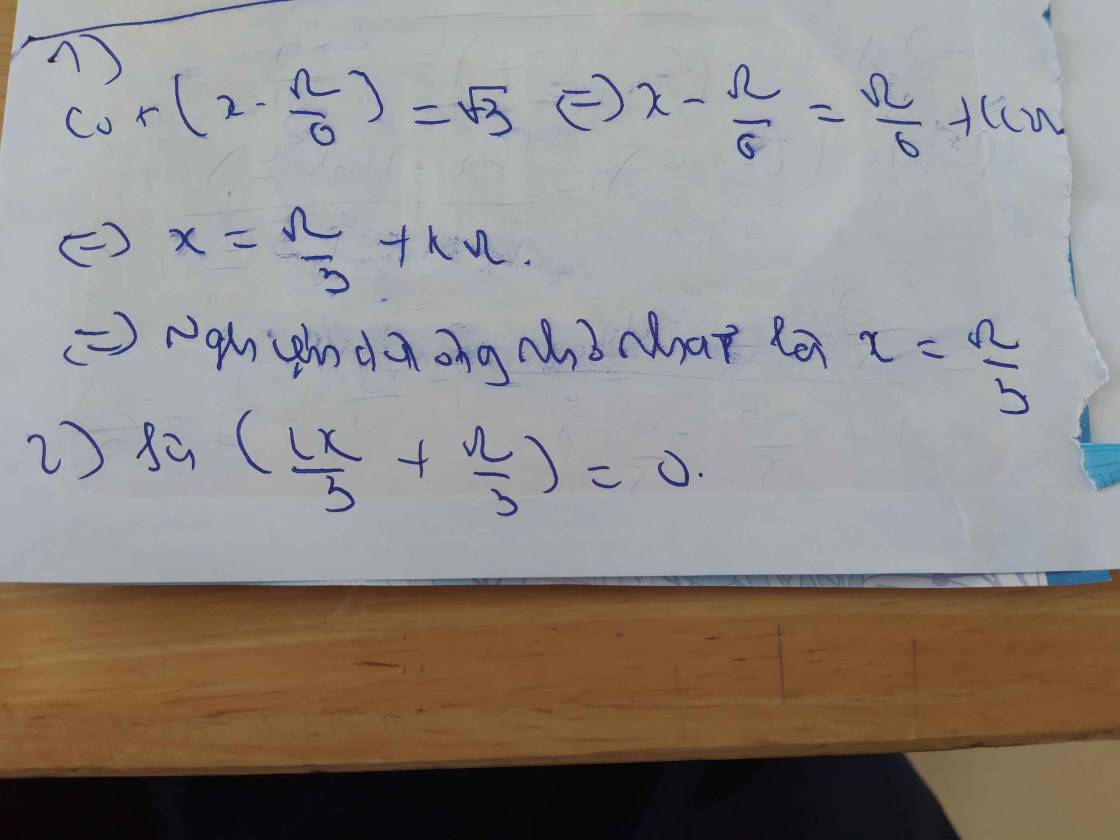Nghiệm lớn nhất của phương trình \(\sqrt{3x^2-9x+1}=\left|x-3\right|\) là...

Những câu hỏi liên quan
giải phương trình :
a, \(\left(x+1\right)\sqrt{x+8}=x^2+x+4\)
b, \(\left(2x+7\right)\sqrt{2x+7}=x^2+9x+7\)
c, \(\left(3x+1\right)\sqrt{x^2+3}=3x^2+2x+3\)
c.
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+3-\left(3x+1\right)\sqrt{x^2+3}+2x^2+2x=0\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{x^2+3}=t>0\)
\(\Rightarrow t^2-\left(3x+1\right)t+2x^2+2x=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(3x+1\right)^2-4\left(2x^2+2x\right)=\left(x-1\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=\dfrac{3x+1-x+1}{2}=x+1\\t=\dfrac{3x+1+x-1}{2}=2x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x^2+3}=x+1\left(x\ge-1\right)\\\sqrt{x^2+3}=2x\left(x\ge0\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2+3=x^2+2x+1\left(x\ge-1\right)\\x^2+3=4x^2\left(x\ge0\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
a.
Đề bài ko chính xác, pt này ko giải được
b.
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge-\dfrac{7}{2}\)
\(2x+7-\left(2x+7\right)\sqrt{2x+7}+x^2+7x=0\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{2x+7}=t\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow t^2-\left(2x+7\right)t+x^2+7x=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(2x+7\right)^2-4\left(x^2+7x\right)=49\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=\dfrac{2x+7-7}{2}=x\\t=\dfrac{2x+7+7}{2}=x+7\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2x+7}=x\left(x\ge0\right)\\\sqrt{2x+7}=x+7\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-2x-7=0\left(x\ge0\right)\\x^2+12x+42=0\left(vn\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow x=1+2\sqrt{2}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình: \(\left(\sqrt{4x^4-12x^3+9x^2+16}-2x^2+3x\right)\left(\sqrt{x+3}+\sqrt{x-1}\right)=8\)
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge1\).
Phương trình đã cho tương đương:
\(\sqrt{x+3}+\sqrt{x-1}=\dfrac{8}{\sqrt{4x^4-12x^3+9x^2+16}-\left(2x^2-3x\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x+3}+\sqrt{x-1}=\dfrac{\sqrt{4x^4-12x^3+9x^2+16}+\left(2x^2-3x\right)}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{4x^4-12x^3+9x^2+16}+\left(2x^2-3x\right)-2\sqrt{x+3}-2\sqrt{x-1}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{4x^4-12x^3+9x^2+16}-2\sqrt{x+3}\right)+\left(2x^2-3x-2\sqrt{x-1}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x^4-12x^3+9x^2-4x+4}{\sqrt{4x^4-12x^3+9x^2+16}+2\sqrt{x+3}}+\dfrac{4x^4-12x^3+9x^2-4x+4}{2x^2-3x+2\sqrt{x-1}}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(4x^3-4x^2+x-2\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{4x^4-12x^3+9x^2+16}+2\sqrt{x+3}}+\dfrac{1}{2x^2-3x+2\sqrt{x-1}}\right)=0\).
Do \(x\ge1\) nên ta có \(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{4x^4-12x^3+9x^2+16}+2\sqrt{x+3}}+\dfrac{1}{2x^2-3x+2\sqrt{x-1}}>0\).
Do đó \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\Leftrightarrow x=2\left(TMĐK\right)\\4x^3-4x^2+x-2=0\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\).
Giải phương trình bậc 3 ở (1) ta được \(x=\dfrac{\sqrt[3]{36\sqrt{13}+53\sqrt{6}}}{\sqrt[6]{279936}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt[6]{7776}\sqrt[3]{36\sqrt{13}+53\sqrt{6}}}+\dfrac{1}{3}\approx1,157298106\left(TMĐK\right)\).
Vậy...
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Vì trong bài làm của mình có một số dòng khá dài nên bạn có thể vào trang cá nhân của mình để đọc tốt hơn!
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a) \(2\left(x^2-2x\right)+\sqrt{x^2-2x-3}-9=0\)
b) \(3\sqrt{2+x}-6\sqrt{2-x}+4\sqrt{4-x^2}=10-3x\)
c) Cho phương trình: \(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{9-x}=\sqrt{-x^2+9x+m}\)
+) Giải phương trình khi m=9
+) Tìm m để phương trình có nghiệm
a, ĐK: \(x\le-1,x\ge3\)
\(pt\Leftrightarrow2\left(x^2-2x-3\right)+\sqrt{x^2-2x-3}-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2\sqrt{x^2-2x-3}+3\right).\left(\sqrt{x^2-2x-3}-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x^2-2x-3}=-\dfrac{3}{2}\left(l\right)\\\sqrt{x^2-2x-3}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-3=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\pm\sqrt{5}\left(tm\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
b, ĐK: \(-2\le x\le2\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{2+x}-2\sqrt{2-x}=t\Rightarrow t^2=10-3x-4\sqrt{4-x^2}\)
Khi đó phương trình tương đương:
\(3t-t^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=0\\t=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2+x}-2\sqrt{2-x}=0\\\sqrt{2+x}-2\sqrt{2-x}=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2+x=8-4x\\2+x=17-4x+12\sqrt{2-x}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{6}{5}\left(tm\right)\\5x-15=12\sqrt{2-x}\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vì \(-2\le x\le2\Rightarrow5x-15< 0\Rightarrow\left(1\right)\) vô nghiệm
Vậy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm \(x=\dfrac{6}{5}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
c, ĐK: \(0\le x\le9\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{9x-x^2}=t\left(0\le t\le\dfrac{9}{2}\right)\)
\(pt\Leftrightarrow9+2\sqrt{9x-x^2}=-x^2+9x+m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(-x^2+9x\right)+2\sqrt{9x-x^2}+9=m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-t^2+2t+9=m\)
Khi \(m=9,pt\Leftrightarrow-t^2+2t=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=0\\t=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}9x-x^2=0\\9x-x^2=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(tm\right)\\x=9\left(tm\right)\\x=\dfrac{9\pm\sqrt{65}}{2}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Phương trình đã cho có nghiệm khi phương trình \(m=f\left(t\right)=-t^2+2t+9\) có nghiệm
\(\Leftrightarrow minf\left(t\right)\le m\le maxf\left(t\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{9}{4}\le m\le10\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Phương trình sqrt{2-fleft(xright)}fleft(xright) có tập nghiệm A {1;2;3}. Phương trình sqrt{2.gleft(xright)-1}+sqrt[3]{3.gleft(xright)-2}2.gleft(xright) có tập nghiệm là B {0;3;4;5} . Hỏi tập nghiệm của phương trình sqrt{fleft(xright)-1}+sqrt{gleft(xright)-1}+fleft(xright).gleft(xright)+1fleft(xright)+gleft(xright)
có bao nhiêu phần tử?
A.1
B.4
C.6
D.7
Đọc tiếp
Phương trình \(\sqrt{2-f\left(x\right)}=f\left(x\right)\) có tập nghiệm A = {1;2;3}. Phương trình \(\sqrt{2.g\left(x\right)-1}+\sqrt[3]{3.g\left(x\right)-2}=2.g\left(x\right)\) có tập nghiệm là B = {0;3;4;5} . Hỏi tập nghiệm của phương trình \(\sqrt{f\left(x\right)-1}+\sqrt{g\left(x\right)-1}+f\left(x\right).g\left(x\right)+1=f\left(x\right)+g\left(x\right)\)
có bao nhiêu phần tử?
A.1
B.4 C.6 D.7
\(\sqrt{2-f\left(x\right)}=f\left(x\right)\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}f\left(x\right)\ge0\\f^2\left(x\right)+f\left(x\right)-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}f\left(x\right)=1\\f\left(x\right)=-2< 0\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(1\right)=f\left(2\right)=f\left(3\right)=1\)
\(\sqrt{2g\left(x\right)-1}+\sqrt[3]{3g\left(x\right)-2}=2.g\left(x\right)\)
\(VT=1.\sqrt{2g\left(x\right)-1}+1.1\sqrt[3]{3g\left(x\right)-2}\)
\(VT\le\dfrac{1}{2}\left(1+2g\left(x\right)-1\right)+\dfrac{1}{3}\left(1+1+3g\left(x\right)-2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow VT\le2g\left(x\right)\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi và chỉ khi \(g\left(x\right)=1\)
\(\Rightarrow g\left(0\right)=g\left(3\right)=g\left(4\right)=g\left(5\right)=1\)
Để các căn thức xác định \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}f\left(x\right)-1\ge0\\g\left(x\right)-1\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có:
\(\sqrt{f\left(x\right)-1}+\sqrt{g\left(x\right)-1}+f\left(x\right).g\left(x\right)-f\left(x\right)-g\left(x\right)+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{f\left(x\right)-1}+\sqrt{g\left(x\right)-1}+\left[f\left(x\right)-1\right]\left[g\left(x\right)-1\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}f\left(x\right)=1\\g\left(x\right)=1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của pt đã cho có đúng 1 phần tử
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(\sqrt{2f^2\left(x\right)+mf\left(x\right)-m-1}=f\left(x\right)-1\). Biết f(x) là hàm số bậc hai và có giá trị lớn nhất là 3. Tìm m để phương trình có 4 nghiệm.
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2t^2+mt-m-1}=t-1\) có 2 nghiệm thỏa mãn \(1\le t< 3\)
\(\Rightarrow2t^2+mt-m-1=t^2-2t+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(t\right)=t^2+\left(m+2\right)t-m-2=0\) có 2 nghiệm \(1< t_1< t_2< 3\) (hiển nhiên \(t=1\) ko là nghiệm)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\Delta=\left(m+2\right)^2+4\left(m+2\right)>0\\f\left(1\right)=1>0\\f\left(3\right)=9+3\left(m+2\right)-m-2>0\\1< \dfrac{t_1+t_2}{2}=\dfrac{-m-2}{2}< 3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(m+2\right)\left(m+6\right)>0\\2m+13>0\\2< -m-2< 6\\\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left[{}\begin{matrix}m>-2\\m< -6\end{matrix}\right.\\m>-\dfrac{13}{2}\\-8< m< -4\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow-\dfrac{13}{2}< m< -6\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1) nghiệm dương nhỏ nhất của phương trình \(cot\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{6}\right)=\sqrt{3}\) là
2) phương trình \(sin\left(\dfrac{2x}{3}+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=0\) có nghiệm là
3) họ nghiệm của phương trình \(cot\)(2x - 30 độ) = \(\sqrt{3}\) là
Cho phương trình \(m^2+m\left(x^2-3x-4-\sqrt{x+7}\right)-\left(x^2-3x-4\right)\sqrt{x+7}=0\) ,với m là tham số.
Có tất cả bao nhiêu số nguyên tố m để phương trình có số nghiệm thực nhiều nhất ?
ĐKXĐ: ...
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2+m\left(x^2-3x-4\right)-m\sqrt{x+7}-\left(x^2-3x-4\right)\sqrt{x+7}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\left(x^2-3x-4+m\right)-\sqrt{x+7}\left(x^2-3x-4+m\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m-\sqrt{x+7}\right)\left(x^2-3x-4+m\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=\sqrt{x+7}\left(1\right)\\m=-x^2+3x+4\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Với \(m\) nguyên tố \(\Rightarrow\) (1) luôn có đúng 1 nghiệm
Để pt có số nghiệm nhiều nhất \(\Rightarrow\) (2) có 2 nghiệm pb
\(\Rightarrow y=m\) cắt \(y=-x^2+3x+4\) tại 2 điểm pb thỏa mãn \(x\ge-7\)
\(\Rightarrow-66\le m\le\dfrac{25}{4}\Rightarrow m=\left\{2;3;5\right\}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:
a. \(\sqrt{25x+75}+3\sqrt{x-2}=2\sqrt{x-2}+\sqrt{9x-18}\)
b. \(\sqrt{\left(2x-1\right)^2}=4\)
c. \(\sqrt{\left(2x+1\right)^2}=3x-5\)
d. \(\sqrt{4x-12}-14\sqrt{\dfrac{x-2}{49}}=\sqrt{9x-18}+8\)
a) Ta có: \(\sqrt{25x+75}+3\sqrt{x-2}=2\sqrt{x-2}+\sqrt{9x-18}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5\sqrt{x+3}+3\sqrt{x-2}=2\sqrt{x-2}+3\sqrt{x-2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{25x+75}=\sqrt{4x-8}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow25x-4x=-8-75\)
\(\Leftrightarrow21x=-83\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{83}{21}\)
b) Ta có: \(\sqrt{\left(2x-1\right)^2}=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|2x-1\right|=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-1=4\\2x-1=-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=5\\2x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) Ta có: \(\sqrt{\left(2x+1\right)^2}=3x-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|2x+1\right|=3x-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=3x-5\left(x\ge-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\\2x+1=5-3x\left(x< \dfrac{1}{2}\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-3x=-5-1\\2x+3x=5-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\left(nhận\right)\\x=\dfrac{4}{5}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
d) Ta có: \(\sqrt{4x-12}-14\sqrt{\dfrac{x-2}{49}}=\sqrt{9x-18}+8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{x-3}-2\sqrt{x-2}=3\sqrt{x-2}+8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{x-3}-5\sqrt{x-2}=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(x-3\right)+25\left(x-2\right)-20\sqrt{x^2-5x+6}=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x-12+25x-50-8=20\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow20\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}=29x-70\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+6=\dfrac{\left(29x-70\right)^2}{400}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+6=\dfrac{841}{400}x^2-\dfrac{203}{20}x+\dfrac{49}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-441}{400}x^2+\dfrac{103}{20}x-\dfrac{25}{4}=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(\dfrac{103}{20}\right)^2-4\cdot\dfrac{-441}{400}\cdot\dfrac{-25}{4}=-\dfrac{26}{25}\)(Vô lý)
vậy: Phương trình vô nghiệm
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(\text{Chứng minh phương trình sau vô nghiệm với }x\ne0\)
\(\frac{9x^2}{\sqrt[3]{\left(3x+2\right)^2}+2\sqrt[3]{3x+2}+4}+x^2+8x+4=0\)