Cho tan x = 2 Khi đó tan( \(\frac{\Pi}{4}\)-2) = ?

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Chứng minh rằng:
a) \(\sin x - \cos x = \sqrt 2 \sin \left( {x - \frac{\pi }{4}} \right)\);
b) \(\tan \left( {\frac{\pi }{4} - x} \right) = \frac{{1 - \tan x}}{{1 + \tan x}}\;\left( {x \ne \frac{\pi }{2} + k\pi ,\;x \ne \frac{{3\pi }}{4} + k\pi ,\;k \in \mathbb{Z}} \right)\;\).
a) Ta có:
\(\sqrt 2 \sin \left( {x - \frac{\pi }{4}} \right) = \sqrt 2 \left( {\sin x\cos \frac{\pi }{4} + \cos x\sin \frac{\pi }{4}} \right) = \sqrt 2 \left( {\sin x.\frac{{\sqrt 2 }}{2} + \cos x.\frac{{\sqrt 2 }}{2}} \right) = \sin x + \cos x\)
b) Ta có:
\(\tan \left( {\frac{\pi }{4} - x} \right) = \frac{{\tan \frac{\pi }{4} - \tan x}}{{1 + \tan \frac{\pi }{4}\tan x}} = \frac{{1 - \tan x}}{{1 + \tan x}}\;\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho hàm số y tan xa) Xét tính chẵn, lẻ của hàm sốb) Hoàn thành bảng giá trị của hàm số y tan x trên khoảng;left( { - frac{pi }{2};frac{pi }{2}} right). x - frac{pi }{3} - frac{pi }{4} - frac{pi }{6}0frac{pi }{6}frac{pi }{4}frac{pi }{3}y tan x???????Bằng cách lấy nhiều điểm Mleft( {x;tan x} right) với x in left( { - frac{pi }{2};frac{pi }{2}} right) và nối lại ta được đồ thị hàm số y tan x trên khoảng left( { - frac{pi }{2};frac{pi }{2}} right).c) Bằng cách làm tương tự c...
Đọc tiếp
Cho hàm số \(y = \tan x\)
a) Xét tính chẵn, lẻ của hàm số
b) Hoàn thành bảng giá trị của hàm số \(y = \tan x\) trên khoảng\(\;\left( { - \frac{\pi }{2};\frac{\pi }{2}} \right)\).
\(x\) | \( - \frac{\pi }{3}\) | \( - \frac{\pi }{4}\) | \( - \frac{\pi }{6}\) | 0 | \(\frac{\pi }{6}\) | \(\frac{\pi }{4}\) | \(\frac{\pi }{3}\) |
\(y = \tan x\) | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? |
Bằng cách lấy nhiều điểm \(M\left( {x;\tan x} \right)\) với \(x \in \left( { - \frac{\pi }{2};\frac{\pi }{2}} \right)\) và nối lại ta được đồ thị hàm số \(y = \tan x\) trên khoảng \(\left( { - \frac{\pi }{2};\frac{\pi }{2}} \right)\).
c) Bằng cách làm tương tự câu b cho các đoạn khác có độ dài bằng chu kỳ \(T = \pi \), ta được đồ thị của hàm số \(y = \tan x\) như hình dưới đây.
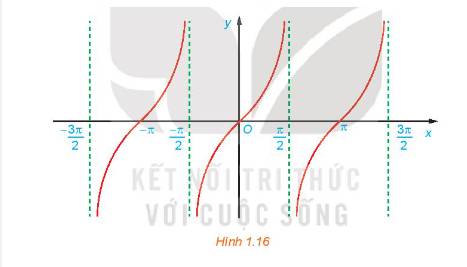
Từ đồ thị ở Hình 1.16, hãy tìm tập giá trị và các khoảng đồng biến của hàm số \(y = \tan x\).
a) Tập xác định của hàm số là \(D = \mathbb{R}\;\backslash \left\{ {\frac{\pi }{2} + k\pi {\rm{|}}\;k\; \in \;\mathbb{Z}} \right\}\)
Do đó, nếu x thuộc tập xác định D thì –x cũng thuộc tập xác định D
Ta có: \(f\left( { - x} \right) = \tan \left( { - x} \right) = - \tan x = - f\left( x \right),\;\forall x\; \in \;D\)
Vậy \(y = \tan x\) là hàm số lẻ.
b)
\(x\) | \( - \frac{\pi }{3}\) | \( - \frac{\pi }{4}\) | \( - \frac{\pi }{6}\) | \(0\) | \(\frac{\pi }{6}\) | \(\frac{\pi }{4}\) | \(\frac{\pi }{3}\) |
\(\tan x\) | \( - \sqrt 3 \) | \( - 1\) | \( - \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{3}\) | \(0\) | \(\frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{3}\) | \(1\) | \(\sqrt 3 \) |
c) Từ đồ thị trên, ta thấy hàm số \(y = \tan x\) có tập xác định là \(\mathbb{R}\backslash \left\{ {\frac{\pi }{2} + k\pi {\rm{|}}\;k\; \in \;\mathbb{Z}} \right\}\), tập giá trị là \(\mathbb{R}\) và đồng biến trên mỗi khoảng \(\left( { - \frac{\pi }{2} + k\pi ;\frac{\pi }{2} + k\pi } \right)\).
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a) Cho tan x = 5 ( \(6\pi< x< \frac{13\pi}{2}\)) tính sin2x
b) Cho sin x = \(\frac{3}{5}\) ( \(\frac{-3\pi}{2}< x< -\pi\)) tính \(tan\left(x-\frac{\pi}{4}\right)\)
\(\cos^2=\frac{1}{1+tan^2x}=\frac{1}{1+25}\\ \Rightarrow cos=\frac{1}{\sqrt{26}}\left(6\pi< x< \frac{13}{2}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow sin=\frac{5}{\sqrt{26}}\\ \Rightarrow sin2x=2sinxcosx=2\times\frac{5}{\sqrt{26}}\times\frac{1}{\sqrt{26}}=\frac{5}{13}\)
b) \(cos^2=1-sin^2x=\frac{16}{25}\\ \Rightarrow cos=-\frac{4}{5}\left(-\frac{3\pi}{2}< x< -\pi\right)\\\Rightarrow tanx=-\frac{3}{4} \\ tan\left(x-\frac{\pi}{4}\right)=\frac{tanx-tan\frac{\pi}{4}}{1+tanxtan\frac{\pi}{4}}=-7\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (2)
Chứng minh rằng
\(\tan\left(x\right)\tan\left(x+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)+\tan\left(x+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)\tan\left(x+\frac{2\pi}{3}\right)+\tan\left(x\right)\tan\left(x+\frac{2\pi}{3}\right)=3\)
Rút gọn biểu thức sau:\(A=\left[tan\frac{17\pi}{4}+tan\left(\frac{7\pi}{2}-x\right)\right]^2+\left[cot\frac{17\pi}{4}+cot\left(7\pi\right)-x\right]^2\)
\(\cot\left(7\pi\right)\) ko xác định bạn ơi
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Thì tách bình thường thôi :)
\(A=\left[\tan\left(4\pi+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)+\tan\left(3\pi+\frac{\pi}{2}-x\right)\right]^2+\left[\cot\left(4\pi+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)+\cot\left(-x\right)\right]^2\)
\(A=\left[\tan\left(\frac{\pi}{4}\right)+\cot x\right]^2+\left[\cot\left(\frac{\pi}{4}\right)-\cot x\right]^2\)
\(A=\left(1+\cot x\right)^2+\left(1-\cot x\right)^2=...\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) \(\cos \left( {3x - \frac{\pi }{4}} \right) = - \frac{{\sqrt 2 }}{2}\);
b) \(2{\sin ^2}x - 1 + \cos 3x = 0\);
c) \(\tan \left( {2x + \frac{\pi }{5}} \right) = \tan \left( {x - \frac{\pi }{6}} \right)\).
a) \(\cos \left( {3x - \frac{\pi }{4}} \right) = - \frac{{\sqrt 2 }}{2}\;\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow \cos \left( {3x - \frac{\pi }{4}} \right) = \cos \frac{{3\pi }}{4}\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{3x - \frac{\pi }{4} = \frac{{3\pi }}{4} + k2\pi }\\{3x - \frac{\pi }{4} = - \frac{{3\pi }}{4} + k2\pi }\end{array}} \right.\;\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{3x = \pi + k2\pi }\\{3x = - \frac{\pi }{2} + k2\pi }\end{array}} \right.\)
\( \Leftrightarrow \;\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{x = \frac{\pi }{3} + \frac{{k2\pi }}{3}}\\{x = - \frac{\pi }{6} + \frac{{k2\pi }}{3}}\end{array}} \right.\;\;\left( {k \in \mathbb{Z}} \right)\)
b) \(2{\sin ^2}x - 1 + \cos 3x = 0\;\;\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow \cos 2x + \cos 3x = 0\;\; \Leftrightarrow 2\cos \frac{{5x}}{2}\cos \frac{x}{2} = 0\;\; \Leftrightarrow \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{\cos \frac{{5x}}{2} = 0}\\{\cos \frac{x}{2} = 0}\end{array}} \right.\)
\( \Leftrightarrow \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{\frac{{5x}}{2} = \frac{\pi }{2} + k\pi }\\{\frac{{5x}}{2} = - \frac{\pi }{2} + k\pi }\\{\frac{x}{2} = \frac{\pi }{2} + k\pi }\\{\frac{x}{2} = - \frac{\pi }{2} + k\pi }\end{array}} \right.\;\;\;\;\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{x = \frac{\pi }{5} + \frac{{k2\pi }}{5}}\\{x = - \frac{\pi }{5} + \frac{{k2\pi }}{5}}\\{x = \pi + k2\pi }\\{x = - \pi + k2\pi }\end{array}} \right.\;\;\;\left( {k \in \mathbb{Z}} \right)\)
c) \(\tan \left( {2x + \frac{\pi }{5}} \right) = \tan \left( {x - \frac{\pi }{6}} \right)\;\; \Leftrightarrow 2x + \frac{\pi }{5} = x - \frac{\pi }{6} + k\pi \;\;\; \Leftrightarrow x = - \frac{{11\pi }}{{30}} + k\pi \;\;\left( {k \in \mathbb{Z}} \right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải pt
a) \(tanx.tan\frac{\pi}{9}=1+tan\frac{\pi}{9}.tan\frac{\pi}{90}+tanx.tan\frac{\pi}{90};\left(-2\pi< x< 2\pi\right)\)
b) \(tan^22x+\frac{1}{cos^22x}=7;\left(0< x< 360^0\right)\)
c) \(tan^3x+\frac{1}{cos^2x}+4\sqrt{3}\left(1+tanx\right)=8+7tanx;\left(-\pi< x< \pi\right)\)
a/ \(\Leftrightarrow tanx.tan\frac{\pi}{9}-1=tan\frac{\pi}{90}\left(tanx+tan\frac{\pi}{9}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{tanx+tan\frac{\pi}{9}}{1-tanx.tan\frac{\pi}{9}}=-\frac{1}{tan\frac{\pi}{90}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow tan\left(x+\frac{\pi}{9}\right)=tan\left(\frac{23\pi}{45}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x+\frac{\pi}{9}=\frac{23\pi}{45}+k\pi\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{2\pi}{5}+k\pi\)
Do \(-2\pi< x< 2\pi\Rightarrow-2\pi< \frac{2\pi}{5}+k\pi< 2\pi\)
\(\Rightarrow k=\left\{-2;-1;0;1;2\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\left\{-\frac{8\pi}{5};-\frac{3\pi}{5};\frac{2\pi}{5};\frac{7\pi}{5};\frac{12\pi}{5}\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
b/
ĐKXĐ: \(cos2x\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow tan^22x+1+tan^22x=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow tan^22x=3\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}tan2x=\sqrt{3}\\tan2x=-\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}tan2x=tan60^0\\tan2x=tan\left(-60^0\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=60^0+k180^0\\2x=-60^0+k180^0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=30^0+k180^0\\x=-30^0+k180^0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bạn tự tìm nghiệm thuộc khoảng đã cho nhé
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
c/ ĐKXĐ: \(cosx\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow tan^3x+1+tan^2x+4\sqrt{3}\left(1+tanx\right)=8+7tanx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow tan^2x\left(1+tanx\right)+\left(4\sqrt{3}-7\right)\left(1+tanx\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(tan^2x-7+4\sqrt{3}\right)\left(1+tanx\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}tanx=-1\\tan^2x=7-4\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}tanx=-1\\tanx=2-\sqrt{3}\\tanx=-2+\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}tanx=tan\left(-\frac{\pi}{4}\right)\\tanx=tan\left(\frac{\pi}{12}\right)\\tanx=tan\left(-\frac{\pi}{12}\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\frac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\x=\frac{\pi}{12}+k\pi\\x=-\frac{\pi}{12}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bạn tự tìm x thuộc khoảng đã cho
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(\tan\left(4x-\frac{\pi}{4}\right)+\tan\left(x+\frac{\pi}{2}\right)=0\)
ĐKXĐ: ...
\(\Leftrightarrow tan\left(4x-\frac{\pi}{4}\right)=-tan\left(x+\frac{\pi}{2}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow tan\left(4x-\frac{\pi}{4}\right)=tanx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x-\frac{\pi}{4}=x+k\pi\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{\pi}{12}+\frac{k\pi}{3}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1: Cho sin αfrac{1}{5} với 0∠α∠frac{pi}{2}. Tính cos (α-frac{pi}{6})
Bài 2: Cho cos xfrac{-2}{3} vớifrac{pi}{2}∠x∠π. Tính tan (frac{pi}{4}+x)
Bài 3: Cho tan αfrac{-4}{7} với frac{3pi}{2}∠α∠2π. Tính cos (2α -frac{pi}{2})
Bài 4: Cho sin α frac{1}{2} với 0∠α∠π. Tính tan (2α -frac{pi}{2}) +sin α
Đọc tiếp
Bài 1: Cho sin α=\(\frac{1}{5}\) với 0∠α∠\(\frac{\pi}{2}\). Tính cos (α-\(\frac{\pi}{6}\))
Bài 2: Cho cos x=\(\frac{-2}{3}\) với\(\frac{\pi}{2}\)∠x∠π. Tính tan (\(\frac{\pi}{4}\)+x)
Bài 3: Cho tan α=\(\frac{-4}{7}\) với \(\frac{3\pi}{2}\)∠α∠2π. Tính cos (2α -\(\frac{\pi}{2}\))
Bài 4: Cho sin α =\(\frac{1}{2}\) với 0∠α∠π. Tính tan (2α -\(\frac{\pi}{2}\)) +sin α
Bài 1:
$\cos ^2a=1-\sin ^2a=1-\frac{1}{5^2}=\frac{24}{25}$
Vì $0< a< \frac{\pi}{2}$ nên $\cos a>0$
$\Rightarrow \cos a=\frac{\sqrt{24}}{5}$
\(\cos (a-\frac{\pi}{6})=\cos a.\cos \frac{\pi}{6}+\sin a\sin \frac{\pi}{6}=\cos a.\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}+\sin a. \frac{1}{2}\)
\(=\frac{\sqrt{24}}{5}.\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}+\frac{1}{5}.\frac{1}{2}=\frac{1+6\sqrt{2}}{10}\)
Bài 2:
$\cos x=\frac{-2}{3}\Rightarrow \sin ^2x=1-\cos ^2x=\frac{5}{9}$
Vì $x\in (\frac{\pi}{2}; \pi)$ nên $\sin x>0\Rightarrow \sin x=\frac{\sqrt{5}}{3}$
\(\Rightarrow \tan x=\frac{\sin x}{\cos x}=\frac{-\sqrt{5}}{2}\)
Do đó:
\(\tan (\frac{\pi}{4}+x)=\frac{\tan \frac{\pi}{4}+\tan x}{1-\tan \frac{\pi}{4}.\tan x}=\frac{1+\tan x}{1-\tan x}=\frac{1-\frac{\sqrt{5}}{2}}{1+\frac{\sqrt{5}}{2}}=-9+4\sqrt{5}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 3:
\(\tan a=\frac{-4}{7}=\frac{\sin a}{\cos a}\)
\(\Rightarrow \frac{\sin ^2a}{\cos ^2a}=\frac{16}{49}\Rightarrow \frac{1}{\cos ^2a}=\frac{65}{49}\) \(\Rightarrow \cos ^2a=\frac{49}{65}\)
Kết hợp điều kiện của $a$ suy ra $\cos a>0\Rightarrow \cos a=\frac{7}{\sqrt{65}}$
$\Rightarrow \sin a=\frac{-4}{7}\cos a=\frac{-4}{\sqrt{65}}$
Do đó:
\(\cos (2a-\frac{\pi}{2})=\cos 2a.\cos \frac{\pi}{2}+\sin 2a.\sin \frac{\pi}{2}\)
\(=(\cos ^2a-\sin ^2a).0+2\sin a\cos a.1=2\sin a\cos a=2.\frac{-4}{\sqrt{65}}.\frac{7}{\sqrt{65}}=\frac{56}{65}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 4:
$\sin a=\frac{1}{2}$ và $0< a< \pi$ nên $a=\frac{\pi}{6}$ hoặc $a=\frac{5}{6}\pi$
Nếu $a=\frac{\pi}{6}$ thì $\tan (2a-\frac{\pi}{2})+\sin a=\tan (2.\frac{\pi}{6}-\frac{\pi}{2})+\frac{1}{2}=\frac{-\sqrt{3}}{3}+\frac{1}{2}=\frac{3-2\sqrt{3}}{6}$
Nếu $a=\frac{5\pi}{6}$ thì:
\(\tan (2a-\frac{\pi}{2})+\sin a=\tan (2.\frac{5\pi}{6}-\frac{\pi}{2})+\frac{1}{2}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}+\frac{1}{2}=\frac{3+2\sqrt{3}}{6}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)












