Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên:
y2 -x(x+1)(x+2)(x+3)=-1

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên: (y2+1)(2x2+x+1)=x+5
Do \(2x^2+x+1>0;\forall x\) nên pt tương đương:
\(y^2+1=\dfrac{x+5}{2x^2+x+1}\)
Ta có: \(6-\dfrac{x+5}{2x^2+x+1}=\dfrac{12x^2+5x+1}{2x^2+x+1}=\dfrac{12\left(x+\dfrac{5}{24}\right)^2+\dfrac{23}{48}}{2\left(x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{7}{8}}>0\) ; \(\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x+5}{2x^2+x+1}< 6\Rightarrow y^2+1< 6\)
\(\Rightarrow y^2< 5\) \(\Rightarrow y^2=\left\{0;1;4\right\}\)
- Với \(y^2=0\Rightarrow y=0\Rightarrow2x^2+x+1=x+5\Rightarrow x^2=2\) (ko tồn tại x nguyên thỏa mãn) \(\Rightarrow\) loại
- Với \(y^2=1\Rightarrow2\left(2x^2+x+1\right)=x+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2+x-3=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=\dfrac{3}{4}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
- Với \(y^2=4\Rightarrow5\left(2x^2+x+1\right)=x+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow10x^2+4x=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-\dfrac{2}{5}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy pt có 4 cặp nghiệm nguyên:
\(\left(x;y\right)=\left(-1;-1\right);\left(-1;1\right);\left(0;-2\right);\left(0;2\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên : x2-x=y2-1
help me
1, giải phương tình nghiệm nguyên dương x^2y+x+y=xy^2z+yz+7z
2,giải phương trình nghiệm tự nhiên 2^x+3^y=z^2
3,giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên dương x^2+x+1=xyz-z
giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên X^3 + (X+1)^3 +(X+2)^3=(X+3)^2
\(x^3+\left(x+1\right)^3+\left(x+2\right)^3=\left(x+3\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+x^3+2x^2+x+x^2+2x+1+x^3+4x^2+4x+2x^2+8x+8=x^2+6x+9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2+9x^2+15x+9=x^2+6x+9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2+9x^2+15x=x^2+6x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^3+9x^2+15x-x^2-6x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^3+8x^2+9x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x^2+8x+9\right)=0\)
mà vì \(3x^2+8x+9>0\) , nên:
x = 0
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
bạn làm số bị sai xem lại nhé nhưng cách của bạn thì làm dúng r
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên 1/x + 1/y = 1/2
Giải phương trình x^2+1/x^2 ++ 1/y^2 + y^2 = 4
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{y+x}{xy}=\frac{1}{2}\)
=>\(\frac{x+y}{xy}-\frac{1}{2}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{-\left(x-2\right)y-2x}{2xy}=0\)
=>(x-2)y-2x=0
=>x-2=0( vì x-2=0 thì nhân y-2x ms =0 )
=>x=2
=>y-2=0
=>y=2
vậy x=y=2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a) Tìm nghiệm nguyên của phương trình: \(2y^2-x+2xy=y+4\)
b) Giải phương trình : ( \(1+x\sqrt{x^2+1}\))(\(\sqrt{x^2+1}-x\)) = 1
\(\left(1+x\sqrt{x^2+1}\right)\left(\sqrt{x^2+1}-x\right)=1\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1+x\sqrt{x^2+1}}{\sqrt{x^2+1}+x}=1\)
\(\Rightarrow1+x\sqrt{x^2+1}=\sqrt{x^2+1}+x\)
\(\Rightarrow1+x\sqrt{x^2+1}-\sqrt{x^2+1}-x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow-\left(x-1\right)+\left(x-1\right)\sqrt{x^2+1}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x^2+1}-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\\sqrt{x^2+1}-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\\sqrt{x^2+1}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x^2+1=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(a,2y^2-x+2xy=y+4\\ \Leftrightarrow2y\left(x+y\right)-\left(x+y\right)=4\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2y-1\right)\left(x+y\right)=4=4\cdot1=\left(-4\right)\left(-1\right)=\left(-2\right)\left(-2\right)=2\cdot2\)
Vì \(x,y\in Z\Leftrightarrow2y-1\) lẻ
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2y-1=1\\x+y=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2y-1=-1\\x+y=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy PT có nghiệm \(\left(x;y\right)=\left\{\left(3;1\right);\left(4;0\right)\right\}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên: y = \(\dfrac{x^2-x+1}{x^2+x+1}\)
Các bn giải theo phương pháp sử dụng đk có nghiệm của phương trình bậc hai giúp mk ạ!
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
mình có 1 cách khác nữa:
vì y ∈ Z nên \(\dfrac{x^2-x+1}{x^2+x+1}\) ∈ Z
=>x2-x+1⋮x2+x+1=> x2+x+1 -2x ⋮x2+x+1
=>2x⋮x2+x+1 (1)
Xét hiệu (x2+x+1)-2x=(x-\(\dfrac{1}{2}\))2+\(\dfrac{3}{4}\)>0
=>x2+x+1 > 2x (2)
Từ (1) và (2) kết hợp với 2x và x2+x+1 ∈ Z
=> 2x =0 => x =0 => y=1
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm (x,y) là (0,1)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên: x+y+xy=x2+y2
\(x+y+xy=x^2+y^2\)
⇔ \(2xy+2x+2y=2x^2+2y^2\)
⇔ \(\left(x^2+y^2-2xy\right)+\left(x^2-2x+1\right)+\left(y^2-2y+1\right)=2\)
⇔ \(\left(x-y\right)^2+\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(y-1\right)^2=2\)
⇔ 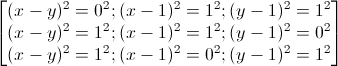
⇔ 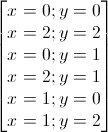
Các cặp số nguyên (x, y) thỏa mãn phương trình là : (0; 0); (2; 2); (0; 1); (2; 1); (1; 0);(1;2).
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên:
x(x+1)(x+2)(x+3)=y3(y+3)
Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên dương : x^2 + x - 1 = 3^(2y+1)
Help !!
























