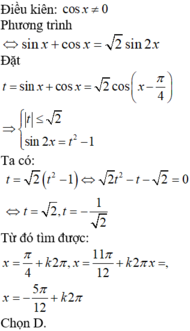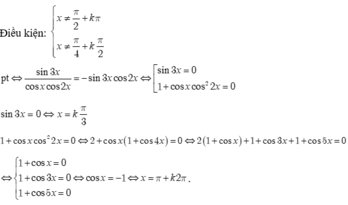Giải phương trình: tanx + tan5x + tan9x = tanx.tan5x.tan9x

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải phương trình √3 tanx + 1 = 0 là phương trình bậc nhất đố với tanx.
√3tanx + 1 = 0 ⇔ tanx = (-√3)/3 ⇔ x = (-π)/6 + kπ, k ∈ Z)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình:
\(Tan3x=Tanx\)
ĐK: \(x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{6}+\dfrac{k\pi}{3}\)
\(tan3x=tanx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=x+k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)
Đối chiếu điều kiện ta được \(x=k\pi\) là nghiệm của phương trình.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình : tanx + cotx=2
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne k\dfrac{\pi}{2}\)
\(tanx+\dfrac{1}{tanx}=2\)
\(\Rightarrow tan^2x+1=2tanx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(tanx-1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow tanx=1\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\) (thỏa mãn)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình: tan3x - tanx = 2
Lời giải:
$\tan 3x-\tan x=2$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{3\tan x-\tan ^3x}{1-3\tan ^2x}-\tan x=2$
Đặt $\tan x=a$ thì:
$\frac{3a-a^3}{1-3a^2}-a=2$
$\Leftrightarrow a^3+3a^2+a-1=0$
$\Leftrihgtarrow a^2(a+1)+2a(a+1)-(a+1)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a+1)(a^2+2a-1)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow a=-1$ hoặc $a=-1\pm \sqrt{2}$
Đến đây thì đơn giản rồi.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\\x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{6}+\dfrac{k\pi}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{sin3x}{cos3x}-\dfrac{sinx}{cosx}=2\)
\(\Rightarrow sin3x.cosx-cos3x.sinx=2cos3x.cosx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin2x=cos4x-cos2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos^22x-sin^22x-sin2x-cos2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(sin2x+cos2x\right)\left(cos2x-sin2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2}sin\left(2x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=0\\cos\left(2x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình sau: tanx = -1
tan x = -1 ⇔ tan x = tan (-π)/4 ⇔ x =(-π)/4 + kπ, k ∈ Z
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình
1
+
tan
x
2
2
sin
x
Đọc tiếp
Giải phương trình 1 + tan x = 2 2 sin x
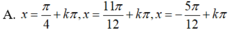
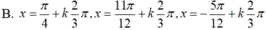
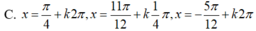
![]()
Giải phương trình tanx + tan2x -sin3x.cos2x. A. x k
π
3
; x π + k2π B. x k
π
3
; x
π
2
+ k2π C. x k
π
3
D. x k2π
Đọc tiếp
Giải phương trình tanx + tan2x = -sin3x.cos2x.
A. x = k π 3 ; x = π + k2π
B. x = k π 3 ; x = π 2 + k2π
C. x = k π 3
D. x = k2π
Giải phương trình sau: tanx = 0
tan x = 0 ⇔ tan x = tan0 ⇔ x = kπ, k ∈ Z
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình sau: tanx = 1
tan x = 1 ⇔ tan x = tan π/4 ⇔ x = π/4 + kπ, k ∈ Z
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình a.sinx + b.cosx = c bằng cách đưa về phương trình theo tanx/2
\(sinx=\dfrac{2tan\dfrac{x}{2}}{tan^2\dfrac{x}{2}+1}\)
\(cosx=\dfrac{1-tan^2\dfrac{x}{2}}{1+tan^2\dfrac{x}{2}}\)
Đặt \(t=tan\dfrac{x}{2}\)
Khi đó pt: \(\Rightarrow a\cdot\dfrac{2t}{t^2+1}+b\cdot\dfrac{1-t^2}{1+t^2}=c\)
\(\Rightarrow2t\cdot a+\left(1-t^2\right)\cdot b=\left(1+t^2\right)\cdot c\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)