Giải các phương trình sau:
a) \(\cot x = 1;\) b) \(\sqrt 3 \cot x + 1 = 0\)
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) \(\sin x = \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\);
b) \(2\cos x = - \sqrt 2 \);
c) \(\sqrt 3 \tan \left( {\frac{x}{2} + {{15}^0}} \right) = 1\);
d) \(\cot \left( {2x - 1} \right) = \cot \frac{\pi }{5}\)
a) \(\sin x = \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\;\; \Leftrightarrow \sin x = \sin \frac{\pi }{3}\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{x = \frac{\pi }{3} + k2\pi }\\{x = \pi - \frac{\pi }{3} + k2\pi }\end{array}} \right.\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{x = \frac{\pi }{3} + k2\pi }\\{x = \frac{{2\pi }}{3} + k2\pi \;}\end{array}\;} \right.\left( {k \in \mathbb{Z}} \right)\)
b) \(2\cos x = - \sqrt 2 \;\; \Leftrightarrow \cos x = - \frac{{\sqrt 2 }}{2}\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow \cos x = \cos \frac{{3\pi }}{4}\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{x = \frac{{3\pi }}{4} + k2\pi }\\{x = - \frac{{3\pi }}{4} + k2\pi }\end{array}\;\;\left( {k \in \mathbb{Z}} \right)} \right.\)
c) \(\sqrt 3 \;\left( {\tan \frac{x}{2} + {{15}^0}} \right) = 1\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow \tan \left( {\frac{x}{2} + \frac{\pi }{{12}}} \right) = \frac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\;\; \Leftrightarrow \tan \left( {\frac{x}{2} + \frac{\pi }{{12}}} \right) = \tan \frac{\pi }{6}\)
\( \Leftrightarrow \frac{x}{2} + \frac{\pi }{{12}} = \frac{\pi }{6} + k\pi \;\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow \frac{x}{2} = \frac{\pi }{{12}} + k\pi \;\;\; \Leftrightarrow x = \frac{\pi }{6} + k\pi \;\left( {k \in \mathbb{Z}} \right)\)
d) \(\cot \left( {2x - 1} \right) = \cot \frac{\pi }{5}\;\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow 2x - 1 = \frac{\pi }{5} + k\pi \;\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow 2x = \frac{\pi }{5} + 1 + k\pi \;\; \Leftrightarrow x = \frac{\pi }{{10}} + \frac{1}{2} + \frac{{k\pi }}{2}\;\;\left( {k \in \mathbb{Z}} \right)\)
1. Giải các phương trình sau:
a) \(\cos\left(x+15^0\right)=\dfrac{2}{5}\)
b) \(\cot\left(2x-10^0\right)=4\)
c) \(\cos\left(x+12^0\right)+\sin\left(78^0-x\right)=1\)
2. Định m để các phương trình sau có nghiệm:
\(\sin\left(3x-27^0\right)=2m^2+m\)
c.
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(x+12^0\right)+cos\left(90^0-78^0+x\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2cos\left(x+12^0\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(x+12^0\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+12^0=60^0+k360^0\\x+12^0=-60^0+k360^0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=48^0+k360^0\\x=-72^0+k360^0\end{matrix}\right.\)
2.
Do \(-1\le sin\left(3x-27^0\right)\le1\) nên pt có nghiệm khi:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2m^2+m\ge-1\\2m^2+m\le1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2m^2+m+1\ge0\left(luôn-đúng\right)\\2m^2+m-1\le0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow-1\le m\le\dfrac{1}{2}\)
a.
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+15^0=arccos\left(\dfrac{2}{5}\right)+k360^0\\x+15^0=-arccos\left(\dfrac{2}{5}\right)+k360^0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-15^0+arccos\left(\dfrac{2}{5}\right)+k360^0\\x=-15^0-arccos\left(\dfrac{2}{5}\right)+k360^0\end{matrix}\right.\)
b.
\(2x-10^0=arccot\left(4\right)+k180^0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=5^0+\dfrac{1}{2}arccot\left(4\right)+k90^0\)
2.
Phương trình \(sin\left(3x-27^o\right)=2m^2+m\) có nghiệm khi:
\(2m^2+m\in\left[-1;1\right]\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2m^2+m\le1\\2m^2+m\ge-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m+1\right)\left(2m-1\right)\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-1\le m\le\dfrac{1}{2}\)
1.Giải các phương trình sau:
a) 2x2 +16 -6 = 4\(\sqrt{x\left(x+8\right)}\)
b) x4 -8x2 + x-2\(\sqrt{x-1}\) + 16=0
2. Gọi x1;x2 là nghiệm phương trình x2 -3x -7 =0. Không giải phương trình tính các giá trị của biểu thức sau:
A = \(\dfrac{1}{x_1-1}+\dfrac{1}{x_2-1}\)
B= \(x^2_1+x_2^2\)
C= |x1 - x2|
D= \(x_1^4+x_2^4\)
E= (3x1 + x2) (3x2 + x1)
2:
\(A=\dfrac{x_2-1+x_1-1}{x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{3-2}{-7-3+1}=\dfrac{1}{-9}=\dfrac{-1}{9}\)
B=(x1+x2)^2-2x1x2
=3^2-2*(-7)
=9+14=23
C=căn (x1+x2)^2-4x1x2
=căn 3^2-4*(-7)=căn 9+28=căn 27
D=(x1^2+x2^2)^2-2(x1x2)^2
=23^2-2*(-7)^2
=23^2-2*49=431
D=9x1x2+3(x1^2+x2^2)+x1x2
=10x1x2+3*23
=69+10*(-7)=-1
Giải phương trình sau:
a) $\tan ^2x+4\cos ^2x+7=4\tan x+8\cot x$
b) $6\sin ^2x+2\cos ^2x-2\sqrt{3}\sin 2x=14\sin \left(x-\frac{\pi }{6}\right)$
Bài 1: Giải các phương trình sau:
a) 3(2,2-0,3x)=2,6 + (0,1x-4)
b) 3,6 -0,5 (2x+1) = x - 0,25(22-4x)
Bài 2: Giải các phương phương trình sau:
a) \(\dfrac{3\left(x-3\right)}{4}\)+\(\dfrac{4x-10,5}{4}\)=\(\dfrac{3\left(x+1\right)}{5}\)+6
b) \(\dfrac{2\left(3x+1\right)+1}{4}\)-5=\(\dfrac{2\left(3x-1\right)}{5}\)-\(\dfrac{3x+2}{10}\)
Mik đang cần gấp nha!!❤
Bài 1: Giải các phương trình sau:
a) 3(2,2-0,3x)=2,6 + (0,1x-4)
<=> 6.6 - 0.9x = 2,6 + 0,1x - 4
<=> - 0.9x - 0,1x = -6.6 -1,4
<=> -x = -8
<=> x = 8
Vậy x = 8
b) 3,6 -0,5 (2x+1) = x - 0,25(22-4x)
<=> 3,6 - x - 0,5 = x - 5,5 + x
<=> - x - 3,1 = -5,5
<=> - x = -2.4
<=> x = 2.4
Vậy x = 2.4
Giải phương trình sau:
a, \(\sin\left(2x\right)+\sin\left(x\right)-\dfrac{1}{2\sin\left(x\right)}-\dfrac{1}{\sin\left(2x\right)}=2\cot\left(2x\right)\)
b, \(\left(\sin\left(2x\right)+cos\left(2x\right)\right)cos\left(x\right)+2cos\left(2x\right)-sin\left(x\right)=0\)
c, \(\sin\left(2x\right)-\cos\left(2x\right)+3\sin\left(x\right)-\cos\left(x\right)-1=0\)
b)
(sin2x + cos2x)cosx + 2cos2x - sinx = 0
⇔ cos2x (cosx + 2) + sinx (2cos2 x – 1) = 0
⇔ cos2x (cosx + 2) + sinx.cos2x = 0
⇔ cos2x (cosx + sinx + 2) = 0
⇔ cos2x = 0
⇔ 2x = 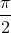 + kπ ⇔ x =
+ kπ ⇔ x = 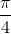 + k
+ k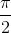 (k ∈
(k ∈ 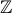 )
)
c)
Đáp án:
x=π6π6+ k2ππ
và x= 5π65π6+k2ππ (k∈Z)
Lời giải:
sin2x-cos2x+3sinx-cosx-1=0
⇔ 2sinxcosx-(1-2sin²x) +3sinx-cosx-1=0
⇔ 2sin²x+2sinxcosx+3sinx-cosx-2=0
⇔ (2sin²x+3sinx-2)+ cosx(2sinx-1)=0
⇔ (2sinx-1)(sinx+2)+cosx(2sinx-1)=0
⇔ (2sinx-1)(sinx+cosx+2)=0
⇔ sinx=1212
⇔ x=π6π6+ k2ππ
hoặc x= 5π65π6+k2ππ (k∈Z)
(sinx+cosx+2)=0 (vô nghiệm do sinx+cosx+2=√22sin(x+π4π4)+2>0)
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) 3x + 6 = x +10
b) x(x + 1) - 2 (x + 1) = 0
\(a,\\ \Leftrightarrow3x-x=10-6\\ \Leftrightarrow2x=4\\ \Leftrightarrow x=2\\ b,\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(a,\Leftrightarrow3x-x=10-6\\ \Leftrightarrow2x=4\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{4}{2}=2\)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = \(\left\{2\right\}\)
\(b,\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x+1=0\) hoặc \(\Leftrightarrow x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-1\) \(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = \(\left\{-1;2\right\}\)
a)3x + 6 = x +10
⟺3x-x=10-6
⟺2x=4 ⟺x=2
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S={2}
b) x(x + 1) - 2 (x + 1) = 0
⟺(x+1)(x-2)=0
⟺x+1=0 ⟺x=-1
x-2=0 ⟺x=2
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S={2;-1}
Giải các phương trình c o t x + π 3 = 3
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) \({2^x} = \frac{1}{{{2^{x + 1}}}};\)
b) \(2{e^{2x}} = 5.\)
\(a,2^{3x-1}=2^{-\left(x+1\right)}\Rightarrow3x-1=-\left(x+1\right)\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(b,ln\left(2e^{2x}\right)=ln5\)
\(\Rightarrow ln2+lne^{2x}=ln5\)
\(\Rightarrow ln2+2x=ln5\)
\(\Rightarrow2x=ln5-ln2=ln\dfrac{5}{2}\)
Như vậy \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}ln\dfrac{5}{2}\)