Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất
A/4x2-6x-20
B/3x2-8x+1
Bài 2: Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất, giá trị lớn nhất (nếu có) của:
a) A = x2 - 4x + 1
b) B = -x2 - 8x + 5
c) C = 2x2 - 8x +19
d) D = -3x2 - 6x +1
a) \(A=x^2-4x+1=\left(x-2\right)^2-3\ge-3\)
\(minA=-3\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
b) \(B=-x^2-8x+5=-\left(x+4\right)^2+21\le21\)
\(maxB=21\Leftrightarrow x=-4\)
c) \(C=2x^2-8x+19=2\left(x-2\right)^2+11\ge11\)
\(minC=11\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
d) \(D=-3x^2-6x+1=-3\left(x+1\right)^2+4\le4\)
\(maxD=4\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
a) A = (x-2)^2 - 3 >= -3
--> A nhỏ nhất bằng -3
<=> x = 2
b) B = -(x+4)^2 + 21 <= 21
--> B lớn nhất bằng 21
<=> x = -4
1. Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của:
a) A= x2 - 8x + 20
b) B = x2 - x + 1
Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của phân thức A = 3 x 2 - 8 x + 6 x 2 - 2 x + 1
ĐKXĐ của phân thức x ≠ 1.
Ta có:
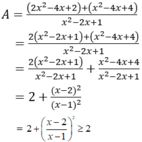
Vậy min A = 2 khi và chỉ khi x - 2 = 0 ⇔ x =2
Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức
M=2x2+4x+7
N=x2-x+1
Tìm giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức
E=-4x2+x-1
F=5x-3x2+6
Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức:
a) Ta có:
\(M=2x^2+4x+7\)
\(M=2\cdot\left(x^2+2x+\dfrac{7}{2}\right)\)
\(M=2\cdot\left(x^2+2x+1+\dfrac{5}{2}\right)\)
\(M=2\cdot\left[\left(x+1\right)^2+2,5\right]\)
\(M=2\left(x+1\right)^2+5\)
Mà: \(2\left(x+1\right)^2\ge0\forall x\) nên:
\(M=2\left(x+1\right)^2+5\ge5\forall x\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra:
\(2\left(x+1\right)^2+5=5\Leftrightarrow2\left(x+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x+1=0\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
Vậy: \(M_{min}=5\) khi \(x=-1\)
b) Ta có:
\(N=x^2-x+1\)
\(N=x^2-2\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot x+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(N=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\)
Mà: \(\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\ge0\forall x\) nên \(N=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\forall x\)
Dấu '=" xảy ra:
\(\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}=\dfrac{3}{4}\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-\dfrac{1}{2}=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy: \(N_{min}=\dfrac{3}{4}\) khi \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Tìm giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức
a) Ta có:
\(E=-4x^2+x-1\)
\(E=-\left(4x^2-x+1\right)\)
\(E=-\left[\left(2x\right)^2-2\cdot2x\cdot\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{16}+\dfrac{15}{16}\right]\)
\(E=-\left[\left(2x-\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{15}{16}\right]\)
Mà: \(\left(2x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{15}{16}\ge\dfrac{15}{16}\forall x\) nên
\(\Rightarrow E=-\left[\left(2x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{15}{16}\right]\le-\dfrac{15}{16}\forall x\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra:
\(-\left[\left(2x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{15}{16}\right]=-\dfrac{15}{16}\Leftrightarrow-\left(2x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2-\dfrac{15}{16}=-\dfrac{15}{16}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(2x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow2x-\dfrac{1}{4}=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{16}\)
Vậy: \(E_{max}=-\dfrac{15}{16}\) khi \(x=\dfrac{1}{16}\)
b) Ta có:
\(F=5x-3x^2+6\)
\(F=-3x^2+5x-6\)
\(F=-\left(3x^2-5x-6\right)\)
\(F=-3\left(x^2-\dfrac{5}{3}x-2\right)\)
\(F=-3\left[\left(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\right)^2-\dfrac{97}{36}\right]\)
\(F=-3\left(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\right)^2+\dfrac{97}{36}\)
Mà: \(-3\left(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\right)^2\le0\forall x\) nên:
\(F=-3\left(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\right)^2+\dfrac{97}{36}\le\dfrac{97}{36}\forall x\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra:
\(-3\left(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\right)^2+\dfrac{97}{36}=\dfrac{97}{36}\Leftrightarrow-3\left(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-\dfrac{5}{6}=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{6}\)
Vậy: \(F_{max}=\dfrac{97}{36}\) khi \(x=\dfrac{5}{6}\)
\(M=2x^2+4x+7\)
\(=2\left(x^2+2x+\dfrac{7}{2}\right)\)
\(=2\left(x^2+2x+1+\dfrac{5}{2}\right)\)
\(=2\left[\left(x+1\right)^2+\dfrac{5}{2}\right]\)
\(=2\left(x+1\right)^2+5\)
Vì \(2\left(x+1\right)^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow2\left(x+1\right)^2+5\ge5\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow M_{min}=5\Leftrightarrow2\left(x+1\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
Tương tự: \(N=x^2-x+1\)
\(=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow N_{min}=\dfrac{3}{4}\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(E=-4x^2+x-1\)
\(=-4\left(x^2-\dfrac{1}{4}x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)\)
\(=-4\left[x^2-2.x.\dfrac{1}{8}+\left(\dfrac{1}{8}\right)^2-\left(\dfrac{1}{8}\right)^2+\dfrac{1}{4}\right]\)
\(=-4\left[\left(x-\dfrac{1}{8}\right)^2+\dfrac{15}{64}\right]\)
\(=-4\left(x-\dfrac{1}{8}\right)^2-\dfrac{15}{16}\)
Vì \(-4\left(x-\dfrac{1}{8}\right)^2\le0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow-4\left(x-\dfrac{1}{8}\right)^2-\dfrac{15}{16}\le-\dfrac{15}{16}\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow E_{max}=-\dfrac{15}{16}\Leftrightarrow-4\left(x-\dfrac{1}{8}\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
Tương tự: \(F=5x-3x^2+6\)
\(=-3x^2+5x+6\)
\(=-3\left(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\right)^2+\dfrac{97}{12}\le\dfrac{97}{12}\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow F_{max}=\dfrac{97}{12}\Leftrightarrow-3\left(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{6}\)
Bài 4: Chứng minh rằng các biểu thức sau luôn luôn âm với mọi giá trị của biến a) M=-x² + 6x – 12 b) N= - 3x-x2 – 4 c)P =- 3x2+ 6x+20 d) Q= - 4x2 + 8x- 9y² – 6y – 35
MN ui mik đang cần gấp giúp mik với !
Đề: Tìm giá trị lớn nhất hoặc giá trị nhỏ nhất của:
1. -7x2 + 8x - 30
2. -4x2 + 9x - 15
Tìm giá trị lớn nhất, nhỏ nhất của biểu thức:
1) A= x2 - 6x +5
2) B= 4x2 + 1 + 18x
3) C= 9 - y2 - 4y
4) D= x2 - 8
1:
=x^2-6x+9-4=(x-3)^2-4>=-4
Dấu = xảy ra khi x=3
3: =-y^2-4y-4+13
=-(y+2)^2+13<=13
Dấu = xảy ra khi y=-2
4: D=x^2-8>=-8
Dấu = xảy ra khi x=0
Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức A,B,C và giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức D,E:
A= x2-4x+1 D= 5-8x-x2
B= 4x2+4x+11 E= 4x-x2+1
C= (x-1).(x+3).(x+2).(x+6)
`A=x^2-4x+1`
`=x^2-4x+4-3`
`=(x-2)^2-3>=-3`
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x=2
`B=4x^2+4x+11`
`=4x^2+4x+1+10`
`=(2x+1)^2+10>=10`
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi `x=-1/2`
`C=(x-1)(x+3)(x+2)(x+6)`
`=[(x-1)(x+6)][(x+3)(x+2)]`
`=(x^2+5x-6)(x^2+5x+6)`
`=(x^2+5x)^2-36>=-36`
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi `x=0\or\x=-5`
`D=5-8x-x^2`
`=21-16-8x-x^2`
`=21-(x^2+8x+16)`
`=21-(x+4)^2<=21`
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi `x=-4`
`E=4x-x^2+1`
`=5-4+4-x^2`
`=5-(x^2-4x+4)`
`=5-(x-2)^2<=5`
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi `x=5`
A= x2 - 4x +1
= x2 - 4x + 4 - 3
= (x-2)2 -3
Ta có (x-2)2 ≥ 0 ∀ x
⇒ (x-2)2 -3 ≥ -3 ∀ x
Vậy AMin= -3 tại x=2
B= 4x2+4x+11
= 4x2+4x+1+10
= (2x+1)2+10
Ta có (2x+1)2 ≥ 0 ∀ x
⇒ (2x+1)2+10 ≥ 10 ∀ x
Vậy BMin=10 tại x= \(\dfrac{-1}{2}\)
C=(x-1)(x+3)(x+2)(x+6)
= (x-1)(x+6)(x+3)(x+2)
= (x2+5x-6) (x2+5x+6)
= (x2+5x)2 -36
Ta có (x2+5x)2 ≥ 0 ∀ x
⇒ (x2+5x)2 -36 ≥ -36 ∀ x
Vậy CMin=-36 tại x=0 hoặc x= -5
Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức A, B, C và giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức D, E:
A = x2 – 4x + 1
B = 4x2 + 4x + 11
C = (x – 1)(x + 3)(x + 2)(x + 6)
D = 5 – 8x – x2
E = 4x – x2 +1
Tính giá trị nhỏ nhất:
\(A=x^2-4x+1=(x^2-4x+4)-3=(x-2)^2-3\)
Vì $(x-2)^2\geq 0, \forall x\in\mathbb{R}$ nên $A=(x-2)^2-3\geq 0-3=-3$
Vậy $A_{\min}=-3$
Giá trị này đạt tại $(x-2)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=2$
$B=4x^2+4x+11=(4x^2+4x+1)+10=(2x+1)^2+10\geq 0+10=10$
Vậy $B_{\min}=10$
Giá trị này đạt tại $(2x+1)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{1}{2}$
$C=(x-1)(x+3)(x+2)(x+6)$
$=(x-1)(x+6)(x+3)(x+2)$
$=(x^2+5x-6)(x^2+5x+6)$
$=(x^2+5x)^2-36\geq 0-36=-36$
Vậy $C_{\min}=-36$. Giá trị này đạt $x^2+5x=0\Leftrightarrow x=0$ hoặc $x=-5$
Tìm giá trị lớn nhất:
$D=5-8x-x^2=21-(x^2+8x+16)=21-(x+4)^2$
Vì $(x+4)^2\geq 0, \forall x\in\mathbb{R}$ nên $D=21-(x+4)^2\leq 21$
Vậy $D_{\max}=21$. Giá trị này đạt tại $(x+4)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=-4$
$E=4x-x^2+1=5-(x^2-4x+4)=5-(x-2)^2\leq 5$
Vậy $E_{\max}=5$. Giá trị này đạt tại $(x-2)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=2$