Tìm giá trị lớn nhất, nhỏ nhất của hs lượng giác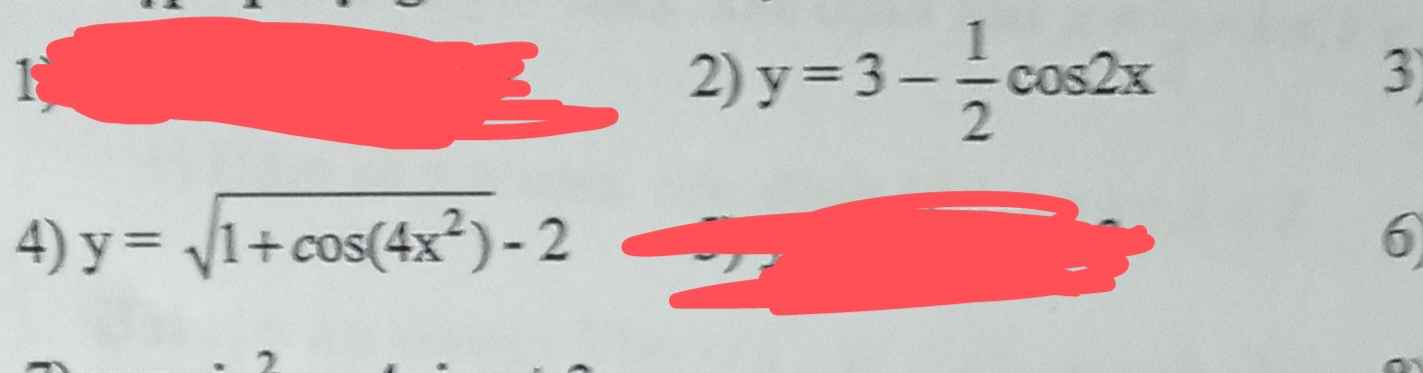

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Tìm giá trị lớn nhất, nhỏ nhất của HS lượng giác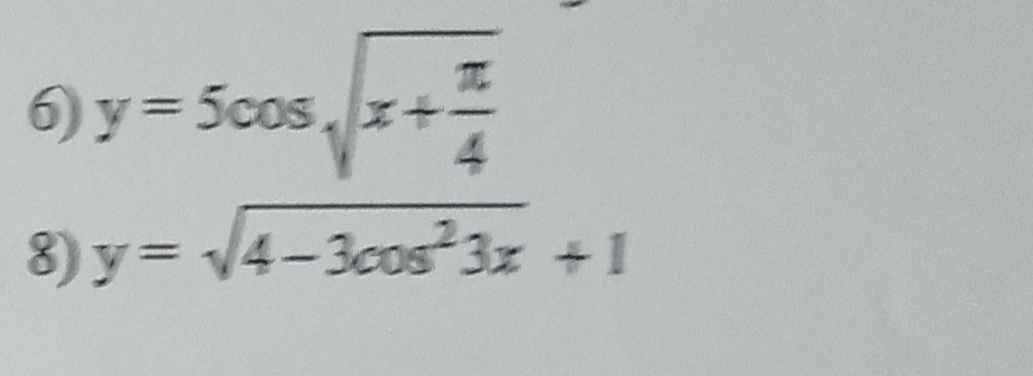
6.
\(cos\sqrt{x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}}\in\left[-1;1\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow-5\le5cos\sqrt{x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}}\le5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-5\le y\le5\)
\(\Rightarrow miny=-5\Leftrightarrow cos\sqrt{x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}}=-1\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}}=\pi+k2\pi\Leftrightarrow...\)
\(maxy=5\Leftrightarrow cos\sqrt{x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}}=1\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}}=k2\pi\Leftrightarrow...\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giúp mik nhanh với tìm giá trị lớn nhất và nhỏ nhất của hs y=-1-cos^2(2x+pi/3)
\(y=-1-cos^2\left(2x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)\)
\(=-\dfrac{3}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}-cos^2\left(2x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)\)
\(=-\dfrac{3}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2}\left[2cos^2\left(2x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)-1\right]\)
\(=-\dfrac{3}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2}cos\left(4x+\dfrac{2\pi}{3}\right)\)
Vì \(cos\left(4x+\dfrac{2\pi}{3}\right)\in\left[-1;1\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow min=-\dfrac{3}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2}=-2\Leftrightarrow cos\left(4x+\dfrac{2\pi}{3}\right)=1\)
\(\Rightarrow max=-\dfrac{3}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}=-1\Leftrightarrow cos\left(4x+\dfrac{2\pi}{3}\right)=-1\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giá trị lớn nhất M , giá trị nhỏ nhất m của hs y =2cos2x +2sinx là? Bài này cách bấm máy làm nhiệm nào ạ?
tìm giá trị lớn nhất, giá trị nhỏ nhất của hàm số bạc hai y = -2x2 + 4x + 3
tìm giá trị lớn nhất, giá trị nhỏ nhất của hàm số bậc hai y = -3x2 + 2x + 1 trên (1;3)
tìm giá trị lớn nhất, giá trị nhỏ nhất của hàm số bậc hai y = x2 - 4x - 5 trên (-1;4)
Câu 1:
$y=-2x^2+4x+3=5-2(x^2-2x+1)=5-2(x-1)^2$
Vì $(x-1)^2\geq 0$ với mọi $x\in\mathbb{R}$ nên $y=5-2(x-1)^2\leq 5$
Vậy $y_{\max}=5$ khi $x=1$
Hàm số không có min.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Câu 2:
Hàm số $y$ có $a=-3<0; b=2, c=1$ nên đths có trục đối xứng $x=\frac{-b}{2a}=\frac{1}{3}$
Lập BTT ta thấy hàm số đồng biến trên $(-\infty; \frac{1}{3})$ và nghịch biến trên $(\frac{1}{3}; +\infty)$
Với $x\in (1;3)$ thì hàm luôn nghịch biến
$\Rightarrow f(3)< y< f(1)$ với mọi $x\in (1;3)$
$\Rightarrow$ hàm không có min, max.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Câu 3:
$y=x^2-4x-5$ có $a=1>0, b=-4; c=-5$ có trục đối xứng $x=\frac{-b}{2a}=2$
Do $a>0$ nên hàm nghịch biến trên $(-\infty;2)$ và đồng biến trên $(2;+\infty)$
Với $x\in (-1;4)$ vẽ BTT ta thu được $y_{\min}=f(2)=-9$
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Khi đu quay hoạt động, vận tốc theo phương ngang của một cabin M phụ thuộc vào góc lượng giác alpha ; ;(Ox,OM) theo hàm số {v_x} 0,3sinalpha ; (m/s) (Hình 11).a) Tìm giá trị lớn nhất và giá trị nhỏ nhất của {v_x}b) Dựa vào đồ thị của hàm số sin, hãy cho biết trong vòng quay đầu tiên (0 le alpha le 2alpha ), góc alpha ở trong các khoảng nào thì {v_x} tăng.
Đọc tiếp
Khi đu quay hoạt động, vận tốc theo phương ngang của một cabin M phụ thuộc vào góc lượng giác \(\alpha \; = \;(Ox,OM)\) theo hàm số \({v_x} = 0,3sin\alpha \;\) (m/s) (Hình 11).
a) Tìm giá trị lớn nhất và giá trị nhỏ nhất của \({v_x}\)
b) Dựa vào đồ thị của hàm số sin, hãy cho biết trong vòng quay đầu tiên \((0 \le \alpha \le 2\alpha )\), góc \(\alpha \)ở trong các khoảng nào thì \({v_x}\) tăng.
a, Do \(-1\le sin\alpha\le1\Rightarrow-0,3\le v_x=0,3sin\alpha\le0,3\)
Vậy giá trị lớn nhất của \(v_x\) là 0,3m/s và giá trị nhỏ nhất là -0,3m/s
b, Ta có đồ thị hàm số:
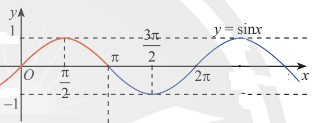
Với góc \(\alpha\in\left(0;\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)\) hoặc \(\alpha\in\left(\dfrac{3\pi}{2};2\pi\right)\) thì \(v_x\) tăng.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho a={3;6;7} , b={0;23;29;6}
Tìm giá trị lớn nhất, giá trị nhỏ nhất Tìm giá trị lớn nhất giá trị nhỏ nhất của phân số a phần b
Tổng giá trị lớn nhất và giá tri nhỏ nhất của hs f(x)= 2x + cos\(\left(\dfrac{\pi x}{2}\right)\) trên đoạn [-2;2] bằng?
\(f'\left(x\right)=2-\dfrac{\pi}{2}sin\left(\dfrac{\pi x}{3}\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(4-\pi sin\left(\dfrac{\pi x}{2}\right)\right)\)
Do \(\left|\pi sin\left(\dfrac{\pi x}{2}\right)\right|\le\pi< 4\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)>0\) ; \(\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) đồng biến trên R
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)_{min}+f\left(x\right)_{max}=f\left(-2\right)+f\left(2\right)=-4+cos\left(-\pi\right)+4+cos\left(\pi\right)=-2\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 3 : Cho tam giác ABC vuông tại A có AB = AC = a . Điểm M chuyển động trên
cạnh BC , gọi D và E thứ tự là hình chiếu của M trên AB và AC .
a)Tìm vị trí của M để S ADME đạt giá trị lớn nhất tính giá trị lớn nhất đó theo a .
b) Tìm vị trí của M để DE đạt giá trị nhỏ nhất tính giá trị nhỏ nhất đó theo a .
tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của \(A=x^2-2x+5\)
tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của \(B=2x^2-6x\)
tìm giá trị lớn nhất của \( C=4x-x^2+3\)
\(A=\left(x^2-2x+1\right)+4=\left(x-1\right)^2+4\ge4\\ A_{min}=4\Leftrightarrow x=1\\ B=2\left(x^2-3x\right)=2\left(x^2-2\cdot\dfrac{3}{2}x+\dfrac{9}{4}\right)-\dfrac{9}{2}\\ B=2\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2-\dfrac{9}{2}\ge-\dfrac{9}{2}\\ B_{min}=-\dfrac{9}{2}\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}\\ C=-\left(x^2-4x+4\right)+7=-\left(x-2\right)^2+7\le7\\ C_{max}=7\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a,\(A=x^2-2x+5=\left(x^2-2x+1\right)+4=\left(x-1\right)^2+4\ge4\)
Dấu "=" \(\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
b,\(B=2\left(x^2-3x\right)=2\left(x^2-3x+\dfrac{9}{4}\right)-\dfrac{9}{2}=2\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2-\dfrac{9}{2}\ge-\dfrac{9}{2}\)
Dấu "=" \(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
c,\(=C=-\left(x^2-4x-3\right)=-\left[\left(x^2-4x+4\right)-7\right]=-\left(x-2\right)^2+7\le7\)
Dấu "=" \(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)



















