Tìm x biết rằng : \(\dfrac{x+2}{x-1}=\dfrac{x-3}{x+1}\)
Giải hộ mk chi tiết nha
Đúng thì tick
\(\dfrac{\sqrt{x+1}}{\sqrt{x-2}}\)\(+\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x+2}}\)\(+\dfrac{2+5\sqrt{x}}{4-x}\)
tìm điều kiện xác định(giải chi tiết hộ mình nha)
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1\ge0\\x-2>0\\x+2>0\\x\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\) và \(4-x\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge-1\\x>2\\x>-2\\x\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\) và \(x\ne4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>2\\x\ne4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tìm x biết:
\(\dfrac{1}{15}+\dfrac{1}{21}+\dfrac{1}{28}+\dfrac{1}{36}+...+\dfrac{2}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{11}{40},\left(x\inℕ^∗\right)\)
Giải chi tiết giúp mik nha.
\(\dfrac{1}{15}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{21}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{28}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{36}\) +...+ \(\dfrac{2}{x\left(x+1\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{11}{40}\) (\(x\in\) N*)
\(\dfrac{1}{2}\).(\(\dfrac{1}{15}\)+\(\dfrac{1}{21}\)+\(\dfrac{1}{28}\)+\(\dfrac{1}{36}\)+.....+ \(\dfrac{2}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)) = \(\dfrac{11}{40}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{30}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{42}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{56}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{72}\)+...+ \(\dfrac{1}{x\left(x+1\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{11}{80}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{5.6}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{6.7}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{7.8}\)+...+ \(\dfrac{1}{x\left(x+1\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{11}{80}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{5}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{6}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{6}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{7}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{7}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{8}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{8}\)-\(\dfrac{1}{9}\)+...+ \(\dfrac{1}{x}\)-\(\dfrac{1}{x+1}\) = \(\dfrac{11}{80}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{5}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{x+1}\) = \(\dfrac{11}{80}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{x+1}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{5}\) - \(\dfrac{11}{80}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{x+1}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{16}\)
\(x\) + 1 = 16
\(x\) = 16 - 1
\(x\) = 15
Tìm x biết:
\(\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{6}+\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{15}+...+\dfrac{1}{x\left(2x+1\right)}=\dfrac{1}{10},\left(x\inℕ^∗\right)\)
Giải chi tiết giúp mik nha.
\(\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{6}+\dfrac{1}{10}+...+\dfrac{1}{x.\left(2x+1\right)}=\dfrac{1}{10}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{6}+\dfrac{1}{12}+\dfrac{1}{20}+...+\dfrac{1}{2x.\left(2x+1\right)}=\dfrac{1}{20}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2.3}+\dfrac{1}{3.4}+\dfrac{1}{4.5}+...+\dfrac{1}{2x.\left(2x+1\right)}=\dfrac{1}{20}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{3}-\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{4}-\dfrac{1}{5}+...+\dfrac{1}{2x}-\dfrac{1}{2x+1}=\dfrac{1}{20}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2x+1}=\dfrac{1}{20}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2x+1}=\dfrac{9}{20}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+1=\dfrac{20}{9}\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{11}{18}\)
Em giải như XYZ olm em nhé
Sau đó em thêm vào lập luận sau:
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{11}{18}\)
Vì \(\in\) N*
Vậy \(x\in\) \(\varnothing\)
\(\dfrac{9}{x^2-4}=\dfrac{x-1}{x+2}+\dfrac{3}{x-2}\) giải chi tiết giúp mk ạ
`9/[x^2-4]=[x-1]/[x+2]+3/[x-2]` `ĐK: x \ne +-2`
`<=>9/[(x-2)(x+2)]=[(x-1)(x-2)+3(x+2)]/[(x-2)(x+2)]`
`=>9=x^2-2x-x+2+3x+6`
`<=>x^2=1`
`<=>x=+-1` (t/m)
Vậy `x=+-1`
\(\dfrac{9}{x^2-4}=\dfrac{x-1}{x+2}+\dfrac{3}{x-2}\left(đkxđ:x\ne\pm2\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{9}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\dfrac{3\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\\ \Rightarrow9=x^2-3x+2+3x+6\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2=1\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2=\pm1\left(TM\right)\)
Vậy PT có tập nghiệm \(S=\left\{-1;1\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+2+3x+6=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=1\)
=>x=1 hoặc x=-1
4. Tìm x biết:
\(\dfrac{1}{3}-\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{20}-\dfrac{1}{30}-\dfrac{1}{42}-\dfrac{1}{56}-\dfrac{1}{72}-\dfrac{1}{90}-\dfrac{1}{110}=x-\dfrac{5}{13}\)
Giải chi tiết giúp mình nha.
\(\dfrac{1}{3}-\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{20}-\dfrac{1}{30}-\dfrac{1}{42}-\dfrac{1}{56}-\dfrac{1}{72}-\dfrac{1}{90}-\dfrac{1}{110}=x-\dfrac{5}{13}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{3}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{3.4}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{4.5}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{5.6}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{6.7}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{7.8}\)- \(\dfrac{1}{8.9}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{9.10}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{10.11}\) = \(x\) - \(\dfrac{5}{13}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{3}\) - (\(\dfrac{1}{3.4}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{4.5}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{5.6}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{6.7}\)+ \(\dfrac{1}{7.8}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{8.9}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{9.10}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{10.11}\) =\(x\)-\(\dfrac{5}{13}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{3}\) - (\(\dfrac{1}{3}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{5}\) +...+ \(\dfrac{1}{9}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{10}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{10}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{11}\)) = \(x\) - \(\dfrac{5}{13}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{3}\) - (\(\dfrac{1}{3}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{11}\)) = \(x\) - \(\dfrac{5}{13}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{3}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{3}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{11}\) = \(x\) - \(\dfrac{5}{13}\)
\(x-\dfrac{5}{13}=\dfrac{1}{11}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{1}{11}\) + \(\dfrac{5}{13}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{68}{143}\)
Tìm tất cả các số x,y,z biết: \(\dfrac{x}{y+z+1}=\dfrac{y}{x+z+2}=\dfrac{z}{x+y-3}=x+y+z\)
Giair chi tiết hộ e vs ạ.
gợi ý nè:
thử cộng chúng lại xem
\(\dfrac{x}{y+z+1}\) = \(\dfrac{y}{x+z+2}\) = \(\dfrac{z}{x+y-3}\) = \(x+y+z\)
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có:
\(\dfrac{x}{y+z+1}\)=\(\dfrac{y}{x+z+2}\)=\(\dfrac{z}{x+y-3}\)=\(\dfrac{x+y+z}{y+z+1+x+z+2+x+y-3}\)
\(x+y+z\) = \(\dfrac{x+y+z}{2.\left(x+y+z\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) (1)
\(\dfrac{x}{y+z+1}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) ⇒ 2\(x\) = y+z+1
⇒ 2\(x\) + \(x\) = \(x+y+z+1\) (2)
Thay (1) vào (2) ta có: 2\(x\) + \(x\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) + 1
3\(x\) = \(\dfrac{3}{2}\) ⇒ \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{y}{x+z+2}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) ⇒ 2y = \(x+z+2\) ⇒ 2y+y = \(x+y+z+2\) (3)
Thay (1) vào (3) ta có: 2y + y = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) + 2
3y = \(\dfrac{5}{2}\) ⇒ y = \(\dfrac{5}{6}\)
Thay \(x=\dfrac{1}{2};y=\dfrac{5}{6}\) vào (1) ta có: \(\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{5}{6}+z\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{5}{6}\) + z = 0 ⇒ z = - \(\dfrac{5}{6}\)
Kết luận: (\(x;y;z\)) = (\(\dfrac{1}{2}\); \(\dfrac{5}{6}\); - \(\dfrac{5}{6}\))
Tìm x và y biết:
|x-5|+|y+1|=2 (x; y) thuộc Z
Giải chi tiết hộ mk nha ai nhanh+ đúng mk tích cho
Tìm tất cả các số x,y,z biết : \(\dfrac{x}{y+z+1}=\dfrac{y}{x+z+2}=\dfrac{z}{x+y-3}=x+y+z\)
Giair chi tiết ra hộ em vs ạ.
TH1: x + y + z 0
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau, ta có:
= = =
= = =
⇒ x + y + z =
⇒ x + y = - z
x + z = - y
y + z = - x
Thay y + z + 1 = - x + 1
⇒ =
⇒ 2x = - x + 1
⇒ 2x + x = + 1
⇒ 3x =
⇒ x =
Thay x + z + 2 = - y + 2
⇒ =
⇒ 2y = - y + 2
⇒ 2y + y = + 2
⇒ 3y =
⇒ y =
Thay x + y - 3 = - z - 3
⇒ \frac{1}{2}$
⇒ 2z = - z - 3
⇒ 2z + z = - 3
⇒ 3z =
⇒ z =
TH2: x + y + z = 0
⇒ = = = 0
⇒ x = y = z = 0
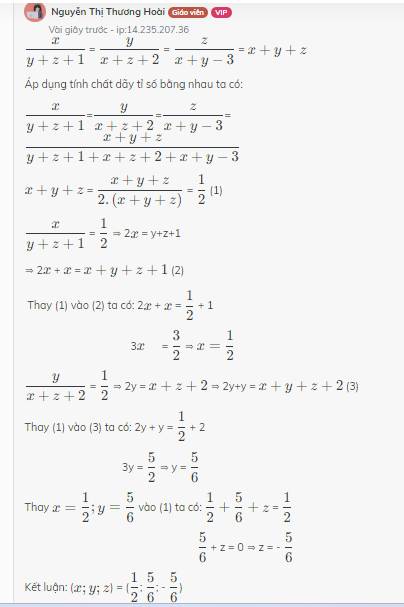
https://olm.vn/cau-hoi/tim-tat-ca-cac-so-xyz-biet-dfracxyz1dfracyxz2dfraczxy-3xyz-giair-chi-tiet-ho-e-vs-a.8297156371934
Rút gọn biểu thức sau
P=\(\dfrac{3-\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}+1:\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}+2}+\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+7}{4-x}\)
giải chi tiết hộ e vs ạ
\(P=\dfrac{3-\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-2}{\sqrt{x}}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-2}+\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+7}{4-x}\left(x>0;x\ne4\right)\\ P=\dfrac{\left(3-\sqrt{x}\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)-\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)+2\sqrt{x}+7}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-2}{\sqrt{x}}\\ P=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+6-x-x-3\sqrt{x}-2+2\sqrt{x}+7}{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2}{\sqrt{x}}\\ P=\dfrac{-2x+11}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2}{\sqrt{x}}\\ P=\dfrac{-2x\sqrt{x}+11\sqrt{x}+\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\left(x-4\right)}{\sqrt{x}\left(x-4\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{-2x\sqrt{x}+11\sqrt{x}+x\sqrt{x}-4\sqrt{x}+2x-8}{\sqrt{x}\left(x-4\right)}\\ P=\dfrac{-x\sqrt{x}+8\sqrt{x}+2x-8}{\sqrt{x}\left(x-4\right)}\)