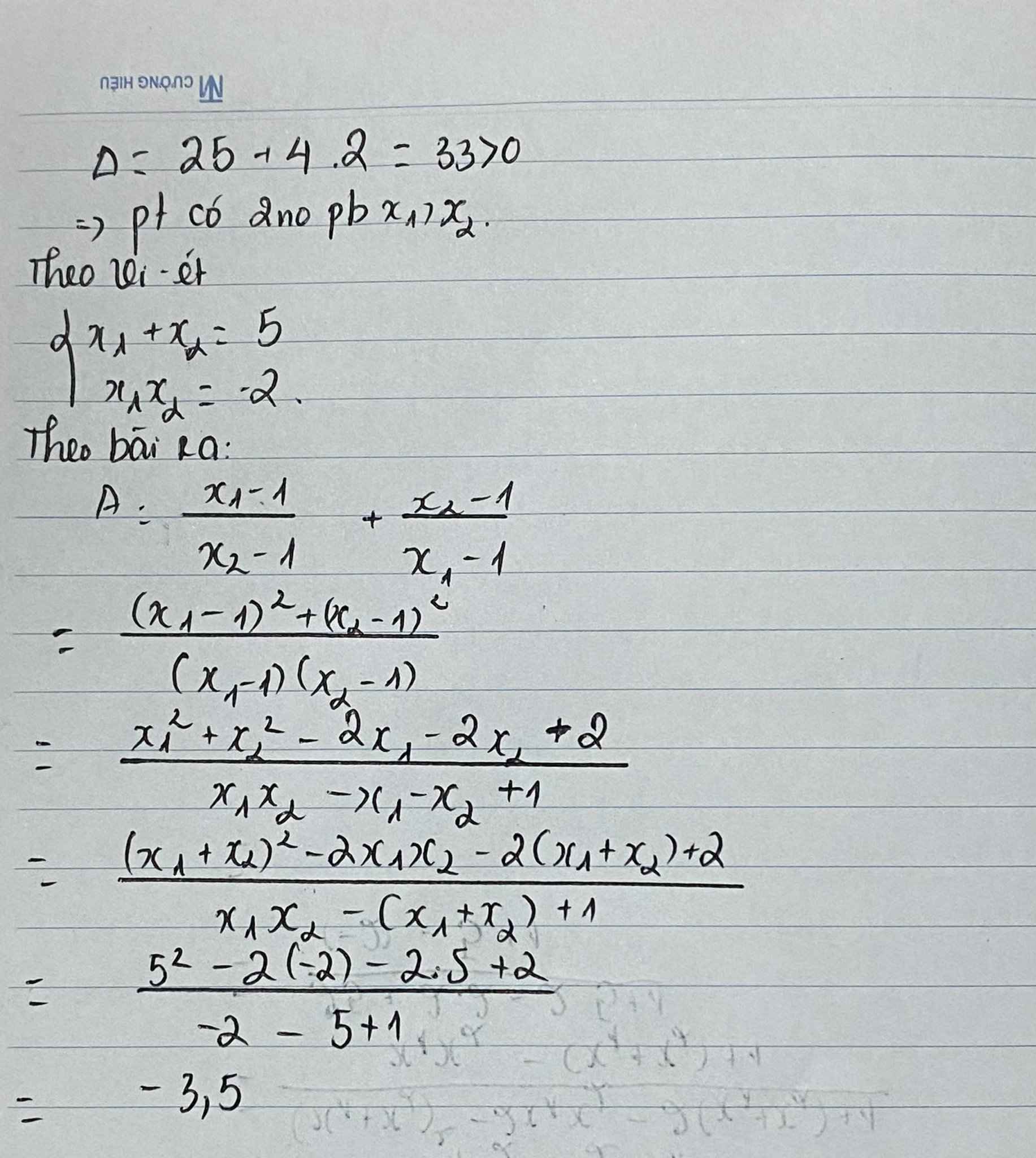CHo pt x-4x-3=0 có 2 nghiệm phân biệt x1,x2 không giải phương trình hãy tính giá trị của biểu thức A=\(\dfrac{x1^2}{x2}+\dfrac{x2^2}{x1}\)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
1. Cho pt 3x^2+4x+10có nghiệm x1,x2, không giải pt, hãy tính giá trị biểu thức Cdfrac{x_1}{x_2-1}+dfrac{x_2}{x_1-1}2. . Cho pt 3x^2-5x-10có nghiệm x1,x2, không giải pt, hãy tính giá trị biểu thức Ddfrac{x_1-x_2}{x_1}+dfrac{x_2-1}{x_2}3. . Cho pt 3x^2-7x-10có nghiệm x1,x2, không giải pt, hãy tính giá trị biểu thức Bdfrac{2x^2_2}{x_1+x_2}+2x_1
Đọc tiếp
1. Cho pt \(3x^2+4x+1=0\)
có nghiệm x1,x2, không giải pt, hãy tính giá trị biểu thức \(C=\dfrac{x_1}{x_2-1}+\dfrac{x_2}{x_1-1}\)
2. . Cho pt \(3x^2-5x-1=0\)
có nghiệm x1,x2, không giải pt, hãy tính giá trị biểu thức \(D=\dfrac{x_1-x_2}{x_1}+\dfrac{x_2-1}{x_2}\)
3. . Cho pt \(3x^2-7x-1=0\)
có nghiệm x1,x2, không giải pt, hãy tính giá trị biểu thức \(B=\dfrac{2x^2_2}{x_1+x_2}+2x_1\)
1. Theo hệ thức Vi-ét, ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{4}{3}\\x_1.x_2=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(C=\dfrac{x_1}{x_2-1}+\dfrac{x_2}{x_1-1}=\dfrac{x_1\left(x_1-1\right)+x_2\left(x_2-1\right)}{\left(x_1-1\right)\left(x_2-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x_1^2-x_1+x_2^2-x_2}{x_1x_2-x_1-x_2+1}=\dfrac{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)}{x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(-\dfrac{4}{3}\right)^2-2.\dfrac{1}{3}-\left(-\dfrac{4}{3}\right)}{\dfrac{1}{3}-\left(-\dfrac{4}{3}\right)+1}=\dfrac{\dfrac{22}{9}}{\dfrac{8}{3}}=\dfrac{11}{12}\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (1)
\(1,3x^2+4x+1=0\)
Do pt có 2 nghiệm \(x_1,x_2\) nên theo đ/l Vi-ét ta có :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}S=x_1+x_2=\dfrac{-b}{a}=-\dfrac{4}{3}\\P=x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có :
\(C=\dfrac{x_1}{x_2-1}+\dfrac{x_2}{x_1-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x_1\left(x_1-1\right)+x_2\left(x_2-1\right)}{\left(x_2-1\right)\left(x_1-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x_1^2-x_1+x_2^2-x_2}{x_1x_2-x_2-x_1+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x_1^2+x_2^2\right)-\left(x_1+x_2\right)}{x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{S^2-2P-S}{P-S+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(-\dfrac{4}{3}\right)^2-2.\dfrac{1}{3}-\left(-\dfrac{4}{3}\right)}{\dfrac{1}{3}-\left(-\dfrac{4}{3}\right)+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{11}{12}\)
Vậy \(C=\dfrac{11}{12}\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
\(3,3x^2-7x-1=0\)
Do pt có 2 nghiệm \(x_1,x_2\) nên theo đ/l Vi-ét ta có :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}S=x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=\dfrac{7}{3}\\P=x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=-\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có :
\(B=\dfrac{2x_2^2}{x_1+x_2}+2x_1\)
\(=\dfrac{2x_2^2+2x_1\left(x_1+x_2\right)}{x_1+x_2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x_2^2+2x_1^2+2x_1x_2}{x_1+x_2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(x_1^2+x_2^2\right)+2x_1x_2}{x_1+x_2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(S^2-2P\right)+2P}{S}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(\dfrac{7}{3}^2-2\left(-\dfrac{1}{3}\right)\right)+2\left(-\dfrac{1}{3}\right)}{\dfrac{7}{3}}\)
\(=\dfrac{104}{21}\)
Vậy \(B=\dfrac{104}{21}\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (4)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Cho pt: x2 -6x+8=0 có 2 nghiệm phân biệt x1;x2. Không giải phương trình, hãy tính giá trị biểu thức B=\(\dfrac{x_1\sqrt{x_1}-x_2\sqrt{x_2}}{x_1-x_2}\)
Theo vi ét: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=6\\x_1x_2=8\end{matrix}\right.\)
Theo đề:
\(B=\dfrac{x_1\sqrt{x_1}-x_2\sqrt{x_2}}{x_1-x_2}=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x_1}-\sqrt{x_2}\right)\left(x_1+\sqrt{x_1x_2}+x_2\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x_1}-\sqrt{x_2}\right)\left(\sqrt{x_1}+\sqrt{x_2}\right)}\left(x_1,x_2\ge0\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{6+\sqrt{8}}{\sqrt{x_1}+\sqrt{x_2}}\)
Tính: \(\left(\sqrt{x_1}+\sqrt{x_2}\right)^2=x_1+x_2+2\sqrt{x_1x_2}=6+2\sqrt{8}=6+4\sqrt{2}=\left(\sqrt{4}+\sqrt{2}\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x_1}+\sqrt{x_2}=\sqrt{4}+\sqrt{2}\) (thỏa mãn \(x_1,x_2\ge0\))
Khi đó: \(P=\dfrac{6+\sqrt{8}}{\sqrt{4}+\sqrt{2}}=4-\sqrt{2}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
Cho phương trình \(2x^2\) + 6x - 3 = 0 có hai nghiệm x1, x2. Không giải phương trình, hãy tính giá trị của biểu thức \(\dfrac{2}{x1^2}+\dfrac{2}{x2^2}\)
Áp dụng hệ thức Vi-et, ta được:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{6}{2}=-3\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{-3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{2}{x_1^2}+\dfrac{2}{x_2^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2_2+2x_1^2}{\left(x_1\cdot x_2\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left[\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2\right]}{\left(-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2}=\dfrac{2\cdot\left[\left(-3\right)^2-2\cdot\dfrac{-3}{2}\right]}{\dfrac{9}{4}}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\cdot12}{\dfrac{9}{4}}=24\cdot\dfrac{4}{9}=\dfrac{96}{9}=\dfrac{32}{3}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Cho phương trình: 3x2 – 5x – 6 = 0 có 2 nghiệm x1, x2. Không giải phương trình, hãy tính giá trị của biểu thức sau: A=1-( \(\dfrac{x1-x2}{x1x2}\))2
1) Cho phương trình 5x^2+3x-1=0 có hai nghiệm x1,x2. Không giải phương trình, hãy tính giá trị của biểu thức A=\(\left(3x_1+2x_2\right)\left(3x_2+x_1\right)\)
2) Cho phương trình 7x^2-2x-3=0 có hai nghiệm là x1,x2 tính giá trị của biểu thức
M=\(\dfrac{7x_1^2-2x_1}{3}+\dfrac{3}{7x_2^2-2x_2}\)
`1)` Ptr có: `\Delta=3^2-4.5.(-1)=29 > 0 =>`Ptr có `2` nghiệm phân biệt
`=>` Áp dụng Viét có: `{(x_1+x_2=[-b]/a=-3/5),(x_1.x_2=c/a=-1/5):}`
Có: `A=(3x_1+2x_2)(3x_2+x_1)`
`A=9x_1x_2+3x_1 ^2+6x_2 ^2+2x_1x_2`
`A=8x_1x_2+3(x_1+x_2)^2=8.(-1/5)+3.(-3/5)^2=-13/25`
Vậy `A=-13/25`
____________________________________________________
`2)` Ptr có: `\Delta'=(-1)^2-7.(-3)=22 > 0=>` Ptr có `2` nghiệm pb
`=>` Áp dụng Viét có: `{(x_1+x_2=[-b]/a=2/7),(x_1.x_2=c/a=-3/7):}`
Có: `M=[7x_1 ^2-2x_1]/3+3/[7x_2 ^2-2x_2]`
`M=[(7x_1 ^2-2x_1)(7x_2 ^2-2x_2)+9]/[3(7x_2 ^2-2x_2)]`
`M=[49(x_1x_2)^2-14x_1 ^2 x_2-14x_1 x_2 ^2+4x_1x_2+9]/[3(7x_2 ^2-2x_2)]`
`M=[49.(-3/7)^2-14.(-3/7)(2/7)+4.(-3/7)+9]/[3x_2(7x_2-2)]`
`M=6/[x_2(7x_2-2)]` `(1)`
Có: `x_1+x_2=2/7=>x_1=2/7-x_2`
Thay vào `x_1.x_2=-3/7 =>(2/7-x_2)x_2=-3/7`
`<=>-x_2 ^2+2/7 x_2+3/7=0<=>x_2=[1+-\sqrt{22}]/7`
`@x_2=[1+\sqrt{22}]/7=>M=6/[[1+\sqrt{22}]/7(7 .[1+\sqrt{22}]/2-2)]=2`
`@x_2=[1-\sqrt{22}]/7=>M=6/[[1-\sqrt{22}]/7(7 .[1-\sqrt{22}]/2-2)]=2`
Vậy `M=2`
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho pt X^2+3X-7=0(1) Gọi X1;X2 là 2 nghiệm phân biệt của Phương trình (1) không giải phương trình hãy tính giá trị của biểu thức F=X1^2-3X2 -2013
\(F=x_1^2-3x_2-2013\)
Áp dụng Viét: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-3\\x_1x_2=-7\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vì \(x_1\) là nghiệm của PT nên \(x_1^2+3x_1-7=0\Leftrightarrow x_1^2=7-3x_1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow F=7-3x_1-3x_2-2013\\ F=-2006-3\left(x_1+x_2\right)=-2006-3\left(-3\right)=-1997\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1 cho pt x^2-2(m+1)x+4m+m^2=0 .Tìm m để phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt x1,x2 sao cho biểu thức A =|x1-x2| đạt giá trị nhỏ nhất
bài 2 cho pt x^2+mx+2m-4=0.Tìm m để phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt x1,x2 thỏa mãn |x1|+|x2|=3
bài 3 cho pt x^2-3x-m^2+1=0.tìm m để phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt x1,x2 thỏa mãn |x1|+2|x2|=3
Cho phương trình bậc hai: x 2 – 5x – 2 = 0. Không giải phương trình để tìm 2 nghiệmx1 ; x2 . Hãy tính giá trị của biểu thức: A =\(\dfrac{x1-1}{x2-1}+\dfrac{x2-1}{x1-1}\)
Gọi x1, x2 là hai nghiệm của phương trình: 3x2 + 5x – 6 = 0.
Không giải phương trình, hãy tính giá trị biểu thức sau: \(\dfrac{x1}{x2-1}\)+\(\dfrac{x2}{x1-1}\)
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{5}{3}\\x_1x_2=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{x_1}{x_2-1}+\dfrac{x_2}{x_1-1}=\dfrac{x_1\left(x_1-1\right)+x_2\left(x_2-1\right)}{\left(x_1-1\right)\left(x_2-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x_1^2+x_2^2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)}{x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)+1}=\dfrac{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)}{x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(-\dfrac{5}{3}\right)^2-2.\left(-2\right)-\left(-\dfrac{5}{3}\right)}{-2-\left(-\dfrac{5}{3}\right)+1}=...\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)