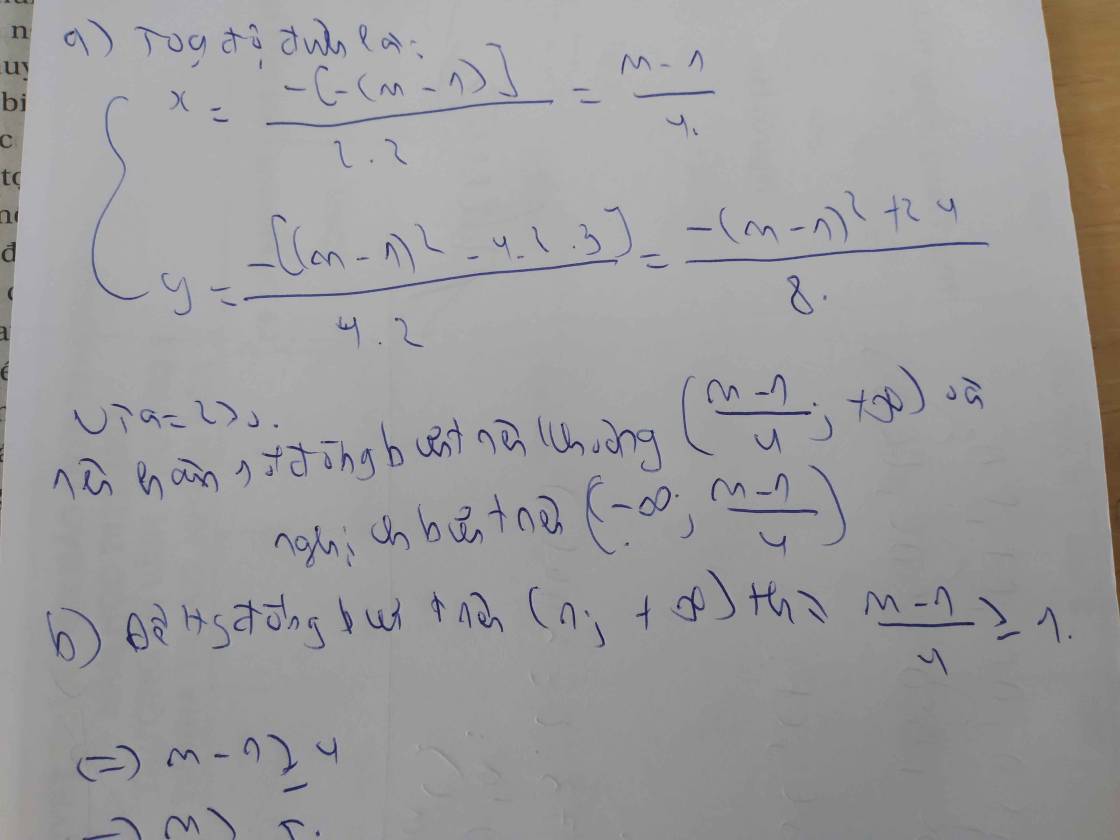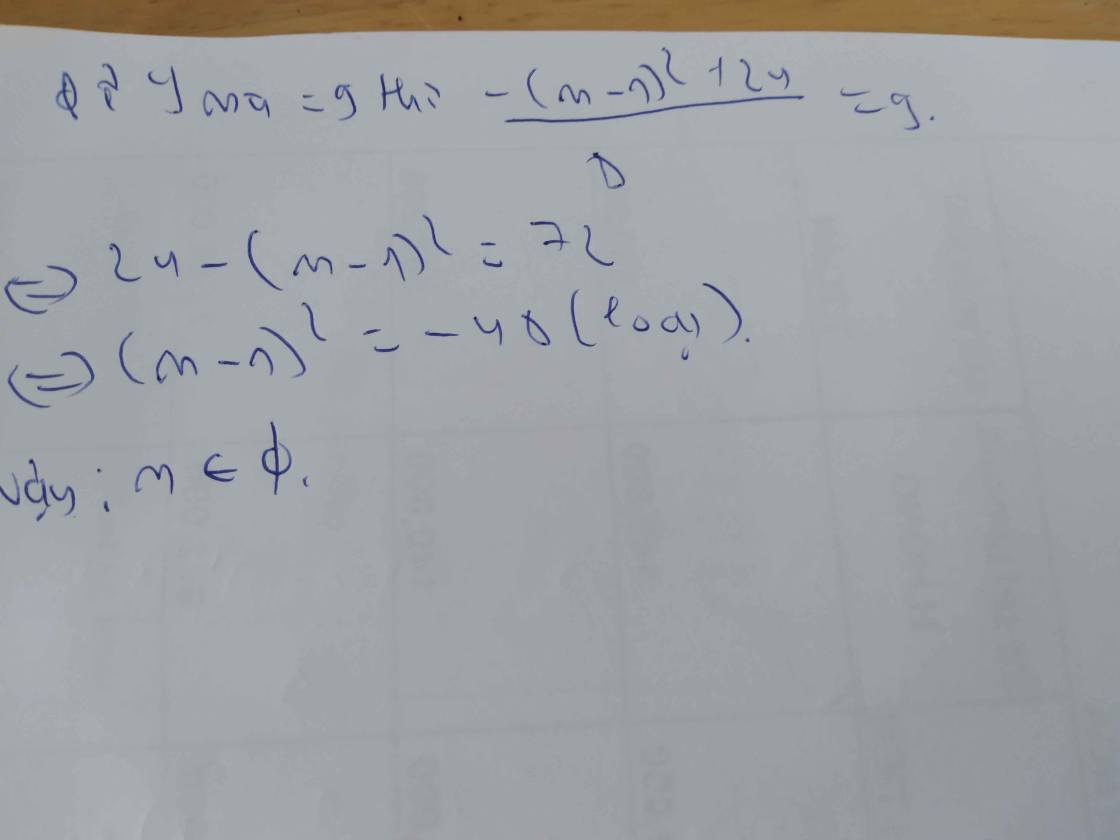Tìm a để hàm số \(y=\frac{a}{\sqrt{x-1}}\) đồng biến trên khoảng (1; +∞)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Câu 1: cho hàm số y=\(\dfrac{\sqrt{m}+3}{\sqrt{m}-2}x-10\)
a,tìm x để hàm số trên là hàm số bậc nhất
b, tìm m để hàm số trên đồng biến trên R
a: Để hàm số trên là hàm số bậc nhất thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\ge0\\m\ne4\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: Để hàm số đồng biến thì \(\sqrt{m}-2>0\)
hay m>4
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Tìm tất cả giá trị của m để hàm số y=\(\sqrt{x^2+2mx+m^2+1}\) đồng biến trên khoảng (1;+∞)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) Với mọi \(x>1\) thì:
\(y'=\dfrac{x+m}{\sqrt{x^2+2mx+m^2+1}}\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge-m\) (\(\forall x>1\))
\(\Leftrightarrow-m\le1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\ge-1\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (3)
cho hàm số y = 2x2 - (m - 1 )x +3, m là tham số
a. tìm khoảng đồng biến, nghịch biến của hàm số
b/ tìm các giái trị của m để hàm số đồng biến trên khoảng 1;+∞
c. tìm m để hàm số nghịch biến trên khoàng -4;8
d. tìm m để giá trị nhỏ nhất của hàm số là 9
Trong các hàm số sau, hàm số nào đồng biến, hàm số nào nghịch biến trên khoảng xác định của hàm số đó? Vì sao?
a) \(y = {\left( {\frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right)^x}\)
b) \(y = {\left( {\frac{{\sqrt[3]{{26}}}}{3}} \right)^x}\)
c) \(y = {\log _\pi }x\)
d) \(y = {\log _{\frac{{\sqrt {15} }}{4}}}x\)
\(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}< 1;\dfrac{\sqrt[3]{26}}{3}< 1;\pi>1;\dfrac{\sqrt{15}}{4}< 1\)
Hàm số đồng biến là: \(log_{\pi}x\)
Hàm số nghịch biến là: \(\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\right)^x;\left(\dfrac{\sqrt[3]{26}}{3}\right)^x;log_{\dfrac{\sqrt{15}}{4}}x\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho hàm số: \(y=-\dfrac{x^3}{3}+\left(a-1\right)x^2+\left(a+3\right)x-4\). Tìm a để hàm số đồng biến trên khoảng (0;3)
\(y'=-x^2+2\left(a-1\right)x+a+3\)
Hàm đồng biến trên khoảng đã cho khi với mọi \(x\in\left(0;3\right)\) ta có:
\(-x^2+2\left(a-1\right)x+a+3\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)a\ge x^2+2x-3\)
\(\Rightarrow a\ge\dfrac{x^2+2x-3}{2x+1}\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x^2+2x-3}{2x+1}\) với \(x\in\left(0;3\right)\)
\(f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{2\left(x^2+x+4\right)}{\left(2x+1\right)^2}>0\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) đồng biến
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)< f\left(3\right)=\dfrac{12}{7}\Rightarrow a\ge\dfrac{12}{7}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
cho hàm số y=-2x2+4(a-1)x+1 (a là tham số). tìm tất cả các giá trị của a để hàm số đã cho đồng biến trên khoảng (1;2)
tìm các giá trị của m để hàm số
a) \(y=\dfrac{x+m}{x+1}\) nghịch biến trên từng khoảng xác định
b) \(y=\dfrac{2x-3m}{x-m}\) đồng biến trên từng khoảng xác định
a: TXĐ: D=R\{-1}
\(y'=\dfrac{\left(x+m\right)'\left(x+1\right)-\left(x+1\right)'\left(x+m\right)}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+1-x-m}{\left(x+1\right)^2}=\dfrac{1-m}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
Để hàm số nghịch biến trên từng khoảng xác định thì \(y'< 0\forall x\)
=>\(\dfrac{1-m}{\left(x+1\right)^2}< 0\)
=>1-m<0
=>m>1
b: TXĐ: D=R\{m}
\(y=\dfrac{2x-3m}{x-m}\)
=>\(y'=\dfrac{\left(2x-3m\right)'\left(x-m\right)-\left(2x-3m\right)\left(x-m\right)'}{\left(x-m\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(x-m\right)-\left(2x-3m\right)}{\left(x-m\right)^2}=\dfrac{2x-2m-2x+3m}{\left(x-m\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{m}{\left(x-m\right)^2}\)
Để hàm số đồng biến trên từng khoảng xác định thì \(y'>0\forall x\)
=>\(\dfrac{m}{\left(x-m\right)^2}>0\)
=>m>0
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho hàm số \(y=\frac{x^2-2mx+3m^2}{x-2m}\)
Tìm m để y có hai khoảng đồng biến trên toàn miền xác định.
Tìm m để y đồng biến trên khoảng \(\left(1,\infty\right)\)
Ta có \(y'=\frac{x^2-2mx+m^2}{\left(x-2m\right)^2},x\ne2m\)
Để y có hai khoảng đồng biến trên toàn miền xác định thì
\(y'\ge0,\forall x\ne2m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4mx+m^2\ge0,\forall x\ne2m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'\le0\Leftrightarrow4m^2-m^2\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3m^2\le0\Leftrightarrow m=0\)
Câu tiếp theo:
y đồng biến trên\(\left(1,\infty\right)\Leftrightarrow y'\ge0,\forall x\in\left(1,+\infty\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}f\left(x\right)=x^2-4mx+m^2\ge0,\forall x>1\\2m\notin\left(1,\infty\right)\end{cases}}\)
Để cj suy nghĩ mai lm tiếp=.=
rõ ràng m=0 thì đk trên thõa mãn.
Với \(m=0:\Delta'=3m^2>0\) nên ta có:
\(f\left(x\right)\ge0,\forall x>1\Leftrightarrow x_1< x_2\le1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}\Delta'>0\\f\left(1\right)\ge\\\frac{S}{2}-1< 0\end{cases}0}\)
\(f\left(1\right)\ge0\Leftrightarrow m^2-4m+1\ge0\Leftrightarrow m\le2-\sqrt{3}\)hay\(m\ge2+\sqrt{3}\)
\(\frac{S}{2}-1< 0\Leftrightarrow2m-1< 0\Leftrightarrow m< \frac{1}{2}\)
\(2m\notin\left(1,\infty\right)\Leftrightarrow2m\le1\Leftrightarrow m\le\frac{1}{2}\)
Vậy \(m\le2-\sqrt{3}\)là giá trị m cần tìm
cho hàm số y=f(x)=-x^2-2x+1. Mệnh đề nào sau đây là đúng? A. Hàm số nghịch biến trên khoảng (-1;+vô cực) B. Hàm số nghịch biến trên khoảng (-vô cực;-1) C. Hàm số đồng biến trên khoảng (-1;+vô cực) D. Hàm số đồng biến trên khoảng (-vô cực;0)
B. Hàm số nghịch biến trên khoảng \(\left(-\infty;-1\right)\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
Cho hàm số \(y=-\frac{2}{3}x^3+\left(m+1\right)x^2+2mx+5\), với tham số thực. Tìm m để hàm số đồng biến trên khoảng (0;2)
Ta có \(y'=-2x^2+2\left(m+1\right)x+2m\)
Hàm số đồng biến trên khoảng (0;2) \(\Leftrightarrow y'\ge0,x\in\left(0;2\right)\) (*)
Vì y'(x) liên tục tại x=0 và x=2 nên (*) \(\Leftrightarrow y'\ge0,x\in\left[0;2\right]\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x^2+2\left(m+1\right)x+2m\ge0,x\in\left[0;2\right]\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\left(x+1\right)\ge x^2-x,x\in\left[0;2\right]\Leftrightarrow m\ge g\left(x\right),x\in\left[0;2\right]\); (trong đó \(g\left(x\right)=\frac{x^2-x}{x+1}\))
\(\Leftrightarrow m\ge Max_{\left[0;2\right]}g\left(x\right)\)
Xét hàm số \(g\left(x\right)=\frac{x^2-x}{x+1}\) trên đoạn \(\left[0;2\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow g'\left(x\right)=\frac{x^2+2x-1}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\Rightarrow g'\left(x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=-1+\sqrt{2},x\in\left[0;2\right]\)
\(g\left(0\right);g\left(2\right)=\frac{2}{3};g\left(-1+\sqrt{2}\right)\Rightarrow Max_{\left(0;+\infty\right)}g\left(x\right)=\frac{2}{3}\) tại x=2
Vậy \(m\ge\frac{2}{3}\) thì hàm số đồng biến trên khoảng (0;2)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Ta có : \(y'=-2x^2+2\left(m+1\right)x+2m,\Delta'=m^2+6m+1\)
Suy ra hàm đồng biến trên khoảng (0; 2) \(\Leftrightarrow y'\ge0,x\in\left(0;2\right)\)(*)
Trường hợp 1 : Nếu \(\Delta'\le0\Leftrightarrow m^2+6m+1\le0\Leftrightarrow-3-2\sqrt{2}\le m\le-3+2\sqrt{2}\)
theo định lí về dấu tam thức bậc 2 ta có \(y'\le0,x\in R\) => (*) không thỏa mãn
Trường hợp 2 : Nếu \(\Delta'>0\Leftrightarrow m^2+6m+1>0\Leftrightarrow m\le-3-2\sqrt{2}\) hoặc \(m\ge-3+2\sqrt{2}\) thì (*) đúng
<=> phương trình \(y'=0\) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt \(x_1;x_2\) (\(x_1\)>\(x_2\)) và thỏa mãn \(x_1\le0<2\le x_2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}\Delta>0\\x_1\le0<2\le x_2\end{cases}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}\left(x_1-2\right)\left(x_2-2\right)\le0\\\Delta>0\\\left(x_1-0\right)\left(x_2-0\right)\le0\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}x_1x_2-2\left(x_1+x_2\right)+4\le0\\\Delta>0\\x_1x_2\le0\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\ge\frac{2}{3}\)
Kết hợp trường hợp 1 và trường hợp 2 ta có \(m\ge\frac{2}{3}\) thì hàm đồng biến trên khoảng (0;2)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)