Giải các bất phương trình sau:
a) \(3x + 2 > 2x + 3;\)
b) \(5x + 4 < - 3x - 2.\)
Giải các bất phương trình sau:
a) \(2{x^2} - 3x + 1 > 0\)
b) \({x^2} + 5x + 4 < 0\)
c) \( - 3{x^2} + 12x - 12 \ge 0\)
d) \(2{x^2} + 2x + 1 < 0.\)
a) \(2{x^2} - 3x + 1 > 0\)
Tam thức \(f\left( x \right) = 2{x^2} - 3x + 1\) có \(a + b + c = 2 - 3 + 1 = 0\) nên hai nghiệm phân biệt \({x_1} = 1\) và \({x_2} = \frac{1}{2}.\)
Mặt khác \(a = 2 > 0,\) do đó ta có bảng xét dấu sau:

Tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là: \(S= \left( { - \infty ;\frac{1}{2}} \right) \cup \left( {1; + \infty } \right).\)
b) \({x^2} + 5x + 4 < 0\)
Tam thức \(f\left( x \right) = {x^2} + 5x + 4\) có \(a - b + c = 1 - 5 + 4 = 0\) nên phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt \(x = - 1\) và \(x = - 4.\)
Mặt khác \(a = 1 > 0,\) do đó ta có bảng xét dấu sau:
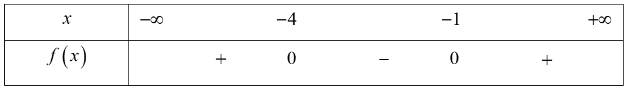
Tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là: \(S = \left( { - 4; - 1} \right).\)
c) \( - 3{x^2} + 12x - 12 \ge 0\)
Tam thức \(f\left( x \right) = - 3{x^2} + 12x - 12 = - 3\left( {{x^2} - 4x + 4} \right) = - 3{\left( {x - 2} \right)^2} \le 0\)
Do đó
\( - 3{x^2} + 12x - 12 \ge 0 \Leftrightarrow - 3{x^2} + 12x - 12 = 0 \Leftrightarrow - 3{\left( {x - 2} \right)^2} = 0 \Leftrightarrow x = 2.\)
Tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là: \(S = \left( { 2} \right).\)
d) \(2{x^2} + 2x + 1 < 0.\)
Tam thức \(f\left( x \right) = 2{x^2} + 2x + 1\) có \(\Delta = - 1 < 0,\) hệ số \(a = 2 > 0\) nên \(f\left( x \right)\) luôn dướng với mọi \(x,\) tức là \(2{x^2} + 2x + 1 > 0\) với mọi \(x \in \mathbb{R}.\)
\( \Rightarrow \) bất phương trình vô nghiệm
Giải các bất phương trình sau:
a)\(\left(x^2+3x-4\right)\left(3-2x\right)\)<0
b) \(\dfrac{x^2+3x+4}{x^2-2}\ge0\)
c) \(\dfrac{x\left(x^2+4x+4\right)}{x^2-1}\ge0\)
a. TH1:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2+3x-4< 0\\3-2x>0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< 1\\x>-4\end{matrix}\right.\\x>\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
TH2:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2+3x-4>0\\3-2x< 0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>1\\x< -4\end{matrix}\right.\\x< \dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy nghiệm của BPT:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< 1\\x>-4\end{matrix}\right.\\x>\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>1\\x< -4\end{matrix}\right.\\x< \dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Giải các bất phương trình sau:
a) \(\sqrt{2-|x-2|}>x-2\)
b) \(x^2+3x+2\geq 2\sqrt{x^2+3x+5}\)
c) \(4\sqrt{x}+\frac{2}{\sqrt{x}}<2x+\frac{1}{2x}+2\)
Giải các bất phương trình sau:
a) 2(3x + 1) - 4(5 - 2x) > 2(4x - 3) - 6
b) 9x2 - 3(10x - 1) < (3x - 5)2 - 21
c) \(\dfrac{x-1}{2}+\dfrac{x-2}{3}+\dfrac{x-3}{4}>\dfrac{x-4}{5}+\dfrac{x-5}{6}\)
a) Ta có: \(2\left(3x+1\right)-4\left(5-2x\right)>2\left(4x-3\right)-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x+2-20+8x>8x-6-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow14x-18-8x+12>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x-6>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x>6\)
hay x>1
Vậy: S={x|x>1}
b) Ta có: \(9x^2-3\left(10x-1\right)< \left(3x-5\right)^2-21\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2-30x+3< 9x^2-30x+25-21\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2-30x+3-9x^2+30x-4< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-1< 0\)(luôn đúng)
Vậy: S={x|\(x\in R\)}
Giải các bất phương trình sau:
a)\(\left|3x-2\right|>7\)
\(\left|3x-2\right|>7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-2\right)^2>49\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2-12x-45>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(3x+5\right)>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>3\\x< -\dfrac{5}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bài 1: Giải các bất phương trình và phương trình sau :
a) 2(3-4x) = 10-(2x – 5)
Giải các bất phương trình và phương trình sau :
a) 3(2-4x) = 11-(3x – 1)
Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(2\left(3-4x\right)=10-\left(2x-5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6-8x-10+2x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x+11=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x=-11\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{11}{6}\)
b) Ta có: \(3\left(2-4x\right)=11-\left(3x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6-12x-11+3x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x=6\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
Bài 2. Giải các phương trình sau:
a) |x-2|+2x=7
b) |x-3| -4x=5
c) |2x+3|+x=2x+3
d) |x+2|=|3x-4|
a, \(x<2\)
\(2-x+2x=7\)
\(x=5(\)ko \(t/m)\)
\(x>2\)
\(-x=5\)
\(x=-5(ko\) \(t/m)\)
a: |x-2|+2x=7
=>|x-2|=-2x+7
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =\dfrac{7}{2}\\\left(-2x+7\right)^2=\left(x-2\right)^2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =\dfrac{7}{2}\\\left(2x-7-x+2\right)\left(2x-7+x-2\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =\dfrac{7}{2}\\\left(x-5\right)\left(3x-9\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
b: |x-3|-4x=5
=>|x-3|=4x+5
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=-\dfrac{5}{4}\\\left(4x+5-x+3\right)\left(4x+5+x-3\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=-\dfrac{5}{4}\\\left(3x+8\right)\left(5x+2\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{2}{5}\)
c: |2x+3|+x=2x+3
=>|2x+3|=x+3
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=-3\\\left(2x+3-x-3\right)\left(2x+3+x+3\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{0;-2\right\}\)
Giải các phương trình sau:
a/ 3x – 2 = 2x – 3
b/ 7 – 2x = 22 – 3x
c) 8x – 3 = 5x + 12
d/ x – 12 + 4x = 25 + 2x – 1
e/ x + 2x + 3x – 19 = 3x + 5
a) \(PT\Leftrightarrow3x-2x=2-3\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-1\right\}\)
b) \(PT\Leftrightarrow-2x+3x=-7+22\Leftrightarrow x=15\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{15\right\}\)
c) \(PT\Leftrightarrow8x-5x=3+12\Leftrightarrow3x=15\Leftrightarrow x=5\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{5\right\}\)
d) \(PT\Leftrightarrow x+4x-2x=12+25-1\Leftrightarrow3x=36\Leftrightarrow x=12\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{12\right\}\)
e) \(PT\Leftrightarrow x+2x+3x-3x=19+5\Leftrightarrow3x=24\Leftrightarrow x=8\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{8\right\}\)
a)3x-2=2x-3
=>x=-1
b)7-2x=22-3x
=>x=15
c)8x-3=5x+12
=>3x=15
=>x=5
d)x-12+4x=25+2x-1
=>3x=12
=>x=4
e)x+2x+3x-19=3x+5
=>3x=24
=>x=8
a)3x-2=2x-3
=>x=-1
b)7-2x=22-3x
=>x=15
c)8x-3=5x+12
=>3x=15
=>x=5
d)x-12+4x=25+2x-1
=>3x=36
=>x=12
e)x+2x+3x-19=3x+5
=>3x=24
=>x=8
Giải các bất phương trình bậc hai sau:
a) \(3{x^2} - 2x + 4 \le 0\)
b) \( - {x^2} + 6x - 9 \ge 0\)
a) Ta có \(a = 3 > 0\) và tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = 3{x^2} - 2x + 4\) có \(\Delta ' = {1^2} - 3.4 = - 11 < 0\)
=> \(f\left( x \right) = 3{x^2} - 2x + 4\) vô nghiệm.
=> \(3{x^2} - 2x + 4 > 0\forall x \in \mathbb{R}\)
b) Ta có: \(a = - 1 < 0\) và \(\Delta ' = {3^2} - \left( { - 1} \right).\left( { - 9} \right) = 0\)
=> \(f\left( x \right) = - {x^2} + 6x - 9\) có nghiệm duy nhất \(x = 3\).
=> \( - {x^2} + 6x - 9 < 0\forall x \in \mathbb{R}\backslash \left\{ 3 \right\}\)
giải các phương trình sau:
a.|2-5x|=|2x-3|
b.|2-5x|-2|x+1|=3x+5
c.|3x-1|+2|x-1|=|5x-3|
a: =>|5x-2|=|2x-3|
=>5x-2=2x-3 hoặc 5x-2=-2x+3
=>3x=-1 hoặc 7x=5
=>x=5/7 hoặc x=-1/3
b: =>|5x-2|-|2x+2|=3x+5
TH1 x<-1
PT sẽ là 2-5x+2x+2=3x+5
=>-3x+4=3x+5
=>-6x=1
=>x=-1/6(loại)
TH2: -1<=x<2/5
Pt sẽ là 2-5x-2x-2=3x+5
=>-7x=3x+5
=>-4x=5
=>x=-5/4(loại)
Th3: x>=2/5
PT sẽ là 5x-2-2x-2=3x+5
=>3x-4=3x+5
=>0x=9(loại)