Rút gọn các biểu thức sau:
a) A(x)= -5x (2x3- 3x2 + x - 4)
b) B(x)= (6x3 + 4x2 - 6x) : (2x) + (2x - 1)(x2 + 5)
Bài 1: Rút gọn biểu thức sau:
a. 3x2(2x3- x+5) - 6x5-3x3+10x2
b. -2x(x3-3x2-xx+11)-2x4+3x3+2x2-22x2x
Bài 2: Chứng minh biểu thức sau không phụ thuộc vào x:
a. x(2x+1)-x2(x+2)+(x2-x+3)
b. 4(x-6)-x2(2+3x)+x(5x-4)+3x2(x-1)
Bài 3: Cho đa thức: f(x)=3x2-x+1
g(x)=x-1
a. Tính f(x).g(x)
b. Tìm x để f(x).g(x)+x2[1-3g(x)]=
Bài 4: Tìm x:
a. \(\dfrac{1}{4}\)x2-(\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)x-4)\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)x=-14
b. 2x(x-4)+3(x-4)+x(x-2)-5(x-2)=3x
(x-4)-5(x-4)
Các bạn giúp mik giải bt nha. Cảm ơn mn nhiêu ạ.
`@` `\text {Ans}`
`\downarrow`
Gửi c!

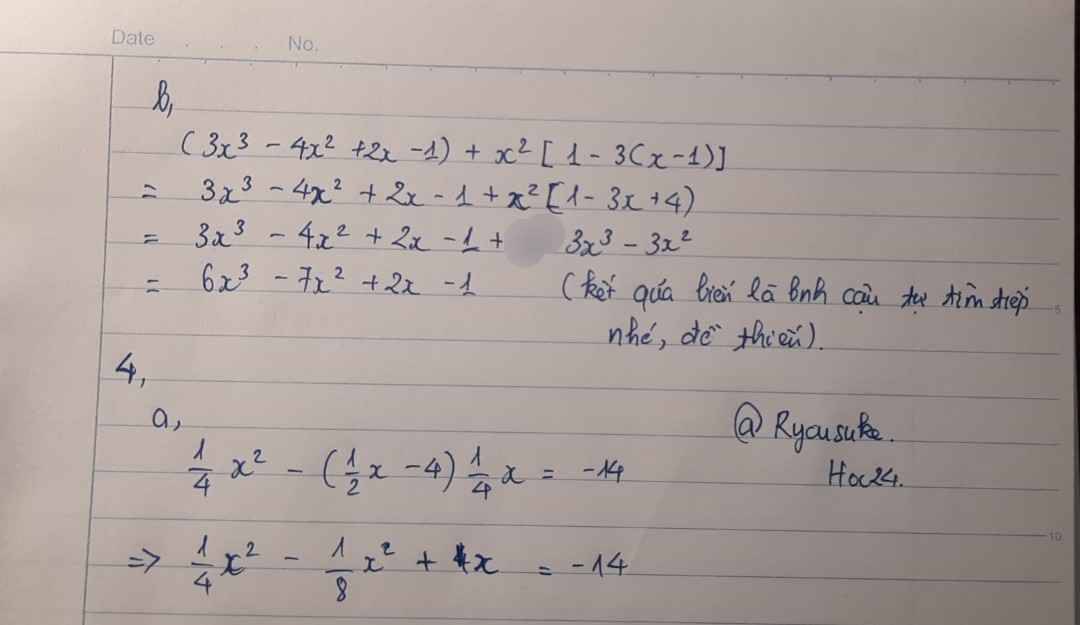

Bài 1:
a) \(3x^2\left(2x^3-x+5\right)-6x^5-3x^3+10x^2\)
\(=6x^5-3x^3+10x^2-6x^5-3x^3+10x^2\)
\(=10x^2+10x^2\)
\(=20x^2\)
b) \(-2x\left(x^3-3x^2-x+11\right)-2x^4+3x^3+2x^2-22x\)
\(=-2x^4+6x^3+2x^2-22x-2x^4+3x^3+2x^2-22x\)
\(=-4x^4+9x^3+4x^2-44x\)
4:
a: =>1/4x^2-1/4x^2+2x=-14
=>2x=-14
=>x=-7
b: =>2x^2-8x+3x-12+x^2-2x-5x+10=3x^2-12x-5x+20
=>3x^2-12x-2=3x^2-17x+20
=>5x=22
=>x=22/5
Bài 1. Làm tính nhân:
a) 3x2 (2 - 5xy)
b) -\(\dfrac{2}{3}\) xy (xy2 - x3 + 4)
c) ( x - 7 y )( xy + 1)
Bài 2. Rút gọn các biểu thức sau:
a) 5x(4x2 - 2x +1) - 2x(10x2 - 5x - 2)
b) 3x( x - 2) - 5x(1- x) - 8(x2 - 3)
d) (x3 - 2x)(x2 +1)
Bài 1:
\(a,6x^2-15x^3y\\ b,=-\dfrac{2}{3}x^2y^3+\dfrac{2}{3}x^4y-\dfrac{8}{3}xy\)
Bài 2:
\(a,=20x^3-10x^2+5x-20x^3+10x^2+4x=9x\\ b,=3x^2-6x-5x+5x^2-8x^2+24=24-11x\\ c,=x^5+x^3-2x^3-2x=x^5-x^3-2x\)
câu d của bài 2 là của bài 1 nha mình để nhầm chỗ huhu
Câu 1
Rút gọn các biểu thức sau:
a. 2x(3x + 2) - 3x(2x + 3)
b. (x + 2)3 + (x - 3)2 - x2(x + 5)
c. (3x3 - 4x2 + 6x) : 3x
Câu 2
Phân tích đa thức sau thành nhân tử: 2x3 - 12x2 + 18x
Câu 3
Tìm x, biết: 3x(x - 5) - x2 + 25 = 0
Câu 4 Cho hình bình hành ABCD (AB > AD). Gọi E và K lần lượt là trung điểm của CD và AB. BD cắt AE, AC, CK lần lượt tại N, O và I. Chứng minh rằng:
a. Tứ giắc AECK là hình bình hành.
b. Ba điểm E, O, K thẳng hàng.
c. DN = NI = IB
d. AE = 3KI
Câu 5 Cho x, y là hai số thực tùy ý, tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức sau:
P = x2 + 5y2 + 4xy + 6x + 16y + 32
Câu 1:
a) 2x(3x+2) - 3x(2x+3) = 6x^2+4x - 6x^2-9x = -5x
b) \(\left(x+2\right)^3+\left(x-3\right)^2-x^2\left(x+5\right)\)
\(=x^3+6x^2+12x+8+x^2-6x+9-x^3-5x^2\)
\(=2x^2+6x+17\)
c) \(\left(3x^3-4x^2+6x\right)\div\left(3x\right)=x^2-\dfrac{4}{3}x+2\)
Câu 2:
\(2x^3-12x^2+18x=2x\left(x^2-6x+9\right)=2x\left(x^2-2.x.3+3^2\right)=2x\left(x-3\right)^2\)
Bài 1: Rút gọn rồi tính giá trị biểu thức:
a) A = 4x2.(-3x2 + 1) + 6x2.( 2x2 – 1) + x2 khi x = -1
b) B = x2.(-2y3 – 2y2 + 1) – 2y2.(x2y + x2) khi x = 0,5 và y = -1/2
Bài 2: Tìm x, biết:
a) 2(5x - 8) – 3(4x – 5) = 4(3x – 4) +11
b) 2x(6x – 2x2) + 3x2(x – 4) = 8
c) (2x)2(4x – 2) – (x3 – 8x2) = 15
Bài 3: Chứng tỏ rằng giá trị của biểu thức sau không phụ thuộc vào giá trị của biến x:
P = x(2x + 1) – x2(x+2) + x3 – x +3
\(1,\\ a,A=4x^2\left(-3x^2+1\right)+6x^2\left(2x^2-1\right)+x^2\\ A=-12x^4+4x^2+12x^2-6x^2+x^2=-x^2=-\left(-1\right)^2=-1\\ b,B=x^2\left(-2y^3-2y^2+1\right)-2y^2\left(x^2y+x^2\right)\\ B=-2x^2y^3-2x^2y^2+x^2-2x^2y^3-2x^2y^2\\ B=-4x^2y^3-4x^2y^2+x^2\\ B=-4\left(0,5\right)^2\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^3-4\left(0,5\right)^2\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\left(0,5\right)^2\\ B=\dfrac{1}{8}-\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{4}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
\(2,\\ a,\Leftrightarrow10x-16-12x+15=12x-16+11\\ \Leftrightarrow-14x=-4\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{2}{7}\\ b,\Leftrightarrow12x^2-4x^3+3x^3-12x^2=8\\ \Leftrightarrow-x^3=8=-2^3\\ \Leftrightarrow x=2\\ c,\Leftrightarrow4x^2\left(4x-2\right)-x^3+8x^2=15\\ \Leftrightarrow16x^3-8x^2-x^3+8x^2=15\\ \Leftrightarrow15x^3=15\\ \Leftrightarrow x^3=1\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
\(P=x\left(2x+1\right)-x^2\left(x+2\right)+x^3-x+3\\ P=2x^2+x-x^3-2x^2+x^3-x+3\\ P=3\left(đfcm\right)\)
Rút gọn các biểu thức sau:
a) 2x(x+3) – 3x2(x+2) + x(3x2 + 4x – 6)
b) 3x(2x2 – x) – 2x2(3x+1) + 5(x2 – 1)
a) 2x(x+3) – 3x2(x+2) + x(3x2 + 4x – 6)
= (2x . x + 2x . 3) – (3x2 . x + 3x2 . 2) + (x . 3x2 + x . 4x – x . 6)
= 2x2 + 6x – (3x3 + 6x2) + (3x3 + 4x2 - 6x)
= 2x2 + 6x – 3x3 – 6x2 + 3x3 + 4x2 - 6x
= (– 3x3 + 3x3 ) + (2x2 - 6x2 + 4x2 ) + (6x – 6x)
= 0 + 0 + 0
= 0
b) 3x(2x2 – x) – 2x2(3x+1) + 5(x2 – 1)
= [3x . 2x2 + 3x . (-x)] – (2x2 . 3x + 2x2 . 1) + [5x2 + 5 . (-1)]
= 6x3 – 3x2 – (6x3 +2x2) + 5x2 – 5
= 6x3 – 3x2 – 6x3 - 2x2 + 5x2 – 5
= (6x3 – 6x3 ) + (-3x2 – 2x2 + 5x2) – 5
= 0 + 0 – 5
= - 5
Bài 5: Tìm nghiệm của các đa thức sau: Dạng 1: a) 4x + 9 b) -5x + 6 c) 7 – 2x d) 2x + 5 Dạng 2: a) ( x+ 5 ) ( x – 3) b) ( 2x – 6) ( x – 3) c) ( x – 2) ( 4x + 10 ) Dạng 3: a) x2 -2x b) x2 – 3x c) 3x2 – 4x d) ( 2x- 1)2 Dạng 4: a) x2 – 1 b) x2 – 9 c)– x 2 + 25 d) x2 - 2 e) 4x2 + 5 f) –x 2 – 16 g) - 4x4 – 25 Dạng 5: a) 2x2 – 5x + 3 b) 4x2 + 6x – 1 c) 2x2 + x – 1 d) 3x2 + 2x – 1
Cho 2 đa thức :
N (x) = x2 + 3x4 - 2x - x2 + 2x3
P (x) = -8 + 5x - 6x3 - 4x + 6
A) rút gọn đa thức N (x) , P (x) và xác định bậc của chúng
B) Tính N(x) + P(x)
C) Tính B(x) = -2x2 ( x3 - 2x + 5x2 -1 )
\(a,N\left(x\right)=x^2+3x^4-2x-x^2+2x^3=3x^4+2x^3+\left(x^2-x^2\right)-2x\\ =3x^4+2x^3-2x\\ P\left(x\right)=-8+5x-6x^3-4x+6=-6x^3+\left(5x-4x\right)+\left(-8+6\right)\\ =-6x^3+x-2\)
Bậc của N(x) là 4
Bậc của P(x) là 3
\(b,P\left(x\right)+N\left(x\right)=3x^4+2x^3-2x-6x^3+x-2\\ =3x^4+\left(2x^3-6x^3\right)+\left(-2x+x\right)-2\\ =3x^4-4x^3-x-2\)
\(c,B\left(x\right)=-2x^2\left(x^3-2x+5x^2-1\right)\\ =\left(-2x^2\right).x^3+\left(-2x^2\right).\left(-2x\right)+\left(-2x^2\right).5x^2+\left(-2x^2\right).\left(-1\right)\\ =-2x^5+4x^3-10x^4+2x^2\\ =-2x^5-10x^4+4x^3+2x^2\)
Bài 1: Rút gọn các biểu thức sau:
a, A = (x-2).(2x-1) - 2x (x+3)
b, B = (3x-2).(2x+1) - (6x-1).(x+2)
c, C = 6x.(2x+3) - (4x-1).(3x-2)
d, D = (2x+3).(5x-2)+(x+4).(2x-1) - 6x.(2x-3)
Bài 2: Chứng tỏ rằng các đa thức không phụ thuộc vào biến.
a, 2x(3x-5).(x+11) - 3x.(2x+3).(x+7)
b, (x2+5x-6).(x-1) - (x+2).(x2-x+1) - x(3x-10)
c, (x2+x+1).(x-1) - x2(x+1) + x2 - 5
Bài 1
A= (x-2)(2x-1)-2x(x+3)=2x2-x-4x+2-2x2-6x=-11x+2
Bài 1:
a) \(A=\left(x-2\right)\left(2x-1\right)-2x\left(x+3\right)\)
\(A=2x^2-x-4x+2-2x^2-6x\)
\(A=-11x+2\)
b) \(B=\left(3x-2\right)\left(2x+1\right)-\left(6x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\)
\(B=6x^2+3x-4x-2-6x^2-12x+x+2\)
\(B=-12x\)
c) \(C=6x\left(2x+3\right)-\left(4x-1\right)\left(3x-2\right)\)
\(C=12x^2+18x-12x^2+8x+3x-2\)
\(C=29x-2\)
d) \(D=\left(2x+3\right)\left(5x-2\right)+\left(x+4\right)\left(2x-1\right)-6x\left(2x-3\right)\)
\(D=10x^2-4x+15x-6+2x^2-x+8x-4-12x^2+18x\)
\(D=36x-10\)
Bài 2:
a: Ta có: \(2x\left(3x-5\right)\left(x+11\right)-3x\left(2x+3\right)\left(x+7\right)\)
\(=2x\left(3x^2+33x-5x-55\right)-3x\left(2x^2+14x+3x+21\right)\)
\(=6x^3+56x^2-110x-6x^2-51x^2-63x\)
\(=-117x\)
b: Ta có: \(\left(x^2+5x-6\right)\left(x-1\right)-\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)-x\left(3x-10\right)\)
\(=x^3+4x^2-11x+6-\left(x^3-x^2+x+2x^2-2x+2\right)-3x^2+10x\)
\(=x^3+x^2-x+6-x^3-x^2+x-2\)
=4
c: Ta có: \(\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)-x^2\left(x+1\right)+x^2-5\)
\(=x^3-1-x^3-x^2+x^2-5\)
=-6
Bài 1: Tính:
a) x2(x-2x3); b) (x2+1)(5-x); c) (x-2)(x2+3x-4); d) (x-2)(x-x2+4); e) (x2-1)(x2+2x); f) (2x-1)(3x+2)(3-x)
Bài 2: Tính:
a) (x-2y)2; b) (2x2+3)3; c) (x-2)(x2+2x+4); d) (2x-1)3
Bài 3: Rút gọn biểu thức:
a) (6x+1)2+(6x-1)2-2(1+6x)(6x-1); b) 3(22+1)(24+1)(28+1)(216+1); c) x(2x2-3)-x2(5x+1)+x2; d) 3x(x-2)-5x(1-x)-8(x2-3)
Bài 4: Tính nhanh:
a) 1012; b) 97.103; c) 772+232+77.46; d) 1052-52; e) A= (x-y)(x2+xy+y2)+2y3 tại x= \(\dfrac{2}{3}\) và y= \(\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Bạn chú ý đăng lẻ câu hỏi! 1/
a/ \(=x^3-2x^5\)
b/\(=5x^2+5-x^3-x\)
c/ \(=x^3+3x^2-4x-2x^2-6x+8=x^3=x^2-10x+8\)
d/ \(=x^2-x^3+4x-2x+2x^2-8=3x^2-x^3+2x-8\)
e/ \(=x^4-x^2+2x^3-2x\)
f/ \(=\left(6x^2+x-2\right)\left(3-x\right)=17x^2+5x-6-6x^3\)
Rút gọn các biểu thức sau:
a) 4x2(5x2 + 3) – 6x(3x3 – 2x + 1) – 5x3 (2x – 1)
b) \(\dfrac{3}{2}x\left( {{x^2} - \dfrac{2}{3}x + 2} \right) - \dfrac{5}{3}{x^2}(x + \dfrac{6}{5})\)
a) 4x2(5x2 + 3) – 6x(3x3 – 2x + 1) – 5x3 (2x – 1)
= 4x2 . 5x2 + 4x2 . 3 – [6x . 3x3 + 6x . (-2x) + 6x . 1] – [5x3 . 2x + 5x3 . (-1)]
= 20x4 + 12x2 – (18x4 – 12x2 + 6x) – (10x4 – 5x3)
= 20x4 + 12x2 - 18x4 + 12x2 - 6x - 10x4 + 5x3
= (20x4 – 18x4 - 10x4 ) + 5x3 + (12x2 + 12x2 ) – 6x
= -8x4 + 5x3 + 24x2 – 6x
\(\begin{array}{l}b)\dfrac{3}{2}x\left( {{x^2} - \dfrac{2}{3}x + 2} \right) - \dfrac{5}{3}{x^2}(x + \dfrac{6}{5})\\ = \dfrac{3}{2}x.{x^2} + \dfrac{3}{2}x.( - \dfrac{2}{3}x) + \dfrac{3}{2}x.2 - (\dfrac{5}{3}{x^2}.x + \dfrac{5}{3}{x^2}.\dfrac{6}{5})\\ = \dfrac{3}{2}{x^3} - {x^2} + 3x - (\dfrac{5}{3}{x^3} + 2{x^2})\\ = \dfrac{3}{2}{x^3} - {x^2} + 3x - \dfrac{5}{3}{x^3} - 2{x^2}\\ = (\dfrac{3}{2}{x^3} - \dfrac{5}{3}{x^3}) + ( - {x^2} - 2{x^2}) + 3x\\ = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{6}{x^3} - 3{x^2} + 3x\end{array}\)