Giải phương trình:
(x2+2x-2)2+2(x2+2x-2)=x+2
Giải các phương trình sau bằng cách đặt ẩn phụ:
a) (x2 -2x)2 +2(x-1)2=1
b) (x2+x+2)(x2+2x+2)=20x2
a: =>(x^2-2x+1-1)^2+2(x-1)^2=1
=>(x-1)^4-2(x-1)^2+1+2(x-1)^2=1
=>(x-1)^4=0
=>x-1=0
=>x=1
b: =>(x^2+2)^2+3x(x^2+2)+2x^2-20x^2=0
=>(x^2+2)^2+3x(x^2+2)-18x^2=0
=>(x^2+2+6x)(x^2-3x+2)=0
=>\(x\in\left\{-3\pm\sqrt{7};1;2\right\}\)
giải các phương trình sau:
a)(x+2)(x2-2x+4)-x(x2-2)=15
b)x(x-5)(x+5)-(x+2)(x2-2x+4)=3
\(a,=>x^3-2x^2+4x+2x^2-4x+8-x^3+2x-15=0\)
\(< =>2x-7=0< =>x=\dfrac{7}{2}\)
b,\(=>x\left(x^2-25\right)-\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)-3=0\)
\(< =>x^3-25x-x^3+2x^2-4x-2x^2+4x-8-3=0\)
\(< =>-25x-11=0\)
\(< =>x=-0,44\)
Giải các phương trình sau:
b) (2x+1)2-2x-1=2
c) (x2-3x)2+5(x2-3x)+6=0
d) (x2-x-1)(x2-x)-2=0
tham khảo
https://hoidapvietjack.com/q/57243/giai-cac-phuong-trinh-sau-a-2x12-2x-12-b-x2-3x-2-5x2-3x60
b) (2x+1)2-2x-1=2
\(< =>4x^2+4x+1-2x-1=2\)
\(< =>4x^2+2x-2=0\)
\(< =>4x^2+4x-2x-2=0\)
\(< =>\left(4x^2+4x\right)-\left(2x+2\right)=0\)
\(< =>4x\left(x+1\right)-2\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(< =>\left(x+1\right)\left(4x-2\right)=0\)
\(=>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0=>x=-1\\4x-2=0=>x=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy....
b) (2x+1)2-2x-1=2
<=>4x2+4x+1−2x−1=2
<=>4x2+2x−2=0
<=>4x2+4x−2x−2=0
<=>(4x2+4x)−(2x+2)=0
<=>4x(x+1)−2(x+1)=0
<=>(x+1)(4x−2)=0
Giải phương trình:
(x2-1)3+(x2+2)3+(2x-1)3+(3x+3)(2x-1)(1-x)(x2+2)=0
Lời giải:
PT $\Leftrightarrow (x^2-1)^3+(x^2+2)^3+(2x-1)^3-3(x^2-1)(x^2+2)(2x-1)=0$
Đặt $x^2-1=a; x^2+2=b; 2x-1=c$ thì pt trở thành:
$a^3+b^3+c^3-3abc=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a+b)^3+c^3-3ab(a+b)-3abc=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a+b+c)[(a+b)^2-c(a+b)+c^2]-3ab(a+b+c)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a+b+c)(a^2+b^2+c^2-ab-bc-ac)=0$
$\Rightarrow a+b+c=0$ hoặc $a^2+b^2+c^2-ab-bc-ac=0$
Nếu $a+b+c=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2-1+x^2+2+2x-1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x^2+2x=0$
$\Rightarrow x=0$ hoặc $x=-1$
Nếu $a^2+b^2+c^2-ab-bc-ac=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a-b)^2+(b-c)^2+(c-a)^2=0$
$\Rightarrow a-b=b-c=c-a=0$ (dễ CM)
$\Leftrightarrow a=b=c$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2-1=x^2+2=2x-1$ (vô lý)
Vậy..........
Bài 1: Giải các bất phương trình sau
a) x+1/x+3 > 1
b) 2x-1/x-3 ≤ 2
c) x2+2x+2/x2+3 ≥ 1
d) 2x+1/x2+2 ≥ 1
a, \(\dfrac{x+1}{x+3}>1\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x+1}{x+3}-1>0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x+1-x-3}{x+3}>0\)
\(\Rightarrow x+3< 0\)do -2 < 0
\(\Rightarrow x< -3\)Vậy tập nghiệm BFT là S = { x | x < -3 }
b, \(\dfrac{2x-1}{x-3}\le2\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x-1}{x-3}-2\le0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x-1-2x+6}{x-3}\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow x-3\le0\)do 5 > 0
\(\Rightarrow x\le3\)Vậy tập nghiệm BFT là S = { x | x \(\le\)3 }
c, \(\dfrac{x^2+2x+2}{x^2+3}\ge1\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2+2x+2}{x^2+3}-1\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2+2x+2-x^2-3}{x^2+3}\ge0\Rightarrow2x-1\ge0\)do x^2 + 3 > 0
\(\Rightarrow x\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\)Vậy tập nghiệm BFT là S = { x | x \(\ge\)1/2 }
mình ko chắc nên mình đăng sau :>
d, \(\dfrac{2x+1}{x^2+2}\ge1\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x+1}{x^2+2}-1\ge0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x+1-x^2-2}{x^2+2}\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow-x^2+2x-1\ge0\Rightarrow-\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0\)vô lí
Giải phương trình bằng cách đưa về phương trình tích:
(x2 + 2x – 5)2 = (x2 – x + 5)2
(x2 + 2x – 5)2 = (x2 – x + 5)2
⇔ (x2 + 2x – 5)2 – (x2 – x + 5)2 = 0
⇔ [(x2 + 2x – 5) – (x2 – x + 5)].[(x2 + 2x – 5) + (x2 – x + 5)] = 0
⇔ (3x – 10)(2x2 + x ) = 0
⇔ (3x-10).x.(2x+1)=0
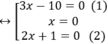
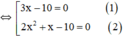
+ Giải (1): 3x – 10 = 0 ⇔ 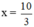
+ Giải (2):
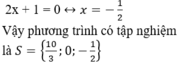
Giải bất phương trình sau
(x+2)(x2-2x+4)-x(x2+2)> hoặc = 5
=>x^3+8-x^3-2x>=5
=>-2x>=-3
=>x<=3/2
Giải các bất phương trình sau
a) (x2+2)2-(x+2)(x-2)(x2+4)-4x(x+1)< hoặc = 20
b) (x+2)(x2-2x+4)-x(x2+2)> hoặc = 15
a) \(\left(x^2+2\right)^2-\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+4\right)-4x\left(x+1\right)\le20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+4x^2+4-x^4+16-4x^2-4x\le20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^4-x^4\right)+\left(4x^2-4x^2\right)-4x+4+16\le20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x+20\le20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x\le20-20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x:-4\ge0:-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge0\)
Vậy nghiệm của bất phương trình là: \(x\ge0\)
b) \(\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)-x\left(x^2+2\right)\ge15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+8-x^3-2x\ge15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^3-x^3\right)+8-2x\ge15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8-2x\ge15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x\ge15-8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x\ge7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x:-2\le7:-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\le-\dfrac{7}{2}\)
Vậy nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(x\le-\dfrac{7}{2}\)
a: =>x^4+4x^2+4-x^4+16-4x^2-4x<=20
=>-4x+20<=20
=>-4x<=0
=>x>=0
b: =>x^3+8-x^3-2x>=15
=>-2x>=7
=>x<=-7/2
Giải phương trình: 20 ( x - 2 x + 1 ) 2 - 5 ( x + 2 x - 1 ) 2 + 48 x 2 - 4 x 2 - 1 = 0 ta được các nghiệm x 1 , x 2 với x 1 < x 2 . Tính 3 x 1 - x 2
A. 25 3
B. -1
C. - 7 3
D. 1
1. Giải phương trình :
a) ( x - 3 )2 = 4
b) x2( x2 + 1 ) = 0
c) ( 3x - 5 )2 - ( x - 1 )2 = 0
d) ( x2 - 1)( 2x - 1 ) = ( x2 - 1 )( x + 3 )
a: =>x-3=2 hoặc x-3=-2
=>x=5 hoặc x=1
b: =>x2=0
hay x=0
c: =>(3x-5-x+1)(3x-5+x-1)=0
=>(2x-4)(4x-6)=0
=>x=2 hoặc x=3/2
d: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(2x-1-x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;-1;4\right\}\)
\(a,\left(x-3\right)^2=4\\\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)^2-2^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow \left(x-3-2\right).\left(x-3+2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right).\left(x-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\\\Rightarrow S=\left\{1;5\right\}\\ b,x^2.\left(x^2+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2=0\\x^2+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x^2=-1\left(vô.lí\right)\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow S=\left\{0\right\}\\ c,\left(3x-5\right)^2-\left(x-1\right)^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x-5-x+1\right).\left(3x-5+x-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x-4\right).\left(4x-6\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2.\left(x-2\right).2.\left(2x-3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\2x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow S=\left\{\dfrac{3}{2};2\right\}\)
\(d,\left(x^2-1\right).\left(2x-1\right)=\left(x^2-1\right).\left(x+3\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-1\right).\left(2x-1-x-3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-1\right).\left(x-4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right).\left(x+1\right).\left(x-4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x+1=0\\x-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-1\\x=4\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow S=\left\{-1;1;4\right\}\)