Dùng định nghĩa tìm các giới hạn sau: lim x → 4 x + 1 3 x - 2

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Dùng định nghĩa, tìm các giới hạn sau :
a) \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow4}\dfrac{x+1}{3x-2}\)
b) \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow+\infty}\dfrac{2-5x^2}{x^2+3}\)
a) Hàm số f(x) = xác định trên R\{
} và ta có x = 4 ∈ (
;+∞).
Giả sử (xn) là dãy số bất kì và xn ∈ (;+∞); xn ≠ 4 và xn → 4 khi n → +∞.
Ta có lim f(xn) = lim =
=
.
Vậy
=
.
b) Hàm số f(x) = xác định trên R.
Giả sử (xn) là dãy số bất kì và xn → +∞ khi n → +∞.
Ta có lim f(xn) = lim = lim
= -5.
Vậy
= -5.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Dùng định nghĩa tìm các giới hạn :
a) \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow5}\dfrac{x+3}{3-x}\)\(\)
b) \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow+\infty}\dfrac{x^3+1}{x^2+1}\)
Sử dụng định nghĩa, tìm các giới hạn sau:
a) \(\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to - 3} {x^2};\)
b) \(\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 5} \frac{{{x^2} - 25}}{{x - 5}}.\)
a) \(\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to - 3} {x^2};\)
Giả sử \(\left( {{x_n}} \right)\) là dãy số bất kì thỏa mãn \(\lim {x_n} = - 3.\)
Ta có \(\lim x_n^2 = {\left( { - 3} \right)^2} = 9\)
Vậy \(\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to - 3} {x^2} = 9.\)
b) \(\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 5} \frac{{{x^2} - 25}}{{x - 5}}.\)
Giả sử \(\left( {{x_n}} \right)\) là dãy số bất kì thỏa mãn \(\lim {x_n} = 5.\)
Ta có \(\lim \frac{{{x_n}^2 - 25}}{{{x_n} - 5}} = \lim \frac{{\left( {{x_n} - 5} \right)\left( {{x_n} + 5} \right)}}{{{x_n} - 5}} = \lim \left( {{x_n} + 5} \right) = \lim {x_n} + 5 = 5 + 5 = 10\)
Vậy \(\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 5} \frac{{{x^2} - 25}}{{x - 5}} = 10.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Dùng định nghĩa tìm các giới hạn lim x → 5 x + 3 x - 3
Dùng đạo hàm tìm giới hạn:
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow2}\dfrac{\sqrt{x^2+x+3}-x^2+1}{x^2-4}\)
sao có GP lại ko có huy hiệu hỏi thôi
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Thấy : \(\sqrt{x^2+x+3}-x^2+1=\sqrt{x^2+x+3}-\left(x^2-1\right)=\dfrac{x^2+x+3-\left(x^2-1\right)^2}{\sqrt{x^2+x+3}+x^2-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+x+3-x^4+2x^2-1}{...}=\dfrac{-x^4+3x^2+x+2}{...}\)
\(=\dfrac{-\left(x-2\right)\left(x^3+2x^2+x+1\right)}{...}\)
\(\dfrac{\sqrt{x^2+x+3}-x^2+1}{x^2-4}=\dfrac{-\left(x^3+2x^2+x+1\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left[\sqrt{x^2+x+3}+x^2-1\right]}\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow2}\dfrac{\sqrt{x^2+x+3}-x^2+1}{x^2-4}=\dfrac{-\left(2^3+2.2^2+2+1\right)}{4.\left[\sqrt{2^2+2+3}+2^2-1\right]}=-\dfrac{19}{24}\)
Đúng 6
Bình luận (1)
Dùng đạo hàm tìm giới hạn:
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow2}\dfrac{\sqrt{x^2+x+3}-x^2+1}{x^2-4}\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow2}\dfrac{\sqrt{x^2+x+3}-x^2+1}{x^2-4}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow2}\dfrac{\dfrac{2x+1}{2\sqrt{x^2+x+3}}-2x}{2x}=\dfrac{\dfrac{2.2+1}{2\sqrt{4+2+3}}-4}{4}=-\dfrac{19}{24}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Dùng định nghĩa tìm các giới hạn sau:
lim
x
→
+
∞
2
-
5
x
2
x
2
+
3
Đọc tiếp
Dùng định nghĩa tìm các giới hạn sau: lim x → + ∞ 2 - 5 x 2 x 2 + 3
TXĐ: D = R.
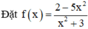
Lấy dãy (xn) bất kì thỏa mãn xn → +∞
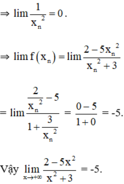
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm các giới hạn sau:
a) \(\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {4^ + }} \frac{1}{{x - 4}}\);
c) \(\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {2^ - }} \frac{x}{{2 - x}}\).
a) Áp dụng giới hạn một bên thường dùng, ta có : \(\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {4^ + }} \frac{1}{{x - 4}} = + \infty \)
b) \(\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {2^ + }} \frac{x}{{2 - x}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {2^+ }} \frac{{ - x}}{{x - 2}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {2^ + }} \left( { - x} \right).\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {2^ + }} \frac{1}{{x - 2}}\)
Ta có: \(\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {2^ + }} \left( { - x} \right) = - \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {2^ + }} x = - 2;\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {2^ +}} \frac{1}{{x - 2}} = +\infty \)
\( \Rightarrow \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {2^ - }} \frac{x}{{2 - x}} = - \infty \)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Sử dụng định nghĩa tính giới hạn $\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 1} \dfrac{2x^2+x-3}{x-1}$.
em gửi câu trả lời bằng ảnh ạ

Xem thêm câu trả lời



















