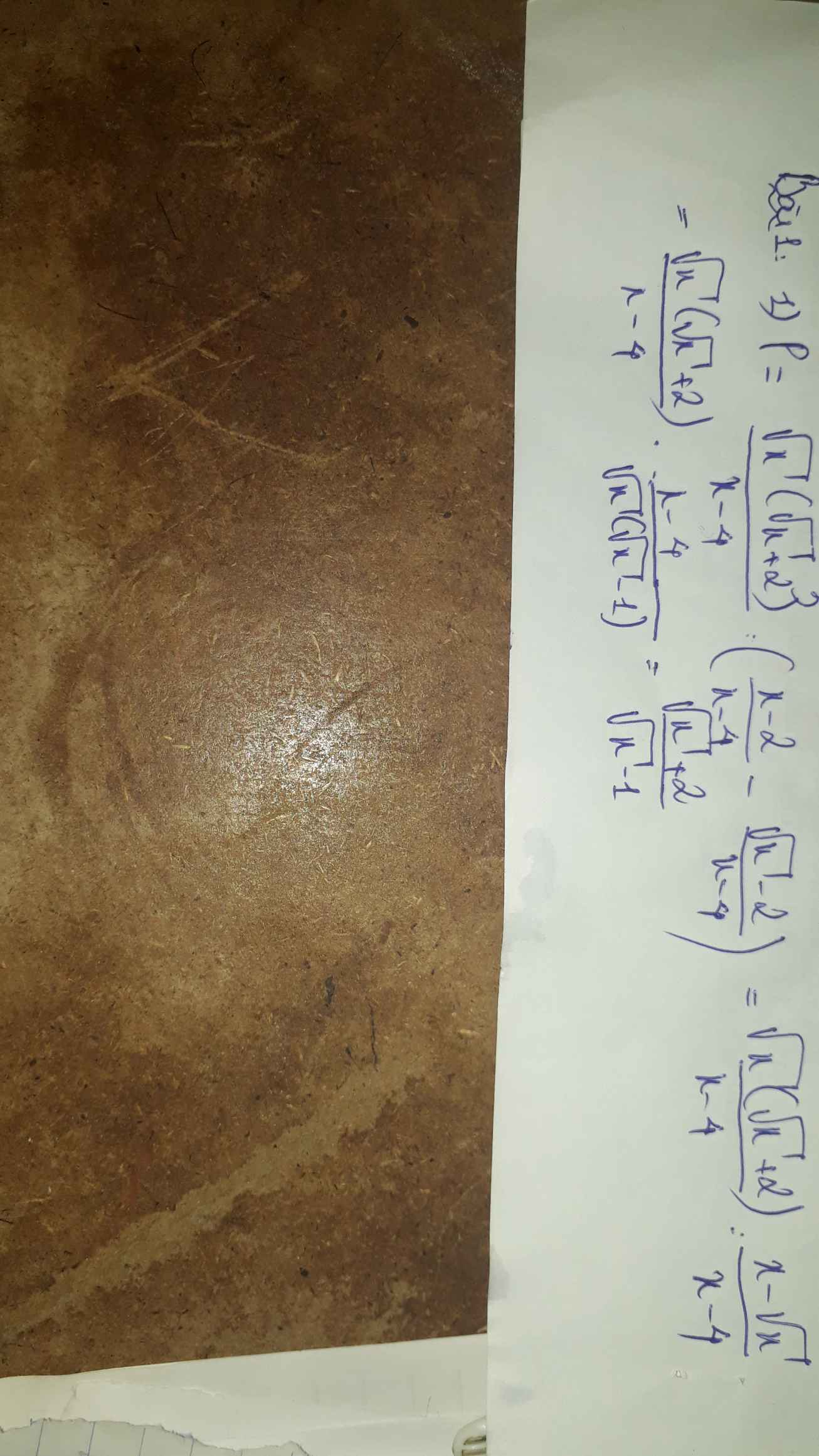Cho phân thức: \(\dfrac{{2{{\rm{x}}^2} - x + 1}}{{x - 2}}\). Tìm giá trị của x sao cho mẫu: \(x - 2 \ne 0\).

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Một phân thức có giá trị bằng 0 khi giá trị của tử thức bằng 0 còn giá trị của mẫu thức khác 0. Ví dụ giá trị của phân thức dfrac{x^2-25}{x+1}0 khi x^2-250 và x+1ne0 hay left(x-5right)left(x+5right)0 và xne-1
Vậy giá trị của phân thức này bằng 0 khi xpm5
Tìm các giá trị của x để giá trị của mỗi phân thức sau bằng 0 :
a) dfrac{98x^2-2}{x-2}
b) dfrac{3x-2}{x^2+2x+1}
Đọc tiếp
Một phân thức có giá trị bằng 0 khi giá trị của tử thức bằng 0 còn giá trị của mẫu thức khác 0. Ví dụ giá trị của phân thức \(\dfrac{x^2-25}{x+1}=0\) khi \(x^2-25=0\) và \(x+1\ne0\) hay \(\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\) và \(x\ne-1\)
Vậy giá trị của phân thức này bằng 0 khi \(x=\pm5\)
Tìm các giá trị của x để giá trị của mỗi phân thức sau bằng 0 :
a) \(\dfrac{98x^2-2}{x-2}\)
b) \(\dfrac{3x-2}{x^2+2x+1}\)
a, Ta có : \(\dfrac{98x^2-2}{x-2}=0\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}98x^2-2=0\\x-2\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
hay \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2=\dfrac{1}{49}\\x\ne2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\dfrac{1}{7}\)
Vậy giá trị của phân thức này bằng 0 khi \(x=\pm\dfrac{1}{7}\)
b, Ta có : \(\dfrac{3x-2}{x^2+2x+1}=0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3x-2}{\left(x+1\right)^2}=0\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-2=0\\\left(x+1\right)^2\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
hay \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\x\ne-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy giá trị của phân thức này bằng 0 khi \(x=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a)
98x^2 -2 =0 =>x^2 =1/49 => x= -+1/7 nhận
b)
3x-2=0=>x=2/3 nhận
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
cho biểu thức P=\(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}:\left(\dfrac{x-2}{x-4}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}+2}\right)\) với x>0;x\(\ne\)1;x\(\ne\)4
1.rút gọn biểu thức P
2.tìm x thỏa mãn P>1
3.tính giá trị của P khi x=\(\dfrac{1}{4}\)
cho biểu thức P=\(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}:\left(\dfrac{x-2}{x-4}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}+2}\right)\) với x>0;x\(\ne\)1;x\(\ne\)4
1.rút gọn biểu thức P
2.tìm x thỏa mãn P>1
3.tính giá trị của P khi x=\(\dfrac{1}{4}\)
Cho biểu thức : P= \(\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-2}-\dfrac{2}{x-4}\right).\left(\sqrt{x}-1+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-4}{\sqrt{x}}\right)\) (với x>0; x\(\ne\)4)
1) Chứng minh rằng P=\(\sqrt{x}\)+3
2) Tìm các giá trị của x sao cho P=x+3
`1)P((\sqrtx+1)/(\sqrtx-2)-2/(x-4)).(\sqrtx-1+(\sqrtx-4)/\sqrtx)(x>0,x ne 4)`
`=((x+3\sqrtx+2-2)/(x-4)).((x-\sqrtx+\sqrtx-4)/\sqrtx)`
`=((x+3\sqrtx-4)/(x-4)).((x-4)/\sqrtx))`
`=(x+3\sqrtx)/\sqrtx`
`=(\sqrtx(\sqrtx+3))/\sqrtx`
`=\sqrtx+3(đpcm)`
`2)P=x+3
`<=>\sqrtx+3=x+3`
`<=>x-\sqrtx=0`
`<=>\sqrtx(\sqrtx-1)=0`
Vì `x>0=>\sqrtx>0`
`=>\sqrtx-1=0<=>x=1(tm)`
Vậy `x=1=>\sqrtx+3=x+3`
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
`1)P((\sqrtx+1)/(\sqrtx-2)-2/(x-4)).(\sqrtx-1+(\sqrtx-4)/\sqrtx)(x>0,x ne 4)`
`=((x+3\sqrtx+2-2)/(x-4)).((x-\sqrtx+\sqrtx-4)/\sqrtx)`
`=((x+3\sqrtx)/(x-4)).((x-4)/\sqrtx))`
`=(x+3\sqrtx)/\sqrtx`
`=(\sqrtx(\sqrtx+3))/\sqrtx`
`=\sqrtx+3(đpcm)`
`2)P=x+3
`<=>\sqrtx+3=x+3`
`<=>x-\sqrtx=0`
`<=>\sqrtx(\sqrtx-1)=0`
Vì `x>0=>\sqrtx>0`
`=>\sqrtx-1=0<=>x=1(tm)`
Vậy `x=1=>\sqrtx+3=x+3`
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho biểu thức \(C=\dfrac{x}{2x-2}-\dfrac{x^2+1}{2-2x^2}\).
a. Tìm x để biểu thức C có nghĩa.
b.Rút gọn biểu thức C.
c.Tìm giá trị của x để giá trị của biểu thức C = \(\dfrac{-1}{2}\).
d. Tìm x để giá trị của phân thức C > 0.
\(a,ĐK:x\ne1;x\ne-1\\ b,C=\dfrac{x^2+x+x^2+1}{2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x^2+2x+1}{2x^2-2}\\ c,C=-\dfrac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow2-2x^2=2x^2+2x+1\\ \Leftrightarrow4x^2+2x-1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\sqrt{5}-1}{4}\\x=\dfrac{-\sqrt{5}-1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\\ d,C>0\Leftrightarrow2x^2-2>0\left(2x^2+2x+1>0\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)>0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>1\\x< -1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
Cho biểu thức
\(A=\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}+\dfrac{x-1}{x+2}+\dfrac{x^2+4x}{4-x^2}\left(x\ne\pm2\right)\)
a) Rút gọn A
b) Tính giá trị của biểu thức A khi x = 4
c) Tìm giá trị nguyên của x để biểu thức A nhận giá trị nguyên dương
a) Tìm x sao cho giá trị biểu thức dfrac{3x-2}{4}không nhỏ hơn giá trị của biểu thức dfrac{3x+3}{6}b) Tìm x sao cho giá trị của biểu thức (x+1)2 nhỏ hơn giá trị của biểu thức (x-1)2.c) Tìm x sao cho giá trị của biểu thức dfrac{2x-3}{35}+dfrac{xleft(x-2right)}{7} không lớn hơn giá trị của biểu thức dfrac{x^2}{7}-dfrac{2x-3}{5}
Đọc tiếp
a) Tìm x sao cho giá trị biểu thức \(\dfrac{3x-2}{4}\)không nhỏ hơn giá trị của biểu thức \(\dfrac{3x+3}{6}\)
b) Tìm x sao cho giá trị của biểu thức (x+1)2 nhỏ hơn giá trị của biểu thức (x-1)2.
c) Tìm x sao cho giá trị của biểu thức \(\dfrac{2x-3}{35}+\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{7}\) không lớn hơn giá trị của biểu thức \(\dfrac{x^2}{7}-\dfrac{2x-3}{5}\)
a: Để \(\dfrac{3x-2}{4}\) không nhỏ hơn \(\dfrac{3x+3}{6}\) thì \(\dfrac{3x-2}{4}>=\dfrac{3x+3}{6}\)
=>\(\dfrac{6\left(3x-2\right)}{24}>=\dfrac{4\left(3x+3\right)}{24}\)
=>18x-12>=12x+12
=>6x>=24
=>x>=4
b: Để \(\left(x+1\right)^2\) nhỏ hơn \(\left(x-1\right)^2\) thì \(\left(x+1\right)^2< \left(x-1\right)^2\)
=>\(x^2+2x+1< x^2-2x+1\)
=>4x<0
=>x<0
c: Để \(\dfrac{2x-3}{35}+\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{7}\) không lớn hơn \(\dfrac{x^2}{7}-\dfrac{2x-3}{5}\) thì
\(\dfrac{2x-3}{35}+\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{7}< =\dfrac{x^2}{7}-\dfrac{2x-3}{5}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x-3+5x\left(x-2\right)}{35}< =\dfrac{5x^2-7\cdot\left(2x-3\right)}{35}\)
=>\(2x-3+5x^2-10x< =5x^2-14x+21\)
=>-8x-3<=-14x+21
=>6x<=24
=>x<=4
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
cho biểu thức P=\(\left(\dfrac{3}{x+1}+\dfrac{x-9}{x^2-1}+\dfrac{2}{1-x}\right):\dfrac{x-3}{x^2-1}\)
a.với đkxđ của P:x\(\ne\pm1;\)x\(\ne\pm3\). hãy rút gọn biểu thức P
b.tính giá trị của biểu thức P biết x^2-9=0
c.tìm các giá trị nguyên của x để P nhận giá trị nguyên
a) Ta có: \(P=\left(\dfrac{3}{x+1}+\dfrac{x-9}{x^2-1}+\dfrac{2}{1-x}\right):\dfrac{x-3}{x^2-1}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{3\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}+\dfrac{x-9}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}-\dfrac{2\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\right):\dfrac{x-3}{x^2-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x-3+x-9-2x-2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{x-3}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x-14}{x-3}\)
b) Ta có: \(x^2-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\left(loại\right)\\x=-3\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay x=-3 vào biểu thức \(P=\dfrac{2x-14}{x-3}\), ta được:
\(P=\dfrac{2\cdot\left(-3\right)-14}{-3-3}=\dfrac{-20}{-6}=\dfrac{10}{3}\)
Vậy: Khi \(x^2-9=0\) thì \(P=\dfrac{10}{3}\)
c) Để P nguyên thì \(2x-14⋮x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-6-8⋮x-3\)
mà \(2x-6⋮x-3\)
nên \(-8⋮x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-3\inƯ\left(-8\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-3\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2;4;-4;8;-8\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{4;2;5;1;7;-1;11;-5\right\}\)
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ, ta được: \(x\in\left\{4;2;5;7;11;-5\right\}\)
Vậy: Để P nguyên thì \(x\in\left\{4;2;5;7;11;-5\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
cho biểu thức A=\(\left\{\dfrac{x}{x^2-4}+\dfrac{2}{2-x}-\dfrac{-1}{x+2}\right\}.(x+2)\) \((x\ne2,x\ne-2)\)
a. Rút gọn A và tính giá trị của A tại x = -1
b. Tìm điều kiện của x để giá trị của ( A ) luôn là sô nguyên
a: \(A=\dfrac{x-2x-4+x-2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\cdot\left(x+2\right)=-\dfrac{6}{x-2}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)