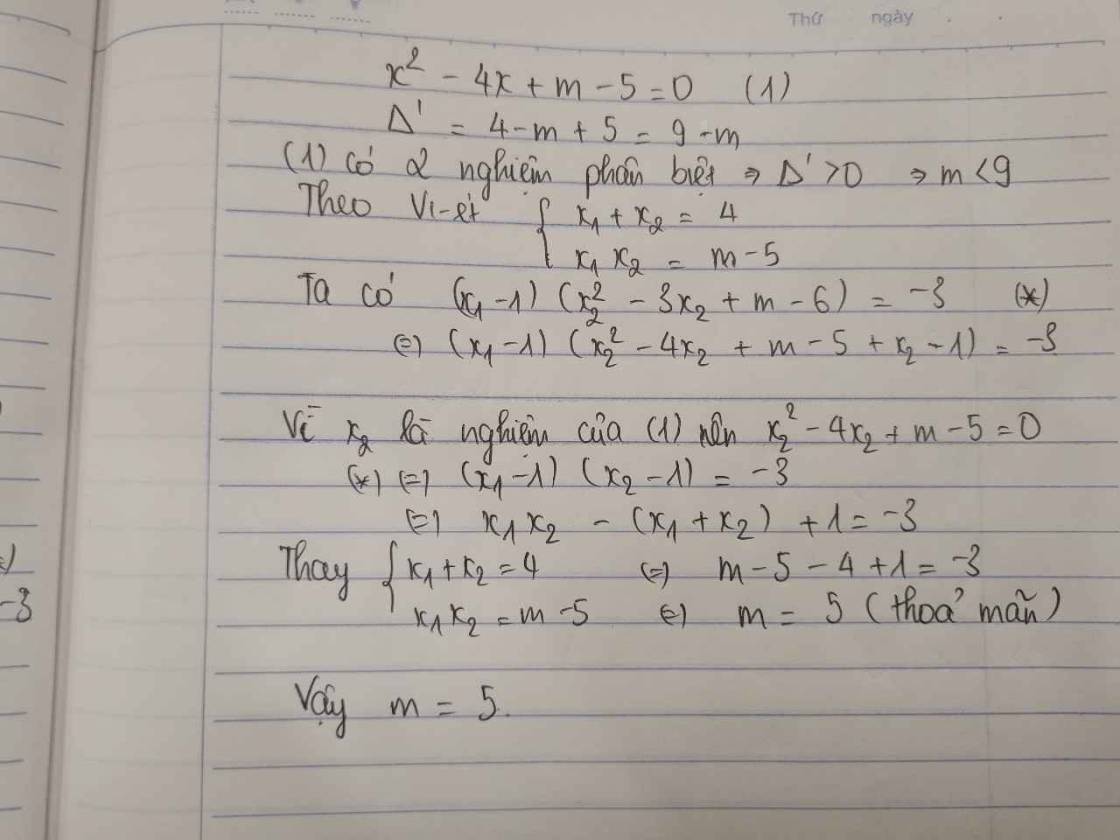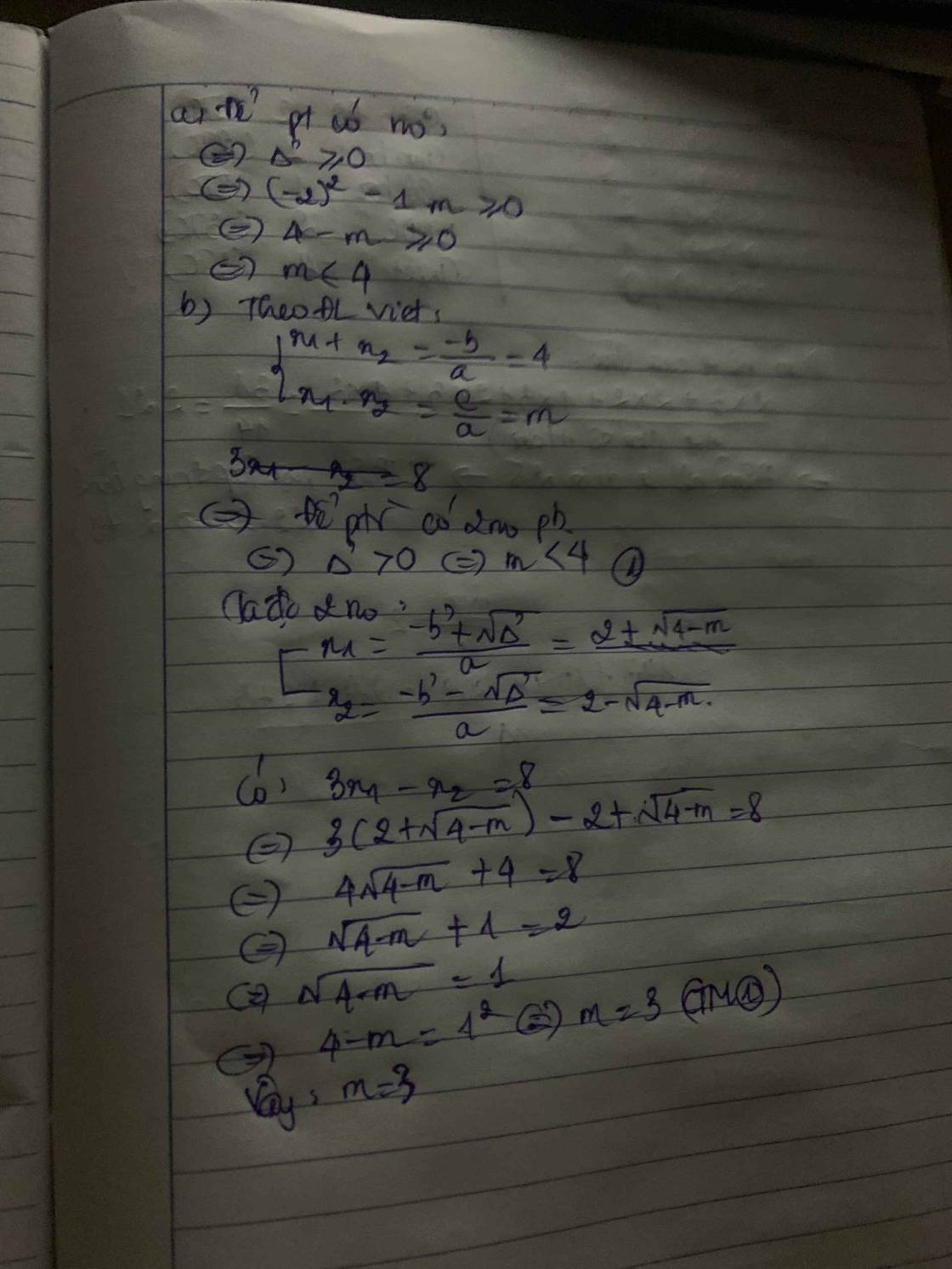cho pt: x^2 - 4x + m + 1 = 0 tìm m để pt có 2 nghiệm pb thỏa x31 + x32 < 100

Những câu hỏi liên quan
cho pt: x2+2x+m−3�2+2�+�−30 (với m là tham số).Tìm m để phương trình có hai nghiệm x1x2�1�2 thỏa mãn m(x31+x32�13+�23)+x21x22�12�229Em đang cần gấp tại hơi nâng cao!
Đọc tiếp
cho pt: =0 (với m là tham số).Tìm m để phương trình có hai nghiệm thỏa mãn m()+=9
Em đang cần gấp tại hơi nâng cao!
9.2
cho `x^2 -4x+m-5=0`
tìm m để pt có 2 nghiệm pb `x_1 ;x_2` thỏa mãn \(\left(x_1-1\right)\left(x_2^2-3x_2+m-6\right)=-3\)
Cho pt x^2-4x+m=0 a)tìm m để pt có nghiệm b)tìm m để pt có nghiệm thỏa 3x1-x2=8
Cho phương trình x^2+2(m+1)x+2m+2=0
a. Tìm m để pt có 2 nghiệm pb
b. Tìm m để pt có nghiệm kép, tính nghiệm đó
c. Tìm m để phương trình có hai nghiệm x1, x2 thỏa x^21+x^22=8
A, ta có: \(\Delta’\)=m2-1
Vậy trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt <=> m2-1>0 => m>1
B,Phương trình có nghiệm kép khi: m2-1=0 => m=+- 1
Nghiem kép đó là: 0
\(x^2+2\left(m+1\right)x+2m+2=0\)
\(\Delta'=\left(m+1\right)^2-\left(2m+2\right)=m^2-1\)
a, Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì:
\(\Delta'>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2>1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-1>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m< -1;m>1\)
b, Phương trinh có nghiệm kép khi:
\(\Delta'\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-1\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\le-1;m\ge1\)
Theo Viet ta có:
\(x_1+x_2=-2\left(m+1\right)\)
\(x_1x_2=2\left(m+1\right)\)
\(x_1^2+x_2^2=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2+4m-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}m=1\\m=-2\end{cases}}\)
So với điều kiện phương trình có nghiệm m=1 ; m =-2
1. Tìm m để pt : \(x^2-\left(2m-3\right)x+m^2-4=0\) có 2 nghiệm pb sao cho tổng bp 2 nghiệm <17
2. Tìm m để pt \(x^4-\left(m+1\right)x^2+m^2-m+2=0\) có 3 nghiệm pb
3. Tìm m để pt \(x^2-6x+m-2=0\) có 2 nghiệm x>0
1.
Yêu cầu bài toán thỏa mãn khi:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\Delta=25-12m>0\\x_1^2+x_2^2< 17\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m< \dfrac{25}{12}\\\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2< 17\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m< \dfrac{25}{12}\\\left(2m-3\right)^2-2\left(m^2-4\right)< 17\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m< \dfrac{25}{12}\\2m^2-12m< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0< m< \dfrac{25}{12}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
3.
Yêu cầu bài toán thỏa mãn khi:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\Delta'=11-m>0\\x_1+x_2>0\\x_1x_2>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m< 11\\6>0\\m-2>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2< m< 11\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
cho pt x^2-4(m-1)x+1=0 (1) tìm điều kiên của m để pt (1) có 2 nghiệm pb x1,x2 thỏa mãn x1^3+x2^3=35
a, cho pt X2-2x+4/x-2=ms+2-2m tìm m để pt có 2 nghiệm pb
b,cho pt mx2+x+m/x-1=0 tìm m để pt có 2 nghiệm dương pb
Cho hàm số y=(x-1)(x2+mx+m)
a. Với m=2, tính y', giải pt
b.Tìm m để tiếp tuyến tại điểm có hoành độ x=-1 song song với đường thẳng y=-2x-3
c. tìm m để pt y=0 có 3 nghiệm phân biệt x1,x2,x3 thỏa mãn x12 + x22 +x32 <4
d. tìm m để pt y=0 có 3 nghiệm phân biệt trong đó có 1 nghiệm lớn hơn 2
bài 10:
Cho pt x2+5x+m-2=0
Tìm m để pt có 2 nghiệm pb thỏa mãn \(\dfrac{1}{x_1-1}+\dfrac{1}{x_2-1}=2\)
Lời giải:
Để pt có 2 nghiệm thì: $\Delta=25-4(m-2)\geq 0$
$\Leftrightarrow m\leq \frac{33}{4}$
Áp dụng hệ thức Viet, với $x_1,x_2$ là 2 nghiệm của pt thì:
$x_1+x_2=-5$
$x_1x_2=m-2$
Khi đó:
$\frac{1}{x_1-1}+\frac{1}{x_2-1}=2$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{x_1+x_2-2}{(x_1-1)(x_2-1)}=2$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{-5-2}{(x_1-1)(x_2-1)}=2$
$\Leftrightarrow (x_1-1)(x_2-1)=\frac{-7}{2}$
$\Leftrightarrow x_1x_2-(x_1+x_2)+1=\frac{-7}{2}$
$\Leftrightarrow m-2+5+1=\frac{-7}{2}$
$\Leftrightarrow m=\frac{-15}{2}$ (tm)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Lời giải:
Để pt có 2 nghiệm thì: $\Delta=25-4(m-2)\geq 0$
$\Leftrightarrow m\leq \frac{33}{4}$
Áp dụng hệ thức Viet, với $x_1,x_2$ là 2 nghiệm của pt thì:
$x_1+x_2=-5$
$x_1x_2=m-2$
Khi đó:
$\frac{1}{x_1-1}+\frac{1}{x_2-1}=2$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{x_1+x_2-2}{(x_1-1)(x_2-1)}=2$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{-5-2}{(x_1-1)(x_2-1)}=2$
$\Leftrightarrow (x_1-1)(x_2-1)=\frac{-7}{2}$
$\Leftrightarrow x_1x_2-(x_1+x_2)+1=\frac{-7}{2}$
$\Leftrightarrow m-2+5+1=\frac{-7}{2}$
$\Leftrightarrow m=\frac{-15}{2}$ (tm)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
cho pt \(x^2-4x+1-2m=0\) (x là ẩn số )
a) tìm m để pt có nghiệm
b) tìm x để 2 nghiệm \(x_1,x_2\) của pt thỏa \(x^2_1+x_2^2=6\)
a.\(\Delta=\left(-4\right)^2-4.\left(1-2m\right)\)
\(=16-4+8m=12+8m\)
Để pt có 2 nghiệm thì \(12+8m>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m>-\dfrac{12}{8}\)
b. Theo hệ thức vi-et, ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=4\\x_1.x_2=1-2m\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_1^2+x^2_2=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4^2-2\left(1-2m\right)=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16-2+4m-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m=-8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=-2\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a, \(\Delta'=\left(-2\right)^2-\left(1-2m\right)=4-1+2m=2m-3\)
Để pt có nghiệm thì \(\Delta'\ge0\Leftrightarrow2m-3\ge0\Leftrightarrow m\ge\dfrac{3}{2}\)
b, Theo Vi-ét:\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=4\\x_1x_2=1-2m\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_1^2+x_2^2=6\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=6\\ \Leftrightarrow4^2-2\left(1-2m\right)=6\\ \Leftrightarrow16-2+4m-6=0\\ \Leftrightarrow4m-8=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m=2\left(tm\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)