Giải các phương trình sau:
a) (x + 2)2 - (x - 1)(x + 1) = -1
b) 9x2 - 16 - x(3x + 16) = 0
1) Giải các phương trình sau : a) x-3/x=2-x-3/x+3 b) 3x^2-2x-16=0 2) Giải bất phương trình sau: 4x-3/4>3x-5/3-2x-7/12
\(a,\dfrac{x-3}{x}=\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}\)\(\left(đk:x\ne0,-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-3}{x}-\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-x\left(x-3\right)}{x\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9-x^2+3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(n\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
\(b,\dfrac{4x-3}{4}>\dfrac{3x-5}{3}-\dfrac{2x-7}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x-3}{4}-\dfrac{3x-5}{3}+\dfrac{2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(4x-3\right)-4\left(3x-5\right)+2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-9-12x+20+2x-7>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+4>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x>-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-2\)
Bài 2. Giải các phương trình sau. a) 3x - 2sqrt(x - 1) = 4 b) sqrt(4x + 1) - sqrt(x + 2) = sqrt(3 - x) c) (sqrt(x - 1) - sqrt(5 - x))(|10 - x| + 2x - 16) = 0
a) \(3x-2\sqrt{x-1}=4\) (ĐK: x ≥ 1)
\(\Rightarrow3x-2\sqrt{x-1}-4=0\)
\(\Rightarrow3x-6-2\sqrt{x-1}+2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow3\left(x-2\right)-2\left(\sqrt{x-1}-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow3\left(x-2\right)-2.\dfrac{x-2}{\sqrt{x-1}+1}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left[3-\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x-1}+1}\right]=0\)
*TH1: x = 2 (t/m)
*TH2: \(3-\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x-1}+1}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow3=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x-1}+1}\)
\(\Rightarrow3\sqrt{x-1}+3=2\)
\(\Rightarrow3\sqrt{x-1}=-1\) (vô lí)
Vậy S = {2}
b) \(\sqrt{4x+1}-\sqrt{x+2}=\sqrt{3-x}\) (ĐK: \(-\dfrac{1}{4}\le x\le3\) )
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{4x+1}-3-\sqrt{x+2}+2-\sqrt{3-x}+1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{4x-8}{\sqrt{4x+1}+3}-\dfrac{x-2}{\sqrt{x+2}+2}+\dfrac{x-2}{\sqrt{3-x}+1}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{4x+1}+3}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x+2}+2}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3-x}+1}\right)=0\)
=> x = 2
\(a,3x-2\sqrt{x-1}=4\left(x\ge1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow-2\sqrt{x-1}=4-3x\\ \Leftrightarrow4\left(x-1\right)=16-24x+9x^2\\ \Leftrightarrow9x^2-28x+20=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(9x-10\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\left(tm\right)\\x=\dfrac{10}{9}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,\sqrt{4x+1}-\sqrt{x+2}=\sqrt{3-x}\left(-\dfrac{1}{4}\le x\le3\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow4x+1+x+2-2\sqrt{\left(4x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}=3-x\\ \Leftrightarrow-2\sqrt{\left(4x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}=2-6x\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{4x^2+9x+2}=3x-1\\ \Leftrightarrow4x^2+9x+2=9x^2-6x+1\\ \Leftrightarrow5x^2-15x-1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\Delta=225+20=245\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{15-\sqrt{245}}{10}=\dfrac{15-7\sqrt{5}}{10}\left(ktm\right)\\x=\dfrac{15+\sqrt{245}}{10}=\dfrac{15+7\sqrt{5}}{10}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{15+7\sqrt{5}}{10}\)
Giải phương trình:
a) 5 + 96/x2-16 = 2x-1/x+4 - 3x-1/4-x
b) 3x+2/3x-2 - 6/2+3x = 9x2/9x2-44
c) 1/x-1 + 1/x+1 = 2/x+2
d) x+1/x-2 - 5/x+2 = 12/x2-4 + 1
b: \(\Leftrightarrow9x^2+12x+4-18x+12=9x^2\)
=>-6x+16=0
=>-6x=-16
hay x=8/3(nhận)
c: \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x+1+x-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2}{x+2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x+2\right)=2\left(x^2-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+4x-2x^2+2=0\)
=>4x+2=0
hay x=-1/2(nhận)
Giải các phương trình sau
a) ( 4x - 1 ) (x - 3) - ( x - 3 ) ( 5x + 2 ) = 0
b) ( x + 3 ) ( x - 5 ) + ( x + 3 ) ( 3x - 4) = 0
c) ( x + 6 ) ( 3x - 1 )+ x2 - 36 = 0
d) ( x + 4 ) ( 5x + 9 ) - x2 + 16 = 0
a) ( 4x - 1 ) (x - 3) - ( x - 3 ) ( 5x + 2 ) = 0
<=> (x - 3)(4x - 1 - 5x - 2) = 0
<=> (x - 3)(-x - 3) = 0
<=> x = 3 hoặc x = -3
b) ( x + 3 ) ( x - 5 ) + ( x + 3 ) ( 3x - 4) = 0
<=> (x + 3)(x - 5 + 3x - 4) = 0
<=> (x + 3)(4x - 9) = 0
<=> x = -3 hoặc x = 9/4
c) ( x + 6 ) ( 3x - 1 )+ x2 - 36 = 0
<=> 3x^2 + 17x - 6 + x^2 - 36 = 0
<=> 4x^2 + 17x - 42 = 0
<=> 4x^2 + 24x - 7x - 42 = 0
<=> 4x(x + 6) - 7(x + 6) = 0
<=> (4x - 7)(x + 6) = 0
<=> x = -6 hoặc x = 7/4
d) ( x + 4 ) ( 5x + 9 ) - x2 + 16 = 0
<=> 5x^2 + 29x + 36 - x^2 + 16 = 0
<=> 4x^2 + 29x + 52 = 0
<=> 4x^2 + 16x + 13x + 42 = 0
<=> 4x(x + 4) + 13(x + 4) = 0
<=> (4x + 13)(x + 4) = 0
<=> x = -13/4 và x = -4
1.Giải các phương trình sau:
a) 2x2 +16 -6 = 4\(\sqrt{x\left(x+8\right)}\)
b) x4 -8x2 + x-2\(\sqrt{x-1}\) + 16=0
2. Gọi x1;x2 là nghiệm phương trình x2 -3x -7 =0. Không giải phương trình tính các giá trị của biểu thức sau:
A = \(\dfrac{1}{x_1-1}+\dfrac{1}{x_2-1}\)
B= \(x^2_1+x_2^2\)
C= |x1 - x2|
D= \(x_1^4+x_2^4\)
E= (3x1 + x2) (3x2 + x1)
2:
\(A=\dfrac{x_2-1+x_1-1}{x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{3-2}{-7-3+1}=\dfrac{1}{-9}=\dfrac{-1}{9}\)
B=(x1+x2)^2-2x1x2
=3^2-2*(-7)
=9+14=23
C=căn (x1+x2)^2-4x1x2
=căn 3^2-4*(-7)=căn 9+28=căn 27
D=(x1^2+x2^2)^2-2(x1x2)^2
=23^2-2*(-7)^2
=23^2-2*49=431
D=9x1x2+3(x1^2+x2^2)+x1x2
=10x1x2+3*23
=69+10*(-7)=-1
giải phương trình sau:
a)4x-10.2x+16=0
b) (2x2-3x-1)2-3(2x2-3x-5)-16=0
a, Đặt \(2^x=t,t>0\)
Pt trở thành: \(t^2-10t+16=0\Leftrightarrow\left(t-2\right)\left(t-8\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}t=2\\t=8\end{cases}\left(tm\right)}\)
Nếu t=2 => x=1
nếu t=8=> x=3
Vậy x=...
b, Đặt: \(2x^2-3x-1=t\)
pt trở thành: \(t^2-3\left(t-4\right)-16=0\Leftrightarrow t^2-3t-4=0\Leftrightarrow\left(t+1\right)\left(t-4\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}t=-1\\t=4\end{cases}}\)
* Nếu t=-1 <=> \(2x^2-3x-1=-1\Leftrightarrow x\left(2x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=\frac{3}{2}\end{cases}}\)
* Nếu t=4 <=> \(2x^2-3x-1=4\Leftrightarrow2x^2-3x-5=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(2x-5\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-1\\x=\frac{5}{2}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy x=...
Giải các bất phương trình sau
a) 5x(x-3)2-5(x-1)3+15(x-4)(x+4)< hoặc = 10
b) (3x-2)(9x2+6x+4)+27x(\(\dfrac{1}{3}\)-x)(\(\dfrac{1}{3}\)+x)> hoặc = 1
a) \(5x\left(x-3\right)^2-5\left(x-1\right)^3+15\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)\le10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x\left(x^2-6x+9\right)-5\left(x^3-3x^2+3x-1\right)+15\left(x^2-16\right)\le10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x^3-30x^2+45x-5x^3+15x^2-15x+5+15x^2-240\le10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(5x^3-5x^3\right)-\left(30x^2-15x^2-15x^2\right)-\left(45x-15x\right)+5-240\le10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow30x-235\le10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow30x\le10+235\)
\(\Leftrightarrow30x\le245\)
\(\Leftrightarrow30x:30\le245:30\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\le\dfrac{49}{6}\)
Vậy nghiệm của bất phương trình là: \(x\le\dfrac{49}{6}\)
b) \(\left(3x-2\right)\left(9x^2+6x+4\right)+27x\left(\dfrac{1}{3}-x\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{2}+x\right)\ge1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow27x^3-8+27x\left(\dfrac{1}{9}-x^2\right)\ge1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow27x^3-8+3x-27x^3\ge1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(27x^3-27x^3\right)-8+3x\ge1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-8+3x\ge1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\ge1+8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\ge9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x:3\ge9:3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge3\)
Vậy nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(x\ge3\)
a: =>5x(x^2-6x+9)-5(x^3-3x^2+3x-1)+15(x^2-16)<=10
=>5x^3-30x^2+45x-5x^3+15x^2-15x+5+15x^2-240<=10
=>30x-235<=10
=>30x<=245
=>x<=49/6
b: =>27x^3-8+27x(1/9-x^2)>=1
=>27x^3-8+3x-27x^3>=1
=>3x>=9
=>x>=3
giải các phương trình sau:
a)x/2(x-3)+x/2(x+1)=2x/(x=1)(x-3)
b)5+76/x^2-16=2x-1/x+4-3x-1/4-x
khó gì fan gao bạc
Giải các phương trình sau
a)(9x2-4)(x+1)=(3x+2)(x2-1)
b) (x-1)2-1+x2=(1-x)(x+3)
a)
\(\left(9x^2-4\right)\left(x+1\right)=\left(3x+2\right)\left(x^2-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(9x^2-4\right)\left(x+1\right)=\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(9x^2-4\right)\left(x+1\right)-\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left[9x^2-4-\left[\left(3x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\right]\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left[9x^2-4-\left(3x^2-3x+2x-2\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(9x^2-4-3x^2+3x-2x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(6x^2+x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0\\6x^2+x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\\left(2x-1\right)\left(3x+2\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=\dfrac{-2}{3}\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{1;\dfrac{-2}{3};\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
b)
\(\left(x-1\right)^2-1+x^2=\left(1-x\right)\left(x+3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1-1+x^2=x+3-x^2-3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-2x=x^2-2x+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\left(\pm1\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
Giải các bất phương trình sau:
a) \(2{x^2} + 3x + 1 \ge 0\)
b) \( - 3{x^2} + x + 1 > 0\)
c) \(4{x^2} + 4x + 1 \ge 0\)
d) \( - 16{x^2} + 8x - 1 < 0\)
e) \(2{x^2} + x + 3 < 0\)
g) \( - 3{x^2} + 4x - 5 < 0\)
a) \(2{x^2} + 3x + 1 \ge 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = 2{x^2} + 3x + 1\) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt \(x = - 1,x = \frac{{ - 1}}{2}\)
hệ số \(a = 2 > 0\)
Ta có bảng xét dấu f(x) như sau:
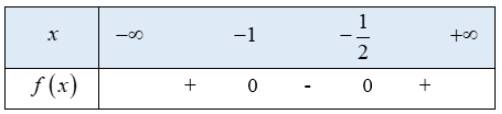
Từ bảng xét dấu ta thấy \(f\left( x \right) \ge 0 \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l}x \le - 1\\x \ge - \frac{1}{2}\end{array} \right.\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(\left( { - \infty ; - 1} \right] \cup \left[ { - \frac{1}{2}; + \infty } \right)\)
b) \( - 3{x^2} + x + 1 > 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = - 3{x^2} + x + 1\) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt \(x = \frac{{1 - \sqrt {13} }}{6},x = \frac{{1 + \sqrt {13} }}{6}\)
Hệ số \(a = - 3 < 0\)
Ta có bảng xét dấu f(x) như sau:

Từ bảng xét dấu ta thấy \(f\left( x \right) > 0\)\( \Leftrightarrow \frac{{1 - \sqrt {13} }}{6} < x < \frac{{1 + \sqrt {13} }}{6}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(\left( {\frac{{1 - \sqrt {13} }}{6};\frac{{1 + \sqrt {13} }}{6}} \right)\)
c) \(4{x^2} + 4x + 1 \ge 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = 4{x^2} + 4x + 1\) có nghiệm duy nhất \(x = \frac{{ - 1}}{2}\)
hệ số \(a = 4 > 0\)
Ta có bảng xét dấu f(x) như sau:

Từ bảng xét dấu ta thấy \(f\left( x \right) \ge 0 \Leftrightarrow x \in \mathbb{R}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(\mathbb{R}\)
d) \( - 16{x^2} + 8x - 1 < 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = - 16{x^2} + 8x - 1\) có nghiệm duy nhất \(x = \frac{1}{4}\)
hệ số \(a = - 16 < 0\)
Ta có bảng xét dấu f(x) như sau:
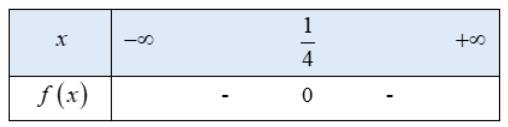
Từ bảng xét dấu ta thấy \(f\left( x \right) < 0 \Leftrightarrow x \ne \frac{1}{4}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(\mathbb{R}\backslash \left\{ {\frac{1}{4}} \right\}\)
e) \(2{x^2} + x + 3 < 0\)
Ta có \(\Delta = {1^2} - 4.2.3 = - 23 < 0\) và có \(a = 2 > 0\)
Sử dụng định lí về dấu của tam thức bậc hai, ta thấy tập hợp những giá trị của x sao cho \(2{x^2} + x + 3\) mang dấu “-” là \(\emptyset \)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình \(2{x^2} + x + 3 < 0\) là \(\emptyset \)
g) \( - 3{x^2} + 4x - 5 < 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = - 3{x^2} + 4x - 5\) có \(\Delta ' = {2^2} - \left( { - 3} \right).\left( { - 5} \right) = - 11 < 0\) và có \(a = - 3 < 0\)
Sử dụng định lí về dấu của tam thức bậc hai, ta thấy tập hợp những giá trị của x sao cho \( - 3{x^2} + 4x - 5\) mang dấu “-” là \(\mathbb{R}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình \( - 3{x^2} + 4x - 5 < 0\) là \(\mathbb{R}\)