\(f\left(x;y;z\right)=\frac{x}{y}+\sqrt{\frac{y}{z}}+\sqrt[3]{\frac{z}{x}}\)
Tìm GTNN của hàm số đã cho
Tìm hàm f: \(R\rightarrow R\) thỏa mãn điều kiện
1. \(f\left(x^2+f\left(y\right)\right)=y+x.f\left(x\right),\forall x,y\in R\)
2. \(f\left(\left(x+1\right).f\left(y\right)\right)=f\left(y\right)+y.f\left(x\right),\forall x,y\in R\)
3. \(f\left(x^3+f\left(y\right)\right)=x^2f\left(x\right)+y,\forall x,y\in R\)
4. \(\hept{\begin{cases}f\left(x+y\right)=f\left(x\right)+f\left(y\right)\\f\left(xy\right)=f\left(x\right).f\left(y\right)\end{cases}},\forall x,y\in R\)
@Lê Minh Đức
@alibaba nguyễn : Giúp với ông ei :) Chắc ông cũng học đến cái này r :))
Bài 1: \(f\left(x\right)=x^{14}-14.x^{13}+14.x^{12}-.....-14.x+14\)
Tìm \(f\left(13\right)\)
Bài 2: Cho các hàm số \(f_1\left(x\right)=x,f_2\left(x\right)=-2x,f_3\left(x\right)=1,f_4\left(x\right)=5,f_5\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{x},f_6\left(x\right)=x^2\). Trong các hàm số nào có tính chất \(f\left(-x\right)=f\left(x\right),f\left(-x\right)=-f\left(x\right),f\left(x_1+x_2\right)=f\left(x_1\right)+f\left(x_2\right),f\left(x_1.x_2\right)=f\left(x_1\right).f\left(x_2\right)?\)
Câu 1/
\(f\left(13\right)=x^{13}\left(x-14\right)+14x^{12}-...-14x+14\)
\(=-x^{13}+14x^{12}-14x^{11}+...-14x+14\)
\(=x^{12}\left(-x+14\right)-14x^{11}+...-14x+14\)
\(=x^{12}-14x^{11}+...-14x+14=...\)
\(=-x+14=1\)
(Bạn để ý quy luật sau các bước rút gọn lần lượt thì mũ chẵn sẽ biến thành hệ số 1, mũ lẻ thành hệ số -1 nên x sẽ có hệ số -1)
Câu 2:
+) \(f\left(-x\right)=f\left(x\right)\) có: \(f_3\left(x\right);f_4\left(x\right);f_6\left(x\right)\)
+) \(f\left(-x\right)=-f\left(x\right)\) có: \(f_1\left(x\right);f_2\left(x\right);f_5\left(x\right)\)
+) \(f\left(x_1+x_2\right)=f\left(x_1\right)+f\left(x_2\right)\) có: \(f_1\left(x\right);f_2\left(x\right)\)
+) \(f\left(x_1x_2\right)=f\left(x_1\right).f\left(x_2\right)\) có: \(f_1\left(x\right);f_3\left(x\right);f_5\left(x\right);f_6\left(x\right)\)
cho hàm số f(x)=2x2+x-3
tìm \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow+\infty}\)\(\dfrac{\sqrt{f\left(x\right)}+\sqrt{f\left(4x\right)}+\sqrt{\left(4^2x\right)}+...+\sqrt{f\left(4^{2018}x\right)}}{\sqrt{f\left(x\right)}+\sqrt{f\left(2x\right)}+\sqrt{\left(2^2x\right)}+...+\sqrt{f\left(2^{2018}x\right)}}\)=\(\dfrac{a^{2019}+b}{c}\) với a,b,c là ba số nguyên dương và b<2019.Tính S=a+b-c
Cho hàm số f(x) thỏa mãn \(\left[f'\left(x\right)\right]^2+f\left(x\right)f''\left(x\right)=15x^4+12x\) ∀x∈R biết
f(0)=f'(0)=1. Tính \(f^2\left(1\right)\)
Vẫn là đạo hàm của tích
Dễ dàng viết được:
\(\left[f'\left(x\right)\right]^2+f\left(x\right).f''\left(x\right)=\left[f\left(x\right)\right]'.f'\left(x\right)+f\left(x\right).\left[f'\left(x\right)\right]'=\left[f'\left(x\right).f\left(x\right)\right]'\)
Do đó giả thiết biến đổi thành:
\(\left[f'\left(x\right).f\left(x\right)\right]'=15x^4+12x\)
Nguyên hàm 2 vế:
\(f'\left(x\right).f\left(x\right)=\int\left(15x^4+12x\right)dx=3x^5+6x^2+C\)
Thay \(x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(0\right).f\left(0\right)=C\Rightarrow C=1\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right).f\left(x\right)=3x^5+6x^2+1\)
Tiếp tục nguyên hàm 2 vế:
\(\int f\left(x\right).f'\left(x\right)dx=\int\left(3x^5+6x^2+1\right)dx\) với chú ý \(\int f\left(x\right).f'\left(x\right)dx=\int f\left(x\right).d\left[f\left(x\right)\right]=\dfrac{1}{2}f^2\left(x\right)+C\)
Nên:
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}f^2\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}x^6+2x^3+x+C\)
Thay \(x=0\Rightarrow C=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}f^2\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}x^6+2x^3+x+\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow f^2\left(1\right)\)
Cho hàm số \(f\left(x\right)\) có đạo hàm \(f'\left(x\right)\) liên tục trên \(R\) và thỏa mãn các điều kiện \(f\left(x\right)>0,\forall x\in R\), \(f\left(0\right)=1\) và \(f'\left(x\right)=-4x^3.\left(f\left(x\right)\right)^2,\forall x\in R\). Tính \(I=\int_0^1x^3f\left(x\right)dx\)
A.\(I=\dfrac{1}{6}\) B. \(I=ln2\) C. \(I=\dfrac{1}{4}\) D. \(I=\dfrac{ln2}{4}\)
Mình cần bài giải ạ, mình cảm ơn nhiều♥
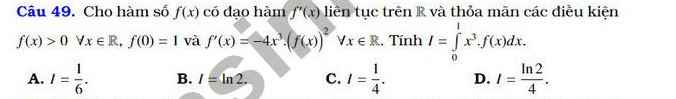
\(f'\left(x\right)=-4x^3\left(f\left(x\right)\right)^2\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{f'\left(x\right)}{\left(f\left(x\right)\right)^2}=4x^3\)
Lấy nguyên hàm hai vế
\(\int-\dfrac{f'\left(x\right)}{\left(f\left(x\right)\right)^2}dx=\int4x^3dx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{f\left(x\right)}=x^4+c\)
Thay x=0 vào tìm được c=1 \(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{x^4+1}\)
\(I=\int\limits^1_0\dfrac{x^3}{x^4+1}dx=\dfrac{1}{4}\int\limits^1_0\dfrac{\left(x^4+1\right)'}{x^4+1}dx=\dfrac{ln2}{4}\)
Chọn D
Cho f(x+y)=f(x)+f(y)
Tìm tất cả các hàm số f: R --> R thoả mãn : (Với mọi x,y thuộc R)
\(f\left(x^3-y^3\right)=xf\left(x^2\right)-yf\left(y^2\right)\)
\(f\left(x^5+y^5+y\right)=x^3f\left(x^2\right)+y^3f\left(y^2\right)+f\left(y\right)\)
@Akai Haruma @Nguyễn Việt Lâm
Giúp em với ạ, em cảm ơn
Bài 1:
Cho $y=0$ thì: $f(x^3)=xf(x^2)$
Tương tự khi cho $x=0$
$\Rightarrow f(x^3-y^3)=xf(x^2)-yf(y^2)=f(x^3)-f(y^3)$
$\Rightarrow f(x-y)=f(x)-f(y)$ với mọi $x,y\in\mathbb{R}$
Cho $x=0$ thì $f(-y)=0-f(y)=-f(y)$
Cho $y\to -y$ thì: $f(x+y)=f(x)-f(-y)=f(x)--f(y)=f(x)+f(y)$ với mọi $x,y\in\mathbb{R}$
Đến đây ta có:
$f[(x+1)^3+(x-1)^3]=f(2x^3+6x)=f(2x^3)+f(6x)$
$=2f(x^3)+6f(x)=2xf(x^2)+6f(x)$
$f[(x+1)^3+(x-1)^3]=f[(x+1)^3-(1-x)^3]$
$=(x+1)f((x+1)^2)-(1-x)f((1-x)^2)$
$=(x+1)f(x^2+2x+1)+(x-1)f(x^2-2x+1)$
$=(x+1)[f(x^2)+2f(x)+f(1)]+(x-1)[f(x^2)-2f(x)+f(1)]$
$=2xf(x^2)+4f(x)+2xf(1)$
Do đó:
$2xf(x^2)+6f(x)=2xf(x^2)+4f(x)+2xf(1)$
$2f(x)=2xf(1)$
$f(x)=xf(1)=ax$ với $a=f(1)$
Cho f(x+y)=f(x)+f(y)
Tìm tất cả các hàm số f: R --> R thoả mãn : (Với mọi x,y thuộc R)
\(f\left(x^3-y^3\right)=xf\left(x^2\right)-yf\left(y^2\right)\)
\(f\left(x^5-y^5+xy\right)=x^3f\left(x^2\right)-y^3f\left(y\right)+f\left(xy\right)\)
Em cảm ơn ạ !!!
\(f\left(x^5+y^5+y\right)=x^3f\left(x^2\right)+y^3f\left(y^2\right)+f\left(y\right)\)
Sửa lại đề câu 2 !!
Cho hàm số \(y = f\left( x \right) = - {x^2} + 1\). Tính \(f\left( { - 3} \right);f\left( { - 2} \right);f\left( { - 1} \right);f\left( 0 \right);f\left( 1 \right)\).
\(f\left( { - 3} \right) = - {\left( { - 3} \right)^2} + 1 = - 9 + 1 = - 8\);
\(f\left( { - 2} \right) = - {\left( { - 2} \right)^2} + 1 = - 4 + 1 = - 3\);
\(f\left( { - 1} \right) = - {\left( { - 1} \right)^2} + 1 = - 1 + 1 = 0\);
\(f\left( 0 \right) = - {0^2} + 1 = 0 + 1 = 1\);
\(f\left( 1 \right) = - {1^2} + 1 = - 1 + 1 = 0\);
Cho hàm số \(y = f\left( x \right) = {x^2} + 4\). Tính \(f\left( { - 3} \right);f\left( { - 2} \right);f\left( { - 1} \right);f\left( 0 \right);f\left( 1 \right)\)
\(f\left( { - 3} \right) = {\left( { - 3} \right)^2} + 4 = 9 + 4 = 13\);
\(f\left( { - 2} \right) = {\left( { - 2} \right)^2} + 4 = 4 + 4 = 8\);
\(f\left( { - 1} \right) = {\left( { - 1} \right)^2} + 4 = 1 + 4 = 5\);
\(f\left( 0 \right) = {0^2} + 4 = 0 + 4 = 4\);
\(f\left( 1 \right) = {1^2} + 4 = 1 + 4 = 5\).
Cho hàm số f(x) liên tục trên \(\left(0;+\infty\right)\) thỏa mãn \(f\left(1\right)=\dfrac{1}{3}\) và \(2f\left(x\right)+x^2\dfrac{f'\left(x\right)}{f\left(x\right)}=3x,f\left(x\right)\ne0\) với mọi \(x\in\left(0;+\infty\right)\) . Biết \(\int_1^2f\left(x\right)dx=a+bln\left(2\right)\), \(\left(a,b\in R\right).\) Tính giá trị T=10a+3b