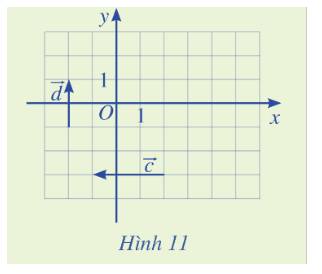
Tìm tọa độ của các vecto \(\overrightarrow c ,\overrightarrow d \) trong Hình 11.
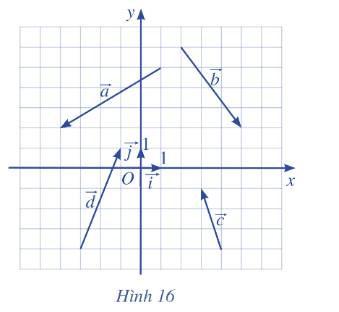
Tìm tọa độ của các vecto trong Hình 16 và biểu diễn mỗi vecto đó qua hai vecto \(\overrightarrow i , \overrightarrow j \)
a) Vẽ các vecto \(\overrightarrow {OA} = \overrightarrow a ,\overrightarrow {OB} = \overrightarrow b ,\overrightarrow {OC} = \overrightarrow c ,\overrightarrow {OD} = \overrightarrow d \)
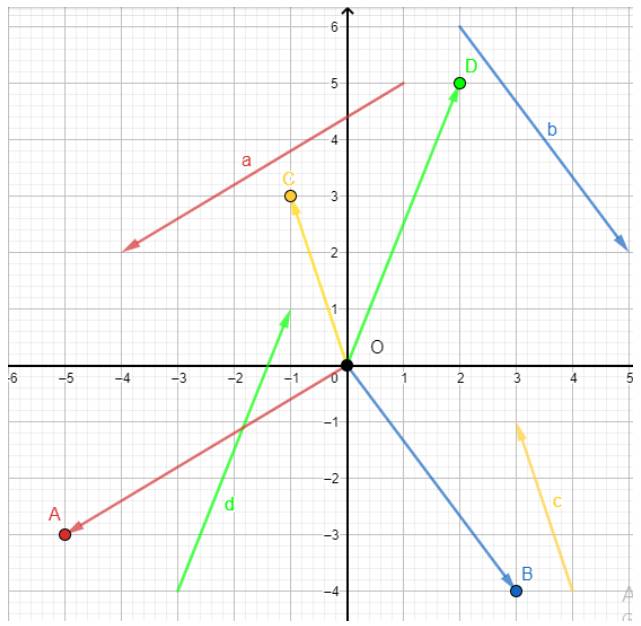
Dựa vào hình vẽ, ta thấy tọa độ của 4 điểm A, B, C, D là:
\(A\left( { - 5; - 3} \right),B\left( {3; - 4} \right),C\left( { - 1;3} \right),D\left( {2;5} \right)\)
Do đó \(\overrightarrow a = \overrightarrow {OA} = \left( { - 5; - 3} \right),\overrightarrow b = \overrightarrow {OB} = \left( {3; - 4} \right),\overrightarrow c = \overrightarrow {OC} = \left( { - 1;3} \right),\overrightarrow d = \overrightarrow {OD} = \left( {2;5} \right)\)
b) Vì \(\overrightarrow a = \overrightarrow {OA} = \left( { - 5; - 3} \right)\)nên \(\overrightarrow a = \left( { - 5} \right)\overrightarrow i + \left( { - 3} \right)\overrightarrow j = - 5\overrightarrow i - 3\overrightarrow j \)
Vì \(\overrightarrow b = \overrightarrow {OB} = \left( {3; - 4} \right)\) nên \(\overrightarrow b = 3\overrightarrow i + \left( { - 4} \right)\overrightarrow j = 3\overrightarrow i - 4\overrightarrow j \)
Vì \(\overrightarrow c = \overrightarrow {OC} = \left( { - 1;3} \right)\) nên \(\overrightarrow c = \left( { - 1} \right)\overrightarrow i + \left( 3 \right)\overrightarrow j = - \overrightarrow i + 3\overrightarrow j \)
Vì \(\overrightarrow d = \overrightarrow {OD} = \left( {2;5} \right)\) nên \(\overrightarrow d = 2\overrightarrow i + 5\overrightarrow j \)
Tìm tọa độ của các vecto sau:
a) \(\overrightarrow a = 3\overrightarrow i \) b) \(\overrightarrow b = - \overrightarrow j \)
c) \(\overrightarrow c = \overrightarrow i - 4\overrightarrow j \) d) \(\overrightarrow d = 0,5\overrightarrow i + \sqrt 6 \overrightarrow j \)
a) Vì \(\overrightarrow a = 3\overrightarrow i \)nên \(\overrightarrow a = \left( {3;0} \right)\)
b) Vì \(\overrightarrow b = - \overrightarrow j \)nên \(\overrightarrow b = \left( {0; - 1} \right)\)
c) Vì \(\overrightarrow c = \overrightarrow i - 4\overrightarrow j \)nên \(\overrightarrow c = \left( {1; - 4} \right)\)
d) Vì \(\overrightarrow d = 0,5\overrightarrow i + \sqrt 6 \overrightarrow j \)nên \(\overrightarrow d = \left( {0,5;\sqrt 6 } \right)\)
Trong mặt phẳng tọa độ Oxy cho các vectơ \(\overrightarrow{a}\) = (2 , 5) , \(\overrightarrow{b}\)= (-1,4) , \(\overrightarrow{c}\)= (3,0)
a, tìm toạ độ của các vecto sau \(\overrightarrow{a}\) + \(\overrightarrow{b}\) ,\(\overrightarrow{b}\) - \(\overrightarrow{c}\) , 5\(\overrightarrow{a}\)
b, hãy biểu diễn vectơ \(\overrightarrow{a}\) theo hai vectơ \(\overrightarrow{b}\) ,\(\overrightarrow{c}\)
c, cho x = ( 3m ; 2m +1 ) , tìm số m sao cho \(\overrightarrow{\text{x}}\) cùng phương vectơ \(\overrightarrow{a}\) + 2\(\overrightarrow{c}\)
Cho hai vecto \(\overrightarrow{a}\) = ( -3 ; 2 ) và \(\overrightarrow{b}\) = ( 4 ; 5 )
a) Hãy biểu thị các vecto \(\overrightarrow{a}\) và \(\overrightarrow{b}\) theo hai vecto \(\overrightarrow{i}\) và\(\overrightarrow{j}\)
b) Tìm tọa độ của các vecto \(\overrightarrow{c}\) = \(\overrightarrow{a}\) - \(\overrightarrow{b}\) ,
\(\overrightarrow{d}\) = 2\(\overrightarrow{a}\)+ \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)\(\overrightarrow{b}\)
Trong hệ trục tọa độ Oxy,cho các vecto \(\overrightarrow{a}\) =(2;3), \(\overrightarrow{b}\)=(1;-4)và \(\overrightarrow{c}\)=(5;12). Tìm cặp số x, y sao cho \(\overrightarrow{c}=x.\overrightarrow{a}+y.\overrightarrow{b}\)
Help me!!!
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5=2x+1.y\\12=3.x-4.y\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{32}{11}\\y=-\dfrac{9}{11}\end{matrix}\right.\)
(1) trong mặt phẳng tọa độ Oxy, cho hai vecto \(\overrightarrow{a}=\left(1;-4\right)\), \(\overrightarrow{b}=\left(0;2\right)\). tọa độ của vecto \(\overrightarrow{u}=2\overrightarrow{a}-\overrightarrow{b}\) là?
(2) trong mặt phẳng tọa độ Oxy, cho hai vecto \(\overrightarrow{a}=\left(-7;3\right)\), \(\overrightarrow{b}=\left(4;1\right)\). tọa độ của vecto \(\overrightarrow{u}=\overrightarrow{b}-2\overrightarrow{a}\) là?
(3) trong mặt phẳng tọa độ Oxy, cho hai vecto \(\overrightarrow{u}=\left(-5;4\right)\), \(\overrightarrow{v}=-3\overrightarrow{j}\). tọa độ của vecto \(\overrightarrow{a}=2\overrightarrow{u}-5\overrightarrow{v}\) là?
(4) trong mặt phẳng tọa độ Oxy, cho hai điểm A (1;1), B (4;-7) và \(\overrightarrow{OM}=2\overrightarrow{OA}-5\overrightarrow{OB}\). tổng hoành độ và tung độ của điểm M là?
giúp mk vs ạ mk cần gấp thank
(1); vecto u=2*vecto a-vecto b
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\cdot1-0=2\\y=2\cdot\left(-4\right)-2=-10\end{matrix}\right.\)
(2): vecto u=-2*vecto a+vecto b
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\cdot\left(-7\right)+4=18\\y=-2\cdot3+1=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
(3): vecto a=2*vecto u-5*vecto v
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2\cdot\left(-5\right)-5\cdot0=-10\\b=2\cdot4-5\cdot\left(-3\right)=15+8=23\end{matrix}\right.\)
(4): vecto OM=(x;y)
2 vecto OA-5 vecto OB=(-18;37)
=>x=-18; y=37
=>x+y=19
Trong mặt phẳng tọa độ Oxy cho \(\overrightarrow{a}=2\overrightarrow{i}\) , \(\overrightarrow{b}=-3\overrightarrow{j}\), \(\overrightarrow{c}=3\overrightarrow{i}-4\overrightarrow{j}\)
Phân tích vecto c theo hai vecto a và vecto b
Giả sử `\vec{c}=m\vec{a}+n\vec{b}`
`<=>(3;-4)=m(2;0)+n(0;-3)`
`<=>(3;-4)=(2m;-3n)`
`<=>{(m=3/2),(n=4/3):}`
`=>\vec{c}=3/2\vec{a}+4/3\vec{b}`
Trong mặt phẳng tọa độ Oxy, cho đường thẳng \(\Delta :x + 2y - 5 = 0\). Tìm mệnh đề sai trong các mệnh đề sau:
A. Vecto \(\overrightarrow n = (1;2)\) là một vecto pháp tuyến của \(\Delta \)
B. Vecto \(\overrightarrow u = ( - 2;1)\) là một vecto chỉ phương của \(\Delta \)
C. Đường thẳng \(\Delta \) song song với đường thẳng \(d:\left\{ \begin{array}{l}x = 1 - 2t\\y = 1 + t\end{array} \right.\)
D. Đường thẳng \(\Delta \)có hệ số góc \(k = 2\)
Xét đường thẳng \(\Delta :x + 2y - 5 = 0\)
Vecto \(\overrightarrow n = (1;2)\) là một VTPT của \(\Delta \) => A đúng => Loại A
Vecto \(\overrightarrow u = ( - 2;1)\) là một VTCP của \(\Delta \) => B đúng => Loại B
Đường thẳng \(\Delta \)có hệ số góc \(k = - \frac{a}{b} = - \frac{1}{2}\) => D sai => Chọn D
Chọn D.
cho vecto a=(2;1); vecto b=(3;4) và vecto c=(7;2)
a) Tìm tọa độ của \(\overrightarrow{u}=2\overrightarrow{a}-3\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}\)
b) Tìm tọa độ của \(\overrightarrow{x}\) thỏa \(\overrightarrow{x}+\overrightarrow{a}=\overrightarrow{b}-\overrightarrow{c}\)
c) Tìm các số m;n thỏa \(\overrightarrow{c}=m\overrightarrow{a}+n\overrightarrow{b}\)