)^2}{4}=.......\)
f/ Xét \(\frac{1}{y}=\frac{x^2+2}{x}=x+\frac{2}{x}\ge2\sqrt{x.\frac{2}{x}}=2\sqrt{2}\)
Suy ra \(y\le\frac{1}{2\sqrt{2}}\)
..........................
g/ Đặt \(t=x^2\) , \(t>0\) (Vì nếu t = 0 thì y = 0)
\(\frac{1}{y}=\frac{t^3+6t^2+12t+8}{t}=t^2+6t+\frac{8}{t}+12\)
\(=t^2+6t+\frac{8}{3t}+\frac{8}{3t}+\frac{8}{3t}+12\)
\(\ge5.\sqrt[5]{t^2.6t.\left(\frac{8}{3t}\right)^3}+12=.................\)
Từ đó đảo ngược y lại rồi đổi dấu \(\ge\) thành \(\le\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
B1
\(\dfrac{3x+5}{2}-1\le\dfrac{x+2}{3}+x\)
Có bnhieu nghiệm nguyên lớn hơn -10
BÀI 2 . Tập nghiệm S của btp\(\left(1-\sqrt{2}\right)x< 3-2\sqrt{2}\)
BÀI 3 \(\left(2X-1\right)\left(x+3\right)-3x+1\le\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)+x^2-5\) có tập nghiệm là?
Bài 1 :
Ta có : \(\dfrac{3x+5}{2}-1\le\dfrac{x+2}{3}+x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3x+5}{2}-1-\dfrac{x+2}{3}-x\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(3x+5\right)-6-2\left(x+2\right)-6x}{6}\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x+15-6-2x-4-6x\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\le-5\)
Mà \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\in Z\\x>-10\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{-5;-6;-7;-8;-9\right\}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
b3\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+5x-3-3x+1\le x^2+2x-3+x^2-5\\ \Leftrightarrow0.x\le-6\Leftrightarrow x\in\varnothing\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các bất phương trình sau:
1) \(\dfrac{2x-5}{x^2-6x-7}\le\dfrac{1}{x-3}\)
2) \(\dfrac{\left(3-2x\right)x^2}{\left(x-1\right)}\ge0\)
3) \(\dfrac{2x}{x-1}\le\dfrac{5}{2x-1}\)
1.
ĐK: \(x\ne7;x\ne-1;x\ne3\)
\(\dfrac{2x-5}{x^2-6x-7}\le\dfrac{1}{x-3}\left(1\right)\)
TH1: \(x< -1\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-5\right)\left(x-3\right)\ge x^2-6x-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-11x+15\ge x^2-6x-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+22\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) Bất phương trình đúng với mọi \(x< -1\)
TH2: \(-1< x< 3\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow\left(3-x\right)\left(2x-5\right)\ge\left(7-x\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x^2+11x-15\ge-x^2+6x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x^2+5x-22\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow\) vô nghiệm
TH3: \(3< x< 7\)
Khi đó \(\dfrac{2x-5}{x^2-6x-7}\le0\); \(\dfrac{1}{x-3}>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Bất phương trình đúng với mọi \(3< x< 7\)
TH4: \(x>7\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-5\right)\left(x-3\right)\le x^2-6x-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-11x+15\le x^2-6x-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+22\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow\) vô nghiệm
Vậy ...
Các bài kia tương tự, chứ giải ra mệt lắm.
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
Giải các bất phương trình, hệ phương trìnha) dfrac{x^2-4x+3}{2x-3}ge x-1b) 3x^2-left|4x^2+x-5right|3c)4x-left|2x^2-8x-15right|le-1d)x+3-sqrt{21-4x-x^2}ge0e)left{{}begin{matrix}xleft(x+5right) 4x+2left(2x-1right)left(x+3right)ge4xend{matrix}right.f)dfrac{1}{x^2-5x+4}ledfrac{1}{x^2-7x+10}
Đọc tiếp
Giải các bất phương trình, hệ phương trình
a) \(\dfrac{x^2-4x+3}{2x-3}\ge x-1\)
b) \(3x^2-\left|4x^2+x-5\right|>3\)
c)\(4x-\left|2x^2-8x-15\right|\le-1\)
d)\(x+3-\sqrt{21-4x-x^2}\ge0\)
e)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\left(x+5\right)< 4x+2\\\left(2x-1\right)\left(x+3\right)\ge4x\end{matrix}\right.\)
f)\(\dfrac{1}{x^2-5x+4}\le\dfrac{1}{x^2-7x+10}\)
Áp dụng bđt cô si để tìm GTLN của các bt sau:
a) yleft(x+3right)left(5-xright) với -3≤x≤5
b) yxleft(6-xright) với 0≤x≤6
c) yleft(x+3right)left(5-2xright) với -3≤x≤frac{5}{2}
d) y(2x+5)(5-x) với frac{-5}{2}le xle5
e) y(6x+3)(5-2x) với frac{-1}{2}le xlefrac{5}{2}
f) yfrac{x}{x^2+2} với x0
g) yfrac{x^2}{left(x^2+3right)^3}
Đọc tiếp
Áp dụng bđt cô si để tìm GTLN của các bt sau:
a) \(y=\left(x+3\right)\left(5-x\right)\) với -3≤x≤5
b) \(y=x\left(6-x\right)\) với 0≤x≤6
c) \(y=\left(x+3\right)\left(5-2x\right)\) với -3≤x≤\(\frac{5}{2}\)
d) y=(2x+5)(5-x) với \(\frac{-5}{2}\le x\le5\)
e) y=(6x+3)(5-2x) với \(\frac{-1}{2}\le x\le\frac{5}{2}\)
f) \(y=\frac{x}{x^2+2}\) với x>0
g) \(y=\frac{x^2}{\left(x^2+3\right)^3}\)
a/ \(y=\left(x+3\right)\left(5-x\right)\le\frac{1}{4}\left(x+3+5-x\right)^2=16\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(x+3=5-x\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
b/ \(y=x\left(6-x\right)\le\frac{1}{4}\left(x+6-x\right)^2=9\)
\("="\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
c/ \(y=\frac{1}{2}\left(2x+6\right)\left(5-2x\right)\le\frac{1}{8}\left(2x+6+5-2x\right)^2=\frac{121}{8}\)
\("="\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{1}{4}\)
d/ \(y=\frac{1}{2}\left(2x+5\right)\left(10-2x\right)\le\frac{1}{8}\left(2x+5+10-2x\right)^2=\frac{225}{8}\)
\("="\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{5}{4}\)
e/ \(y=3\left(2x+1\right)\left(5-2x\right)\le\frac{3}{4}\left(2x+1+5-2x\right)^2=27\)
\("="\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
f/ \(\frac{x}{x^2+2}\le\frac{x}{2\sqrt{x^2.2}}=\frac{1}{2\sqrt{2}}\)
\("="\Leftrightarrow x=\sqrt{2}\)
g/ \(y=\frac{x^2}{\left(x^2+\frac{3}{2}+\frac{3}{2}\right)^3}\le\frac{x^2}{\left(3\sqrt[3]{\frac{9}{4}x^2}\right)^3}=\frac{4}{243}\)
\("="\Leftrightarrow x^2=\frac{3}{2}\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\sqrt{\frac{3}{2}}\)
Tập nghiệm của bất pta) left|x+2right|+left|-2x+1right|le x+1b) left|x+2right|-left|x-1right| x-dfrac{3}{2}c) left|x+1right|-left|x-2right|ge3d) left|dfrac{-5}{x+2}right| left|dfrac{10}{x-1}right|e) left|dfrac{2-3left|xright|}{1+x}right|le1
Đọc tiếp
Tập nghiệm của bất pt
a) \(\left|x+2\right|+\left|-2x+1\right|\le x+1\)
b) \(\left|x+2\right|-\left|x-1\right|< x-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
c) \(\left|x+1\right|-\left|x-2\right|\ge3\)
d) \(\left|\dfrac{-5}{x+2}\right|< \left|\dfrac{10}{x-1}\right|\)
e) \(\left|\dfrac{2-3\left|x\right|}{1+x}\right|\le1\)
a, \(\left|x+2\right|+\left|-2x+1\right|\le x+1\left(1\right)\)
TH1: \(x\le-2\)
\(\Rightarrow x+1\le-1< \left|x+2\right|+\left|-2x+1\right|\)
\(\Rightarrow\) vô nghiệm
TH2: \(-2< x\le\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow x+2-2x+1\le x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge1\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left[1;\dfrac{1}{2}\right]\)
TH3: \(x>\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow x+2+2x-1\le x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow\) vô nghiệm
Vậy \(x\in\left[1;\dfrac{1}{2}\right]\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
b, \(\left|x+2\right|-\left|x-1\right|< x-\dfrac{3}{2}\left(2\right)\)
TH1: \(x\le-2\)
\(\left(2\right)\Leftrightarrow-x-2+x-1< x-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\) vô nghiệm
TH2: \(-2< x\le1\)
\(\left(2\right)\Leftrightarrow x+2+x-1< x-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< -\dfrac{5}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\) vô nghiệm
TH3: \(x>1\)
\(\left(2\right)\Leftrightarrow x+2-x+1< x-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>\dfrac{9}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left(\dfrac{9}{2};+\infty\right)\)
Vậy \(x\in\left(\dfrac{9}{2};+\infty\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
c, Tương tự a,b
d, ĐK: \(x\ne-2;x\ne1\)
\(\left|\dfrac{-5}{x+2}\right|< \left|\dfrac{10}{x-1}\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{\left|x+2\right|}< \dfrac{2}{\left|x-1\right|}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left|x+2\right|>\left|x-1\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(x+2\right)^2>\left(x-1\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(x^2+4x+4\right)>x^2-2x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2+18x+15>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\)
e, ĐK: \(x\ne-1\)
\(\left|\dfrac{2-3\left|x\right|}{1+x}\right|\le1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|2-3\left|x\right|\right|\le\left|x+1\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2-3\left|x\right|\right)^2\le\left(x+1\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4+9x^2-12\left|x\right|\le x^2+2x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8x^2-12\left|x\right|-2x+3\le0\)
Đến đây dễ rồi, xét hai trường hợp để phá dấu giá trị tuyệt đối rồi đối chiếu điêì kiện.
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Tìm m để \(\sqrt{\left(x+5\right)\left(3-x\right)}\le x^2+2x+m\) dùng \(\forall x\in\left(-5;3\right)\)
ĐK: \(-5\le x\le3\)
\(\sqrt{\left(x+5\right)\left(3-x\right)}\le x^2+2x+m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x^2-2x+15+\sqrt{-x^2-2x+15}-15\le m\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{-x^2-2x+15}=t\left(0\le t\le4\right)\)
Bất phương trình đã cho tương đương:
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(t\right)=t^2+t-15\le m\)
Yêu cầu bài toán thỏa mãn khi \(m\ge maxf\left(t\right)=f\left(4\right)=5\)
Vậy \(m\ge5\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm max
\(A=3\sqrt{2x-1}+x\sqrt{5-4x^2}\left(\frac{1}{2}\le x\le\frac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\right)\)
\(B=\frac{xyz\left(x+y+z+\sqrt{x^2+y^2+z^2}\right)}{\left(x^2+y^2+z^2\right)\left(xy+yz+zx\right)}\left(x,y,z>0\right)\)
A
Áp dụng BĐT cosi ta có
\(\sqrt{\left(2x-1\right).1}\le\frac{2x-1+1}{2}=x\)
\(x\sqrt{5-4x^2}\le\frac{x^2+5-4x^2}{2}=\frac{-3x^2+5}{2}\)
Khi đó
\(A\le3x+\frac{-3x^2+5}{2}=\frac{-3x^2+6x+5}{2}=\frac{-3\left(x-1\right)^2}{2}+4\le4\)
MaxA=4 khi \(\hept{\begin{cases}2x-1=1\\x^2=5-4x^2\\x=1\end{cases}\Rightarrow}x=1\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
B
Áp dụng BĐT cosi ta có :
\(x^2+y^2+z^2\ge\frac{1}{3}\left(x+y+z\right)^2\)
=> \(x+y+z\le\sqrt{3\left(x^2+y^2+z^2\right)}\)
=> \(B\le\frac{xyz.\left(\sqrt{3\left(x^2+y^2+z^2\right)}+\sqrt{x^2+y^2+z^2}\right)}{\left(x^2+y^2+z^2\right)\left(xy+yz+xz\right)}=\frac{xyz.\left(\sqrt{3}+1\right)}{\left(xy+yz+xz\right)\sqrt{x^2+y^2+z^2}}\)
Lại có \(x^2+y^2+z^2\ge3\sqrt[3]{x^2y^2z^2}\); \(xy+yz+xz\ge3\sqrt[3]{x^2y^2z^2}\)
=> \(\sqrt{x^2+y^2+z^2}\left(xy+yz+xz\right)\ge3\sqrt[3]{x^2y^2z^2}.\sqrt{3\sqrt[3]{x^2y^2z^2}}=3\sqrt{3}.xyz\)
=> \(B\le\frac{\sqrt{3}+1}{3\sqrt{3}}=\frac{3+\sqrt{3}}{9}\)
\(MaxB=\frac{3+\sqrt{3}}{9}\)khi x=y=z
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các bất phương trình:
\(a,\left(2x+1\right)^2+\left(1-x\right)3x\le\left(x+2\right)^2\)
\(b,\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)\ge\left(x+3\right)^2+5\)
\(\left(x-4\right).\left(x+4\right)\ge\left(x+3\right)^2+5\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-16\ge x^2+6x+9+5\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-16\ge x^2+6x+14\)
\(\Rightarrow-30\ge6x\Rightarrow-5\ge x\)
Vậy...
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)