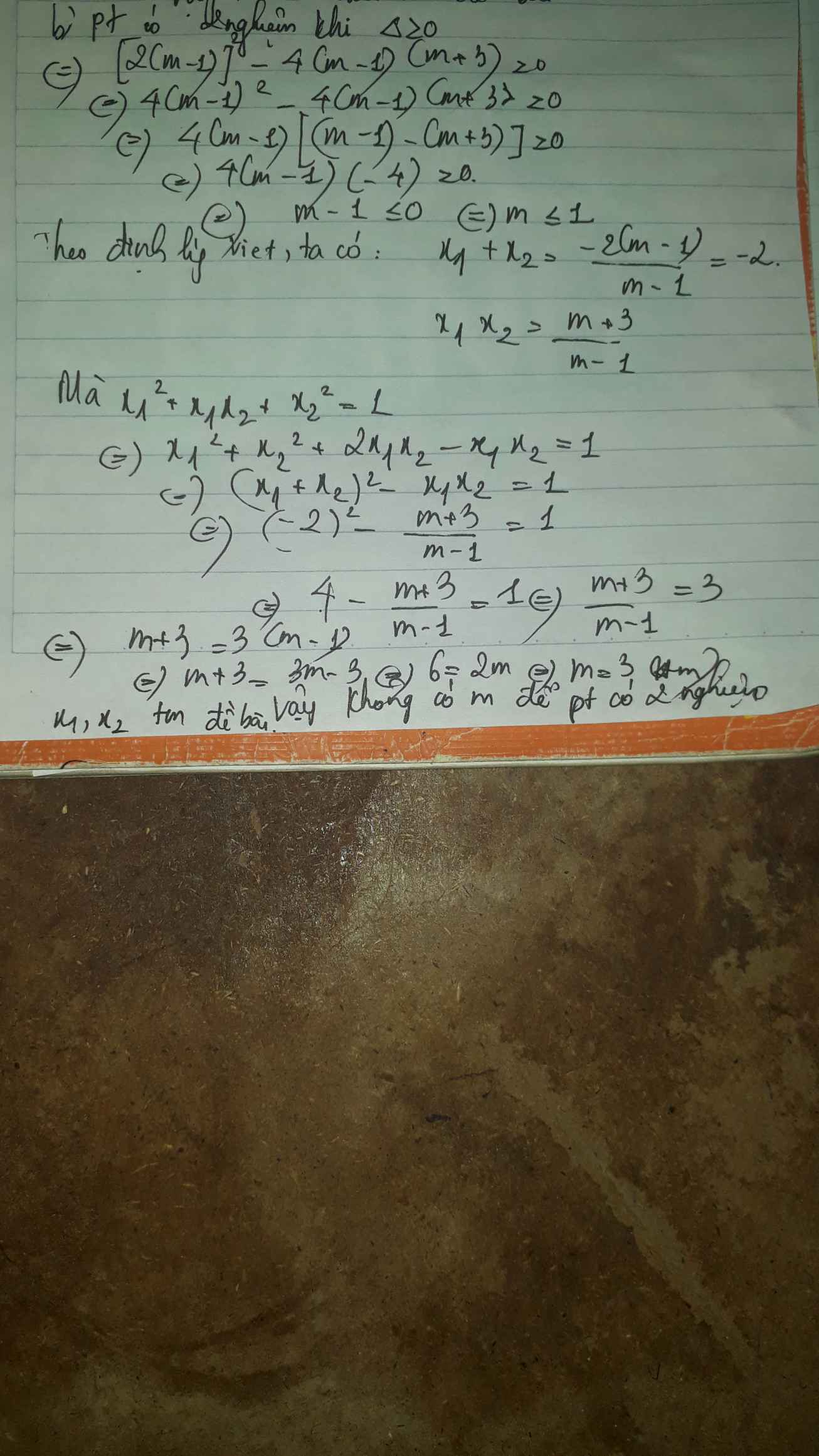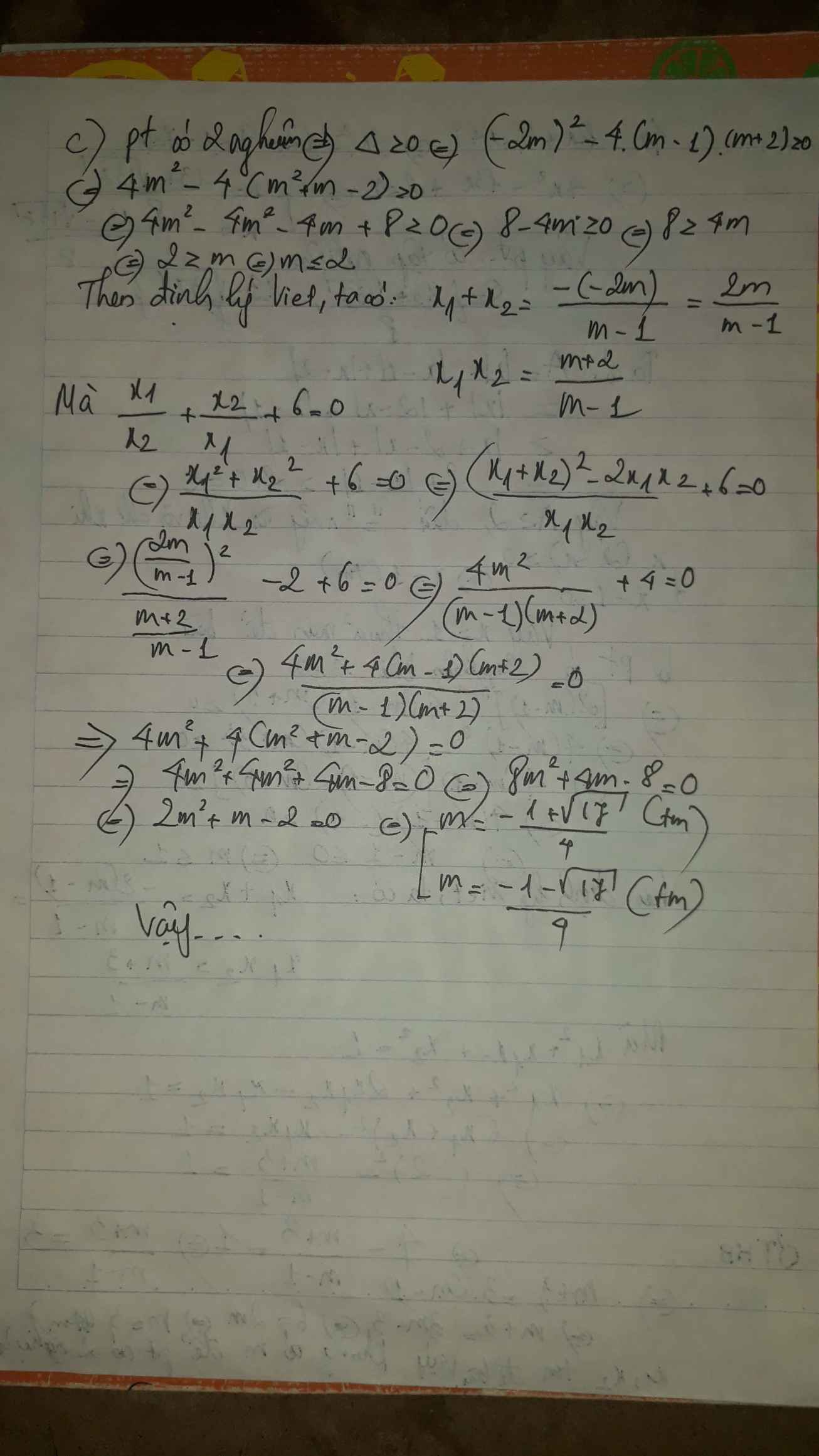tìm m để phương trình x2 -6x +m+3=0
có 2 nghiệm phân biệt / \(|x_1-1|\) + 3x2=9
Tuyển Cộng tác viên Hoc24 nhiệm kì 26 tại đây: https://forms.gle/dK3zGK3LHFrgvTkJ6

Những câu hỏi liên quan
tìm m để phương trình x2−(m−1)x−2=0x2−(m−1)x−2=0có 2 nghiệm phân biệt x1 và x2 (x1>x2) thỏa mãn |2x1|−|x2|=2+x1
1) \(2x-x^2-\sqrt{6x^2-12x+7}=0\)
2) cho phương trình x2 - 2(m+1)x+m2+3=0 .Xác định m để phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt x1 ,x2 thoả \(x_1^2+x_2^2=2x_1x_2+8\)
1.
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-12x+7-6\sqrt{6x^2-12x+7}-7=0\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{6x^2-12x+7}=t>0\)
\(\Rightarrow t^2-6t-7=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=-1\left(loại\right)\\t=7\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{6x^2-12x+7}=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-12x+7=49\Rightarrow x=1\pm2\sqrt{2}\)
2.
\(\Delta'=\left(m+1\right)^2-m^2-3=2m-2>0\Rightarrow m>1\)
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m+1\right)\\x_1x_2=m^2+3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=2x_1x_2+8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(m+1\right)^2-4\left(m^2+3\right)-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m-4=0\Rightarrow m=2\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
b Tìm m để phương trình left(m-1right)x^2+2left(m-1right)x+m+30 có hai nghiệm x1,x2 thỏa mãn x_1^2+x_1.x_2+x_2^21c Tìm m để phương trình left(m-1right)x^2-2mx+m+20 có hai nghiệm x1,x2 phân biệt thỏa mãn dfrac{x_1}{x_2}+dfrac{x_2}{x_1}+60d Tìm m để phương trình 3x^2+4left(m-1right)x+m^2-4m+10 có hai nghiệm phân biệt x1,x2 thỏa mãn dfrac{1}{x_1}+dfrac{1}{x_2}dfrac{1}{2} (x1+x2)
Đọc tiếp
b Tìm m để phương trình \(\left(m-1\right)x^2+2\left(m-1\right)x+m+3=0\) có hai nghiệm x1,x2 thỏa mãn \(x_1^2+x_1.x_2+x_2^2=1\)
c Tìm m để phương trình \(\left(m-1\right)x^2-2mx+m+2=0\) có hai nghiệm x1,x2 phân biệt thỏa mãn \(\dfrac{x_1}{x_2}+\dfrac{x_2}{x_1}+6=0\)
d Tìm m để phương trình \(3x^2+4\left(m-1\right)x+m^2-4m+1=0\) có hai nghiệm phân biệt x1,x2 thỏa mãn \(\dfrac{1}{x_1}+\dfrac{1}{x_2}=\dfrac{1}{2}\) (x1+x2)
b) phương trình có 2 nghiệm \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m-1\right)^2-\left(m-1\right)\left(m+3\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-2m+1-m^2-3m+m+3\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4m+4\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\le1\)
Ta có: \(x_1^2+x_1x_2+x_2^2=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=1\)
Theo viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=2\left(m-1\right)\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=m+3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[-2\left(m-1\right)^2\right]-2\left(m+3\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-8m+4-2m-6-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-10m-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m_1=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{37}}{4}\left(ktm\right)\\m_2=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{37}}{4}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow m=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{37}}{4}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
Cho phương trình: x2 - (m + 2).x + 2m = 0. Tìm m để phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt x1, x2 thỏa mãn: \(\dfrac{1}{x_1}+\dfrac{1}{x_2}=\dfrac{x_1.x_2}{4}\)
Δ=(m+2)^2-4*2m=(m-2)^2
Để PT có hai nghiệm pb thì m-2<>0
=>m<>2
\(\dfrac{1}{x_1}+\dfrac{1}{x_2}=\dfrac{x_1x_2}{4}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x_1+x_2}{x_1x_2}=\dfrac{x_1x_2}{4}\)
=>\(\dfrac{m+2}{2m}=\dfrac{2m}{4}=\dfrac{m}{2}\)
=>2m^2=2m+4
=>m^2-m-2=0
=>m=2(loại) hoặc m=-1
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho phương trình: x2 - 5x + m - 1 = 0 (*). Tìm m để phương trình (*) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt x1;x2 sao cho: 2x2 = \(\sqrt{x_1}\)
\(\Delta=\left(-5\right)^2-4\left(m-1\right)\)
\(=25-4m+4\)
\(=29-4m\)
Để pt có 2 nghiệm thì \(\Delta>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m< \dfrac{29}{4}\)
Theo hệ thức Vi-ét, ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=5\\x_1x_2=m-1\end{matrix}\right.\) (1)
\(2x_2=\sqrt{x_1}\) ; \(ĐK:x_1;x_2\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x_2^2=\left|x_1\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x_2^2=x_1\) (2)
Thế \(x_1=4x^2_2\) vào \(\left(1\right)\), ta được:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x_2^2+x_2-5=0\\4x_2^3-m+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_2=-\dfrac{5}{4}\left(ktm\right)\\x_2=1\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\\4.1^3-m+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_2=1\\m=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(2\right)\Rightarrow x_1=4\)
Vậy \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=5\\x_1=4\\x_2=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
Cho phương trình x^2 -4x+m-5=0 tìm các giá trị m để phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt x1,x2 thoã mãn(x1-1).(x2^2-3x2+m-6)=-3
=>(x1-1)[x2^2-x2(x1+x2-1)+x1x2+1]=-3
=>(x1-1)[-x1x2+x2+x1x2+1]=-3
=>(x1-1)(x2+1)=-3
=>x1x2+(x1-x2)-1=-3
=>(x1-x2)=-3+1-x1x2=-2-m+5=-m+3
=>(x1+x2)^2-4x1x2=m^2-6m+9
=>4^2-4(m-5)=m^2-6m+9
=>4m-20=16-m^2+6m-9=-m^2+6m+7
=>4m-20+m^2-6m-7=0
=>m^2-2m-27=0
=>\(m=1\pm2\sqrt{7}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho phương trình x2 - 2(m + 1)x + 4m = 0. Tìm m để phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt x1, x2 thỏa mãn x1=-3x2
\(x^2-2\left(m+1\right)x+4m=0\)
\(\text{∆}=4\left(m+1\right)^2-16m=4\left(m-1\right)^2\)
để phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt:
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m-1\right)^2>0\Leftrightarrow m\ne1\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{2\left(m+1\right)+2\left(m-1\right)}{2}=2m\\x_2=\dfrac{2\left(m+1\right)-2\left(m-1\right)}{2}=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có:
\(x_1=-3x_2\)
\(\Rightarrow2m=-6\Rightarrow m=-3\left(TM\right)\)
Vậy ...
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho phương trình x2 - (m + 1)x + m + 4 = 0, m là tham số. Tìm m để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt x1 , x2, thỏa mãn \(\sqrt{x_1}+\sqrt{x_2}=2\sqrt{3}\)
\(x^2-\left(m+1\right)x+m+4=0\left(1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta>0\Leftrightarrow\left(m+1\right)^2-4\left(m+4\right)>0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m< -3\\m>5\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\left(2\right)\)
\(ddkt-thỏa:\sqrt{x1}+\sqrt{x2}=2\sqrt{3}\)
\(x1=0\Rightarrow\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow m=-4\Rightarrow\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow x^2+3x=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x1=0\\x2=-3< 0\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x1\ne0\) \(\Rightarrow0< x1< x2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x1+x2>0\\x1x2>0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m+1>0\\m+4>0\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Rightarrow m>-1\)\(\left(3\right)\)
\(\left(2\right)\left(3\right)\Rightarrow m>5\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x1}+\sqrt{x2}=2\sqrt{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x1+x2+2\sqrt{x1x2}=12\Leftrightarrow m+1+2\sqrt{m+4}=12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m+4+2\sqrt{m+4}-15=0\)
\(đặt:\sqrt{m+4}=t>5\Rightarrow t^2+2t-15=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=-5\left(ktm\right)\\t=3\left(ktm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow m\in\phi\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (1)
Để pt có 2 nghiệm pb
\(\left(m+1\right)^2-4\left(m+4\right)=m^2+2m+1-4m-16\)
\(=m^2-2m-15>0\)
Theo Vi et \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=m+1\\x_1x_2=m+4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có : \(\left(\sqrt{x_1}+\sqrt{x_2}\right)^2=12\Leftrightarrow x_1+2\sqrt{x_1x_2}+x_2=12\)
Thay vào ta được \(m+1+2\sqrt{m+4}=12\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{m+4}=11-m\)đk : m >= -4
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(m+4\right)=121-22m+m^2\Leftrightarrow m^2-26m+105=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=21\left(ktm\right);m=5\left(ktm\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
X^2-2(m-1)x-2m=0 a, Tìm m để phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt t/m x1^2+x1-x2=5-2m b,Tìm m để p trình có 2 nghiệm pb t/m x1=3x2 c,Tìm m để phương trình có 2 no pb t/m x1/x2=3
b: x1=3x2 và x1+x2=2m-2
=>3x2+x2=2m-2 và x1=3x2
=>x2=0,5m-0,5 và x1=1,5m-1,5
x1*x2=-2m
=>-2m=(0,5m-0,5)(1,5m-1,5)
=>-2m=0,75(m^2-2m+1)
=>0,75m^2-1,5m+0,75+2m=0
=>\(m\in\varnothing\)
c: x1/x2=3
x1+x2=2m-2
=>x1=3x2 và x1+x2=2m-2
Cái này tương tự câu b nên kết quả vẫn là ko có m thỏa mãn
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)