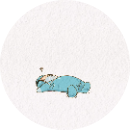
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{x}-\dfrac{3}{y}=-2\\\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{3}{y}=8\end{matrix}\right.\)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải hệ phương trình:
a)left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{3x+2}{x-1}-dfrac{3y-1}{y+2}0dfrac{2}{x-1}+dfrac{3}{y+2}1end{matrix}right.
b)left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{4x-5}{x+1}+dfrac{2y-3}{y-5}8dfrac{3}{x+1}-dfrac{2}{y-5}-1end{matrix}right.
c)left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{x+y-2}{x+1}+dfrac{3-x}{y+1}dfrac{5}{4}dfrac{3left(x+y-2right)}{x+1}-dfrac{5-x+2y}{y+1}dfrac{3}{4}end{matrix}right.
d)left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{x-y+1}{x-3}+dfrac{x+1}{y-3}dfrac{-7}{2}dfrac{2left(x-y+1right)}{x-3}-dfrac{x+y-2}{y-3}-dfrac{9}{2}...
Đọc tiếp
Giải hệ phương trình:
a)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3x+2}{x-1}-\dfrac{3y-1}{y+2}=0\\\dfrac{2}{x-1}+\dfrac{3}{y+2}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
b)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{4x-5}{x+1}+\dfrac{2y-3}{y-5}=8\\\dfrac{3}{x+1}-\dfrac{2}{y-5}=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
c)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{x+y-2}{x+1}+\dfrac{3-x}{y+1}=\dfrac{5}{4}\\\dfrac{3\left(x+y-2\right)}{x+1}-\dfrac{5-x+2y}{y+1}=\dfrac{3}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
d)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{x-y+1}{x-3}+\dfrac{x+1}{y-3}=\dfrac{-7}{2}\\\dfrac{2\left(x-y+1\right)}{x-3}-\dfrac{x+y-2}{y-3}=-\dfrac{9}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
e)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-y^2+2y=1\\\left(x+y\right)^2-2x-2y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
f)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x^2+y^2-4xy=4\\x^2+y^2-2\left(xy+8\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Giải hệ phương trình:
a) left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{5}{x}+dfrac{6}{y}9dfrac{2}{x}-dfrac{6}{y}7end{matrix}right. c) left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{2}{x}+dfrac{7}{y}21-dfrac{2}{x}-dfrac{5}{y}-11end{matrix}right.
b) left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{5}{x}+dfrac{1}{y}14dfrac{8}{x}-dfrac{1}{y}-8end{matrix}right. d) left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{9}{x}+dfrac{2}{y}22dfrac{5}{x}-dfrac{2}{y}13end{matrix}right. e) left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{3}{x}+dfrac{5}{y}10-dfrac{3}{x}-dfrac{7}{y}8end{matrix}right.
Đọc tiếp
Giải hệ phương trình:
a) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{5}{x}+\dfrac{6}{y}=9\\\dfrac{2}{x}-\dfrac{6}{y}=7\end{matrix}\right.\) c) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{x}+\dfrac{7}{y}=21\\-\dfrac{2}{x}-\dfrac{5}{y}=-11\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{5}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=14\\\dfrac{8}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=-8\end{matrix}\right.\) d) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{9}{x}+\dfrac{2}{y}=22\\\dfrac{5}{x}-\dfrac{2}{y}=13\end{matrix}\right.\) e) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{x}+\dfrac{5}{y}=10\\-\dfrac{3}{x}-\dfrac{7}{y}=8\end{matrix}\right.\)
a) ĐK xác định : x≠0;y≠0
ta có : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{5}{x}+\dfrac{6}{y}=9\\\dfrac{2}{x}-\dfrac{6}{y}=7\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{7}{x}=16\\\dfrac{2}{x}-\dfrac{6}{y}=7\end{matrix}\right.< =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{7}{16}\\y=-\dfrac{42}{17}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy S = {(\(\dfrac{7}{16};-\dfrac{42}{17}\))}
b) Đk xác định : x≠0;y≠0
ta có : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{5}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=14\\\dfrac{8}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=-8\end{matrix}\right.< =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{13}{x}=6\\\dfrac{5}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=14\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{13}{6}\\y=\dfrac{13}{152}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy S={(\(\dfrac{13}{6};\dfrac{13}{152}\))}
c) ĐK xác định : x≠0;y≠0
ta có : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{x}+\dfrac{7}{y}=21\\-\dfrac{2}{x}-\dfrac{5}{y}=-11\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{y}=10\\\dfrac{2}{x}+\dfrac{7}{y}=21\end{matrix}\right.< =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{1}{5}\\x=-\dfrac{1}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy S={(\(-\dfrac{1}{7};\dfrac{1}{5}\))}
d) ĐK xác định : x≠0;y≠0
ta có : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{9}{x}+\dfrac{2}{y}=22\\\dfrac{5}{x}-\dfrac{2}{y}=13\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{14}{x}=35\\\dfrac{5}{x}-\dfrac{2}{y}=13\end{matrix}\right.< =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{5}\\y=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy S={(0,4;-4)}
e) ĐKXĐ : x≠0;y≠0
ta có : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{x}+\dfrac{5}{y}=10\\-\dfrac{3}{x}-\dfrac{7}{y}=8\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-\dfrac{2}{y}=18\\\dfrac{3}{x}+\dfrac{5}{y}=10\end{matrix}\right.< =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-\dfrac{1}{9}\\x=\dfrac{3}{55}\end{matrix}\right.\) 'Vậy....
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải hệ phương trình
a,left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{2}{x}+dfrac{3}{y}5dfrac{1}{x}-dfrac{4}{y}-3end{matrix}right.
b,left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{12}{x-3}-dfrac{5}{y+2}63dfrac{8}{x-3}+dfrac{15}{y+2}-13end{matrix}right.
c,left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{4}{x+2}-dfrac{1}{x-2y}1dfrac{20}{x+2y}+dfrac{3}{x-2y}1end{matrix}right.
d,left{{}begin{matrix}left|x-1right|+left|y-2right|2left|x-1right|+y3end{matrix}right.
Đọc tiếp
giải hệ phương trình
a,\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{x}+\dfrac{3}{y}=5\\\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{4}{y}=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b,\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{12}{x-3}-\dfrac{5}{y+2}=63\\\dfrac{8}{x-3}+\dfrac{15}{y+2}=-13\end{matrix}\right.\)
c,\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{4}{x+2}-\dfrac{1}{x-2y}=1\\\dfrac{20}{x+2y}+\dfrac{3}{x-2y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
d,\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|x-1\right|+\left|y-2\right|=2\\\left|x-1\right|+y=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
a: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{x}+\dfrac{3}{y}=5\\\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{4}{y}=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{x}+\dfrac{3}{y}=5\\\dfrac{2}{x}-\dfrac{8}{y}=-6\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{11}{y}=11\\\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{4}{y}=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=1\\\dfrac{1}{x}=-3+\dfrac{4}{y}=-3+4=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{12}{x-3}-\dfrac{5}{y+2}=63\\\dfrac{8}{x-3}+\dfrac{15}{y+2}=-13\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{36}{x-3}-\dfrac{15}{y+2}=189\\\dfrac{8}{x-3}+\dfrac{15}{y+2}=-13\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{44}{x-3}=176\\\dfrac{8}{x-3}+\dfrac{15}{y+2}=-13\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3=\dfrac{1}{4}\\\dfrac{15}{y+2}=-13-\dfrac{8}{x-3}=-13-32=-45\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{13}{4}\\y=-\dfrac{1}{3}-2=-\dfrac{7}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2+y^2=\dfrac{1}{2}\\x^3+3xy^2=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(1+x^2\right)^2\left(1+\dfrac{1}{y^4}\right)=8\\\left(1+y^2\right)^2\left(1+\dfrac{1}{x^4}\right)=8\end{matrix}\right.\)
Em cảm ơn ạ !!!
a.
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2+y^2=\dfrac{1}{2}\\x^3+3xy^2=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y^2=\dfrac{1}{2}-x^2\\x^3+3xy^2=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow x^3+3x\left(\dfrac{1}{2}-x^2\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^3-3x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
- Với \(x=-1\) thế vào pt đầu: \(1+y^2=\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow y^2=-\dfrac{1}{2}\) (vô nghiệm)
- Với \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\) thế vào pt đầu: \(\dfrac{1}{4}+y^2=\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow y=\pm\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2+y^2=\dfrac{1}{2}\\x^3+3xy^2=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Dễ thấy x = 0 không phải nghiệm ta nhân tử mẫu phương trình đầu cho 3x thì được
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x^3+3xy^2=\dfrac{3x}{2}\left(1\right)\\x^3+3xy^2=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Lấy (1) - (2) thì đơn giản rồi ha
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
b.
Trừ vế cho vế:
\(\left(1+x^2\right)^2\left(1+\dfrac{1}{y^4}\right)-\left(1+y^2\right)^2\left(1+\dfrac{1}{x^4}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(1+x^2\right)^2-\left(1+y^2\right)^2+\left(\dfrac{1+x^2}{y^2}\right)^2-\left(\dfrac{1+y^2}{x^2}\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-y^2\right)\left(x^2+y^2+2\right)+\left(\dfrac{x^4+x^2-y^4-y^2}{x^2y^2}\right)\left(\dfrac{1+x^2}{y^2}+\dfrac{1+y^2}{x^2}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-y^2\right)\left(x^2+y^2+2\right)+\left(\dfrac{\left(x^2-y^2\right)\left(x^2+y^2+1\right)}{x^2y^2}\right)\left(\dfrac{x^2+1}{y^2}+\dfrac{y^2+1}{x^2}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-y^2\right)\left(x^2+y^2+2+\left(\dfrac{x^2+y^2+1}{x^2y^2}\right)\left(\dfrac{x^2+1}{y^2}+\dfrac{y^2+1}{x^2}\right)\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=y^2\) (ngoặc to hiển nhiên dương)
Thế vào pt đầu:
\(\left(1+x^2\right)^2\left(1+\dfrac{1}{x^4}\right)=8\)
Ta có: \(\left(1+x^2\right)^2\left(1+\dfrac{1}{x^4}\right)\ge4x^2.2\sqrt{1.\dfrac{1}{x^4}}=8\)
Đẳng thức xảy ra khi và chỉ khi \(x^2=1\)
Vậy nghiệm của hệ là \(x^2=y^2=1\Rightarrow x;y\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Giải hệ phương trình :
a) left{{}begin{matrix}4dfrac{1}{x}+dfrac{1}{y}12dfrac{1}{x}+dfrac{1}{y}-3end{matrix}right.
b) left{{}begin{matrix}5dfrac{1}{x}+2dfrac{1}{y}62dfrac{1}{x}-dfrac{1}{y}3end{matrix}right.
c) left{{}begin{matrix}3dfrac{1}{x}-6dfrac{1}{y}2dfrac{1}{x}-dfrac{1}{y}5end{matrix}right.
d) left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{1}{x}-4dfrac{1}{y}52dfrac{1}{x}-3dfrac{1}{y}1end{matrix}right.
e) left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{1}{x}-3dfrac{1}{y}46dfrac{1}{x}-dfrac{1}{y}2end{matrix}right.
Đọc tiếp
Giải hệ phương trình :
a) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=12\\\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5\dfrac{1}{x}+2\dfrac{1}{y}=6\\2\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3\dfrac{1}{x}-6\dfrac{1}{y}=2\\\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
d) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}-4\dfrac{1}{y}=5\\2\dfrac{1}{x}-3\dfrac{1}{y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
e) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}-3\dfrac{1}{y}=4\\6\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(a.\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=12\\\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=-3\end{matrix}\right.\) (1)
ĐK xác định : x≠0 ; y≠0
Đặt ẩn phụ : a = \(\dfrac{1}{x}\) ; b = \(\dfrac{1}{y}\)
Thay vào (1) ta được :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4a+b=12\\a+b=-3\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3a=15\\a+b=-3\end{matrix}\right.< =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=5\\b=-8\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{5}\\y=-\dfrac{1}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy S = {(\(\dfrac{1}{5};-\dfrac{1}{8}\))}
\(b.\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5\dfrac{1}{x}+2\dfrac{1}{y}=6\\2\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=3\end{matrix}\right.\) (2)
ĐK xác định : x≠0 ; y≠0
Đặt ẩn phụ : a = 1/x ; b = 1/y
Thay vào (2) ta được : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5a+2b=6\\2a-b=3\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5a+2b=6\\4a-2b=6\end{matrix}\right.< =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}9a=12\\2a-b=3\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=\dfrac{4}{3}\\b=-\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{4}\\y=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy S = {(\(\dfrac{3}{4};-3\) )}
c) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3\dfrac{1}{x}-6\dfrac{1}{y}=2\\\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
ĐK xác định : x≠0 ; y ≠0
Áp dụng quy tác cộng đại số ta có :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3\dfrac{1}{x}-6\dfrac{1}{y}=2\\\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=5\end{matrix}\right.< =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3\dfrac{1}{x}-6\dfrac{1}{y}=2\\3\dfrac{1}{x}-3\dfrac{1}{y}=15\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-3\dfrac{1}{y}=-13\\\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=5\end{matrix}\right.< =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{3}{13}\\x=\dfrac{3}{28}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy S = {(\(\dfrac{3}{28};\dfrac{3}{13}\))}
d) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}-4\dfrac{1}{y}=5\\2\dfrac{1}{x}-3\dfrac{1}{y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
ĐK xác định : x≠0 ; y≠0
áp dụng quy tắc cộng đại số ta có :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}-4\dfrac{1}{y}=5\\2\dfrac{1}{x}-3\dfrac{1}{y}=1\end{matrix}\right.< =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2\dfrac{1}{x}-8\dfrac{1}{y}=10\\2\dfrac{1}{x}-3\dfrac{1}{y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-5\dfrac{1}{y}=9\\\dfrac{1}{x}-4\dfrac{1}{y}=5\end{matrix}\right.< =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-\dfrac{5}{9}\\x=-\dfrac{5}{11}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy S = {(\(-\dfrac{5}{11};-\dfrac{5}{9}\))}
e) ĐK xác định x≠0 ; y≠0
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}-3\dfrac{1}{y}=4\\6\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=2\end{matrix}\right.< =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}-3\dfrac{1}{y}=4\\18\dfrac{1}{x}-3\dfrac{1}{y}=6\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-17\dfrac{1}{x}=-2\\\dfrac{1}{x}-3\dfrac{1}{y}=4\end{matrix}\right.\) <=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{17}{2}\\y=-\dfrac{17}{22}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy S={(\(\dfrac{17}{2};-\dfrac{17}{22}\))}
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5y-5x=xy\\\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{4}{5}\\\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{2x-3y}+\dfrac{5}{3x+y}=\dfrac{5}{8}\\\dfrac{3}{2x-3y}-\dfrac{5}{3x+y}=-\dfrac{3}{8}\\\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-y=2\\y-3z=2\\-3x-2y+z=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
a) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5y-5x=xy\\\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{4}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5y-5x=xy\\\dfrac{x+y}{xy}=\dfrac{4}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5y-5x=xy\\5\left(x+y\right)=4xy\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5y-5x=xy\\5\left(x+y\right)=4\left(5y-5x\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5y-5x=xy\\5x+5y=20y-20x\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5y-5x=xy\\5x+5y-20y+20x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5y-5x=xy\\-15y+25x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5y-5x=xy\\-5\left(3y-5x\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5y-5x=xy\\3y-5x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5y-5x=xy\\5x=3y\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5y-3y=xy\\5x=3y\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2y=xy\\5x=3y\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=\dfrac{10}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
b) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{2x-3y}+\dfrac{5}{3x+y}=\dfrac{5}{8}\\\dfrac{2}{2x-3y}-\dfrac{5}{3x+y}=\dfrac{-3}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đặt \(\dfrac{1}{2x-3y}=a;\dfrac{1}{3x+y}=b\)
=> hpt <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+5b=\dfrac{5}{8}\\2a-5b=\dfrac{-3}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+5b=\dfrac{5}{8}\\2a-5b+a+5b=\dfrac{-3}{8}+\dfrac{5}{8}=0,25\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+5b=\dfrac{5}{8}\\3a=0,25\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+5b=\dfrac{5}{8}\\a=\dfrac{1}{12}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=\dfrac{1}{12}\\b=\dfrac{13}{120}\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{2x-3y}=\dfrac{1}{12}\\\dfrac{1}{3x+y}=\dfrac{13}{120}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-3y=12\\3x+y=\dfrac{120}{13}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{516}{143}\\y=-\dfrac{228}{143}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
c) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-y=2\\y-3z=2\\-3x-2y+z=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=y+2\\y=3z+2\\-3\left(y+2\right)-2\left(3z+2\right)+z=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=y+2\\y=3z+2\\-3y-6-6z-4+z=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=y+2\\y=3z+2\\-3y-5z=8\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=y+2\\y=3z+2\\-3\left(3z+2\right)-5z=8\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=y+2\\y=3z+2\\-9z-6-5z=8\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=y+2\\y=3z+2\\-14z=14\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\left(-1\right)+2=1\\y=3\left(-1\right)+2=-1\\z=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy...
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1)left{{}begin{matrix}2x+dfrac{1}{y}dfrac{3}{x}2y+dfrac{1}{x}dfrac{3}{y}end{matrix}right.2)left{{}begin{matrix}x^33x+8yy^33y+8xend{matrix}right.3)left{{}begin{matrix}x^2+y^2+x-2y2x^2+y^2+2x+2y11end{matrix}right.4)left{{}begin{matrix}x^3-y13x^2-3xy+y^21end{matrix}right.5)left{{}begin{matrix}x^3-y^39left(x-yright)left(x^2+y^2right)15end{matrix}right.
Đọc tiếp
1)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{3}{x}\\2y+\dfrac{1}{x}=\dfrac{3}{y}\end{matrix}\right.\)
2)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^3=3x+8y\\y^3=3y+8x\end{matrix}\right.\)
3)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2+y^2+x-2y=2\\x^2+y^2+2x+2y=11\end{matrix}\right.\)
4)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^3-y=1\\3x^2-3xy+y^2=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
5)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^3-y^3=9\\\left(x-y\right)\left(x^2+y^2\right)=15\end{matrix}\right.\)
Giải các hệ phương trình sau bằng cách đặt ẩn số phụ:
1) left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{1}{x}+dfrac{1}{y}dfrac{1}{12}dfrac{8}{x}+dfrac{15}{y}1end{matrix}right.
2) left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{2}{x+2y}+dfrac{1}{y+2x}3dfrac{4}{x+2y}-dfrac{3}{y+2x}1end{matrix}right.
3) left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{3x}{x+1}-dfrac{2}{y+4}4dfrac{2x}{x+1}-dfrac{5}{y+4}9end{matrix}right.
4) left{{}begin{matrix}x^2+y^2133x^2-2y^2-6end{matrix}right.
5) left{{}begin{matrix}3sqrt{x}+2sqrt{y}162sqrt{x}-3sqrt{y}-11end{matrix}right....
Đọc tiếp
Giải các hệ phương trình sau bằng cách đặt ẩn số phụ:
1) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{1}{12}\\\dfrac{8}{x}+\dfrac{15}{y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
2) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{x+2y}+\dfrac{1}{y+2x}=3\\\dfrac{4}{x+2y}-\dfrac{3}{y+2x}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
3) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3x}{x+1}-\dfrac{2}{y+4}=4\\\dfrac{2x}{x+1}-\dfrac{5}{y+4}=9\end{matrix}\right.\)
4) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2+y^2=13\\3x^2-2y^2=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
5) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3\sqrt{x}+2\sqrt{y}=16\\2\sqrt{x}-3\sqrt{y}=-11\end{matrix}\right.\)
6) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}|x|+4|y|=18\\3|x|+|y|=10\end{matrix}\right.\)
GIẢI GIÚP MÌNH VỚI M.N
hỏi trước tí, bạn biết giải cái hệ này chứ?
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+y=3\\2x-3y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (8)
ba cái đồ êu!!
câu số 6 (con số của quỷ sa tăng :v)
đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=\left|x\right|\\b=\left|y\right|\end{matrix}\right.\) (a,b >/ 0)
hpt trở thành : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+4b=18\\3a+b=10\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2\\b=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|x\right|=2\\\left|y\right|=4\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=4\\y=-4\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy hpt có các ng (x;y) là: (có 4 nghiệm tự kết luận)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
1, \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{1}{12}\\\dfrac{8}{x}+\dfrac{15}{y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\) (I) (ĐKXĐ: x, y \(\ne\)0)
Đặt \(\dfrac{1}{x}=a\) ; \(\dfrac{1}{y}=b\)
Hệ pt (I) trở thành :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b=\dfrac{1}{12}\\8a+15b=1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}8a+8b=\dfrac{2}{3}\\8a+15b=1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-7b=\dfrac{-1}{3}\\a+b=\dfrac{1}{12}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}b=\dfrac{1}{21}\\a+\dfrac{1}{21}=\dfrac{1}{12}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}b=\dfrac{1}{21}\left(tm\right)\\a=\dfrac{1}{28}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}=\dfrac{1}{28}\\\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{1}{21}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=28\left(tm\right)\\y=21\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Giải các hệ phương trình sau bằng cách đặt ẩn số phụ:a) left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{1}{x}+dfrac{1}{y}dfrac{4}{5}dfrac{1}{x}-dfrac{1}{y}dfrac{1}{5}end{matrix}right.;b) left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{15}{x}-dfrac{7}{y}9dfrac{4}{x}+dfrac{9}{y}35end{matrix}right.;c) left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{1}{x+y}+dfrac{1}{x-y}dfrac{5}{8}dfrac{1}{x+y}-dfrac{1}{x-y}-dfrac{3}{8}end{matrix}right.;d) left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{4}{2x-2y}+dfrac{5}{3x+y}-2dfrac{3}{3x+y}-dfrac{5}{2x-3y}21end{matrix}right.;e) left{{}begin{matrix}d...
Đọc tiếp
Giải các hệ phương trình sau bằng cách đặt ẩn số phụ:
a) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{4}{5}\\\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\);
b) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{15}{x}-\dfrac{7}{y}=9\\\dfrac{4}{x}+\dfrac{9}{y}=35\end{matrix}\right.\);
c) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x+y}+\dfrac{1}{x-y}=\dfrac{5}{8}\\\dfrac{1}{x+y}-\dfrac{1}{x-y}=-\dfrac{3}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\);
d) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{4}{2x-2y}+\dfrac{5}{3x+y}=-2\\\dfrac{3}{3x+y}-\dfrac{5}{2x-3y}=21\end{matrix}\right.\);
e) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{7}{x-y+2}-\dfrac{5}{x+y-1}=4,5\\\dfrac{3}{x-y+2}+\dfrac{2}{x+y-1}=4\end{matrix}\right.\).
Giải hệ phương trìnha)left{{}begin{matrix}x+ydfrac{x-3}{2}x+2ydfrac{2-4y}{15}end{matrix}right. b)left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{1}{x}+dfrac{1}{y}-1dfrac{3}{x}-dfrac{2}{y}7end{matrix}right.c)left{{}begin{matrix}sqrt{x+3}-2sqrt{y+1}22sqrt{x+3}+sqrt{y+1}4end{matrix}right. d)left{{}begin{matrix}dfrac{7}{sqrt{x}-7}-dfrac{4}{sqrt{y}+6}dfrac{5}{3}dfrac{5}{sqrt{x}-7}+dfrac{3}{sqrt{y}+6}2dfrac{1}{9}end{matrix}right.
Đọc tiếp
Giải hệ phương trình
a)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=\dfrac{x-3}{2}\\x+2y=\dfrac{2-4y}{15}\end{matrix}\right.\) b)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=-1\\\dfrac{3}{x}-\dfrac{2}{y}=7\end{matrix}\right.\)
c)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x+3}-2\sqrt{y+1}=2\\2\sqrt{x+3}+\sqrt{y+1}=4\end{matrix}\right.\) d)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{7}{\sqrt{x}-7}-\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{y}+6}=\dfrac{5}{3}\\\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}-7}+\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{y}+6}=2\dfrac{1}{9}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{x}+\dfrac{3}{y}=-3\\\dfrac{3}{x}-\dfrac{2}{y}=7\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{5}{y}=-10\\\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)