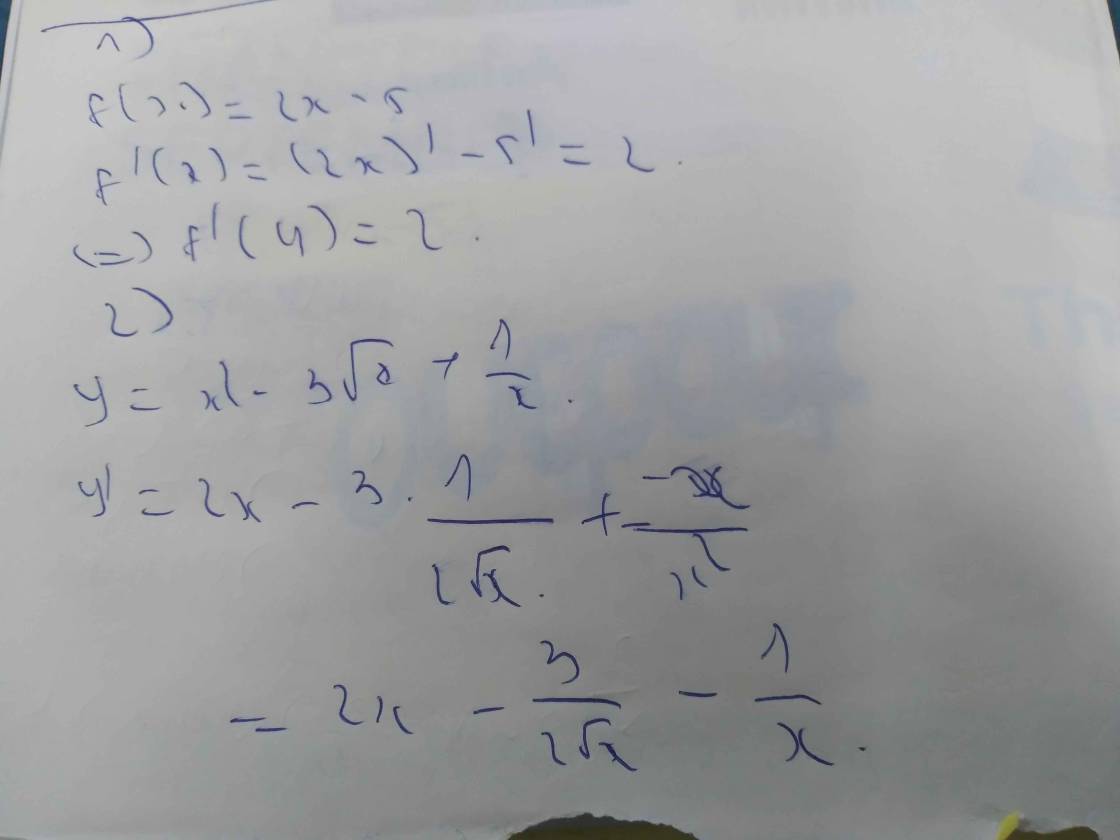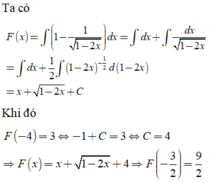tính nguyên hàm của hàm số f(x)=\(\dfrac{2x+1}{x^4+2x^3+x^2}\)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
1. đạo hàm của hàm số f(x) = 2x - 5 tại \(x_0=4\)
2. đạo hàm của hàm số \(y=x^2-3\sqrt{x}+\dfrac{1}{x}\)
3. đạo hàm của hàm số \(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x+9}{x+3}+4\sqrt{x}\) tại điểm x = 1
1) \(f\left(x\right)=2x-5\)
\(f'\left(x\right)=2\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(4\right)=2\)
2) \(y=x^2-3\sqrt[]{x}+\dfrac{1}{x}\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=2x-\dfrac{3}{2\sqrt[]{x}}-\dfrac{1}{x^2}\)
3) \(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x+9}{x+3}+4\sqrt[]{x}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1.\left(x+3\right)-1.\left(x+9\right)}{\left(x-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{4}{2\sqrt[]{x}}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x+3-x-9}{\left(x-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{2}{\sqrt[]{x}}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{12}{\left(x-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{2}{\sqrt[]{x}}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=2\left[\dfrac{6}{\left(x-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt[]{x}}\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(1\right)=2\left[\dfrac{6}{\left(1-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt[]{1}}\right]=2\left(\dfrac{3}{2}+1\right)=2.\dfrac{5}{2}=5\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
Hàm số nào bên dưới không là nguyên hàm của hàm số \(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x^2-1}{x^2}\)
A. F(x)=\(\dfrac{x^2-x+1}{x}\)
B. F(x)=\(\dfrac{x^2+1}{x}\)
C. F(x)=\(\dfrac{x^2+2x+1}{x}\)
D. F(x)\(=\dfrac{x^2-1}{x}\)
\(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x^2-1}{x^2}=1-\dfrac{1}{x^2}\)
\(\int f\left(x\right)dx=\int\left(1-\dfrac{1}{x^2}\right)dx=\int1dx-\int x^{-2}dx\)
=\(x-\dfrac{x^{-2+1}}{-2+1}+C=x-\dfrac{x^{-1}}{-1}+C=x+\dfrac{1}{x}+C\)
C=-1 ta được phương án A(ko tm câu hỏi)
C=0 ta được phương án B(ko tm câu hỏi)
C=2 ta được phương án C(ko tm câu hỏi)
=>chọn D
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm nguyên hàm của hàm số:
1. \(f\left(x\right)=\left(2x-1\right)e^{\dfrac{1}{x}}\)
2. \(f\left(x\right)=e^{3x}.3^x\)
2.
\(I=\int e^{3x}.3^xdx\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u=3^x\\dv=e^{3x}dx\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}du=3^xln3dx\\v=\dfrac{1}{3}e^{3x}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow I=\dfrac{1}{3}e^{3x}.3^x-\dfrac{ln3}{3}\int e^{3x}.3^xdx=\dfrac{1}{3}e^{3x}.3^x-\dfrac{ln3}{3}.I\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(1+\dfrac{ln3}{3}\right)I=\dfrac{1}{3}e^{3x}.3^x\)
\(\Rightarrow I=\dfrac{1}{3+ln3}.e^{3x}.3^x+C\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1.
\(I=\int\left(2x-1\right)e^{\dfrac{1}{x}}dx=\int2x.e^{\dfrac{1}{x}}dx-\int e^{\dfrac{1}{x}}dx\)
Xét \(J=\int2x.e^{\dfrac{1}{x}}dx\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u=e^{\dfrac{1}{x}}\\dv=2xdx\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}du=-\dfrac{e^{\dfrac{1}{x}}}{x^2}dx\\v=x^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow J=x^2.e^{\dfrac{1}{x}}+\int e^{\dfrac{1}{x}}dx\)
\(\Rightarrow I=x^2.e^{\dfrac{1}{x}}+C\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
Để tìm nguyên hàm của hàm số, ta cần xác định giá trị của hàm tại một điểm nào đó.
Trong trường hợp này, ta chọn điểm nhân nguyên tố nhất là 3.
Để tính giá trị của hàm tại điểm 3, ta đặt x=3 vào hàm số:
f ( x )
( 2 x − 1 ) e 1 x
= ( 2 ( 3 ) − 1 ) e 1 ( 3 )
= ( 6 − 1 ) e 1 3
= ( 5 ) e 1 3
f ( x )
e 3 x
= e 3 ( 3 )
= e 3 3
Ta tiến hành tính toán:
f ( 3 )
( 5 ) e 1 3
= 5 e 1 3
f ( 3 )
e 3 3
= e 3 3
Như vậy, giá trị của hàm tại điểm 3 là 5e^3 hoặc e^33, tùy thuộc vào hàm số cụ thể.
Tóm lại, để tìm nguyên hàm của hàm số, ta đã tìm được rằng giá trị của hàm tại điểm 3 là 5e^3 hoặc e^33, tùy thuộc vào hàm số cụ thể.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
Tìm nguyên hàm của hàm số \(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x^2+2x}{x+1}\).
Lời giải:
\(\int f(x)dx=\int \frac{x^2+2x}{x+1}dx=\int \frac{(x+1)^2-1}{x+1}dx=\int (x+1-\frac{1}{x+1})dx\)
\(=\int (x+1)dx-\int \frac{1}{x+1}dx=\frac{x^2}{2}+x-\ln |x+1|+c\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
1. Tính đạo hàm của các hàm số sau:a, ydfrac{2x-1}{x-1}b, ydfrac{2x+1}{1-3x}c, ydfrac{x^2+2x+2}{x+1}d, ydfrac{2x^2}{x^2-2x-3}e, yx+1-dfrac{2}{x-1}g, ydfrac{2x^2-4x+5}{2x+1}2. Tính đạo hàm của các hàm số sau:a, yleft(x^2+x+1right)^4b, y (1-2x2)5c, yleft(dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}right)^3d, ydfrac{left(x+1right)^2}{left(x-1right)^3}e, ydfrac{1}{left(x^2-2x+5right)^2}f, yleft(3-2x^2right)^4
Đọc tiếp
1. Tính đạo hàm của các hàm số sau:
a, \(y=\dfrac{2x-1}{x-1}\)
b, \(y=\dfrac{2x+1}{1-3x}\)
c, \(y=\dfrac{x^2+2x+2}{x+1}\)
d, \(y=\dfrac{2x^2}{x^2-2x-3}\)
e, \(y=x+1-\dfrac{2}{x-1}\)
g, \(y=\dfrac{2x^2-4x+5}{2x+1}\)
2. Tính đạo hàm của các hàm số sau:
a, \(y=\left(x^2+x+1\right)^4\)
b, y= (1-2x2)5
c, \(y=\left(\dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}\right)^3\)
d, \(y=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)^3}\)
e, \(y=\dfrac{1}{\left(x^2-2x+5\right)^2}\)
f, \(y=\left(3-2x^2\right)^4\)
a. \(y'=\dfrac{-1}{\left(x-1\right)}\)
b. \(y'=\dfrac{5}{\left(1-3x\right)^2}\)
c. \(y=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2+1}{x+1}=x+1+\dfrac{1}{x+1}\Rightarrow y'=1-\dfrac{1}{\left(x+1\right)^2}=\dfrac{x^2+2x}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
d. \(y'=\dfrac{4x\left(x^2-2x-3\right)-2x^2\left(2x-2\right)}{\left(x^2-2x-3\right)^2}=\dfrac{-4x^2-12x}{\left(x^2-2x-3\right)^2}\)
e. \(y'=1+\dfrac{2}{\left(x-1\right)^2}=\dfrac{x^2-2x+3}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
g. \(y'=\dfrac{\left(4x-4\right)\left(2x+1\right)-2\left(2x^2-4x+5\right)}{\left(2x+1\right)^2}=\dfrac{4x^2+4x-14}{\left(2x+1\right)^2}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
2.
a. \(y'=4\left(x^2+x+1\right)^3.\left(x^2+x+1\right)'=4\left(x^2+x+1\right)^3\left(2x+1\right)\)
b. \(y'=5\left(1-2x^2\right)^4.\left(1-2x^2\right)'=-20x\left(1-2x^2\right)^4\)
c. \(y'=3\left(\dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}\right)^2.\left(\dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}\right)'=3\left(\dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}\right)^2.\left(\dfrac{-3}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\right)=\dfrac{-9\left(2x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)^4}\)
d. \(y'=\dfrac{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)^3-3\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)^6}=\dfrac{-x^2-6x-5}{\left(x-1\right)^4}\)
e. \(y'=-\dfrac{\left[\left(x^2-2x+5\right)^2\right]'}{\left(x^2-2x+5\right)^4}=-\dfrac{2\left(x^2-2x+5\right)\left(2x-2\right)}{\left(x^2-2x+5\right)^4}=-\dfrac{4\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x^2-2x+5\right)^3}\)
f. \(y'=4\left(3-2x^2\right)^3.\left(3-2x^2\right)'=-16x\left(3-2x^2\right)^3\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Biết F(x) là một nguyên hàm của hàm số
f
(
x
)
1
-
1
1
-
2
x
và F(-4) 3. Tính
F
-
3
2
Đọc tiếp
Biết F(x) là một nguyên hàm của hàm số f ( x ) = 1 - 1 1 - 2 x và F(-4) = 3. Tính F - 3 2
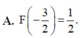
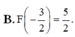
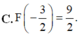
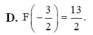
Cho hàm số fleft(xright)left{{}begin{matrix}2sin^2x+1,x 02^x;xge0end{matrix}right.. Giả sử Fleft(xright) là một nguyên hàm của hàm số fleft(xright) trên R và thỏa mãn điều kiện Fleft(1right)dfrac{2}{ln2}. Tính Fleft(-piright) A. Fleft(-piright)-2pi+dfrac{1}{ln2} B. Fleft(-piright)-2pi-dfrac{1}{ln2}C. Fleft(-piright)-pi-dfrac{1}{ln2} D. Fleft(-piright)-2piMình cần bài giải ạ, mình cảm ơn nhiều ♥
Đọc tiếp
Cho hàm số \(f\left(x\right)=\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2\sin^2x+1,x< 0\\2^x;x\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\). Giả sử \(F\left(x\right)\) là một nguyên hàm của hàm số \(f\left(x\right)\) trên \(R\) và thỏa mãn điều kiện \(F\left(1\right)=\dfrac{2}{ln2}\). Tính \(F\left(-\pi\right)\)
A. \(F\left(-\pi\right)=-2\pi+\dfrac{1}{ln2}\) B. \(F\left(-\pi\right)=-2\pi-\dfrac{1}{ln2}\)
C. \(F\left(-\pi\right)=-\pi-\dfrac{1}{ln2}\) D. \(F\left(-\pi\right)=-2\pi\)
Mình cần bài giải ạ, mình cảm ơn nhiều ♥
Xem thêm câu trả lời
cho hàm số f(x) = \(\dfrac{\left(sinx+2x\right)\left[\left(x^2+1\right)sinx-x\left(cosx+2\right)\right]}{\left(cosx+2\right)^2\sqrt{\left(X^2+1\right)^3}}\). Biết F(x) là một nguyên hàm của f(x) và F(0)=2021. Tính giá trị biểu thức T=F(-1) + F(1).
Tính đạo hàm của các hàm số sau:
a) y=\(\dfrac{3x^2-18x-2}{1-2x}-\dfrac{2x-3}{x+4}\)
b) y=\(-\dfrac{\sin x}{3\cos^3x}+\dfrac{4}{3}\tan x\)