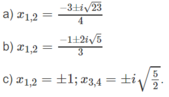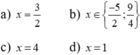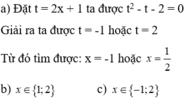1.giải phương trình : x8-2x4+x2-2x+2=0

Những câu hỏi liên quan
1. Giải phương trình: 2x4 - 3x2 - 5 = 0
2. Cho phương trình bậc 2 ẩn x: x2 - (m+5)x-m+6=0 (1) (m là tham số)
a. Giải pt (1) khi m = 1
b. Tìm m để pt (1) có 2 nghiệm x1, x2 thỏa mãn: x12x2 + x1x22 = 18
#help me, hứa sẽ vote.
Bài 1:
$2x^4-3x^2-5=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (2x^4+2x^2)-(5x^2+5)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x^2(x^2+1)-5(x^2+1)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x^2+1)(2x^2-5)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x^2-5=0$ (do $x^2+1\geq 1>0$ với mọi $x\in\mathbb{R}$)
$\Leftrightarrow x^2=\frac{5}{2}$
$\Leftrightarrow x=\pm \sqrt{\frac{5}{2}}$
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 2:
a. Khi $m=1$ thì pt trở thành:
$x^2-6x+5=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x^2-x)-(5x-5)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x(x-1)-5(x-1)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-1)(x-5)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-1=0$ hoặc $x-5=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=1$ hoặc $x=5$
b.
Để pt có 2 nghiệm $x_1,x_2$ thì:
$\Delta=(m+5)^2-4(-m+6)\geq 0$
$\Leftrightarrow m^2+14m+1\geq 0(*)$
Áp dụng định lý Viet:
$x_1+x_2=m+5$
$x_1x_2=-m+6$
Khi đó:
$x_1^2x_2+x_1x_2^2=18$
$\Leftrightarrow x_1x_2(x_1+x_2)=18$
$\Leftrightarrow (m+5)(-m+6)=18$
$\Leftrightarrow -m^2+m+12=0$
$\Leftrightarrow m^2-m-12=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (m+3)(m-4)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow m=-3$ hoặc $m=4$
Thử lại vào $(*)$ thấy $m=4$ thỏa mãn.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình:
(x2-1)3+(x2+2)3+(2x-1)3+(3x+3)(2x-1)(1-x)(x2+2)=0
Lời giải:
PT $\Leftrightarrow (x^2-1)^3+(x^2+2)^3+(2x-1)^3-3(x^2-1)(x^2+2)(2x-1)=0$
Đặt $x^2-1=a; x^2+2=b; 2x-1=c$ thì pt trở thành:
$a^3+b^3+c^3-3abc=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a+b)^3+c^3-3ab(a+b)-3abc=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a+b+c)[(a+b)^2-c(a+b)+c^2]-3ab(a+b+c)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a+b+c)(a^2+b^2+c^2-ab-bc-ac)=0$
$\Rightarrow a+b+c=0$ hoặc $a^2+b^2+c^2-ab-bc-ac=0$
Nếu $a+b+c=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2-1+x^2+2+2x-1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x^2+2x=0$
$\Rightarrow x=0$ hoặc $x=-1$
Nếu $a^2+b^2+c^2-ab-bc-ac=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a-b)^2+(b-c)^2+(c-a)^2=0$
$\Rightarrow a-b=b-c=c-a=0$ (dễ CM)
$\Leftrightarrow a=b=c$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2-1=x^2+2=2x-1$ (vô lý)
Vậy..........
Đúng 1
Bình luận (2)
Các cặp phương trình sau đây có tương đương không? Vì sao?a)
x
2
−
6
x
+
9
0
và
x
2
+
1
2
x
−
6
0
b)
x
2...
Đọc tiếp
Các cặp phương trình sau đây có tương đương không? Vì sao?
a) x 2 − 6 x + 9 = 0 và x 2 + 1 2 x − 6 = 0
b) x 2 + 1 2 x − 1 = 0 và 2 x 4 + 1 = 0
cho phương trình 4x2-2x-1=0 có 2 nghiệm x1,x2.Không giải phương trình,tính A=(x1-x2)2 -x12+1/2x1
A=(x1-x2)^2-x1^2+x1(x1+x2)
=(x1-x2)^2+x1x2
=(x1+x2)^2-x1x2
=(1/2)^2-(-1/4)=1/4+1/4=1/2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:
b) (2x+1)2-2x-1=2
c) (x2-3x)2+5(x2-3x)+6=0
d) (x2-x-1)(x2-x)-2=0
tham khảo
https://hoidapvietjack.com/q/57243/giai-cac-phuong-trinh-sau-a-2x12-2x-12-b-x2-3x-2-5x2-3x60
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
b) (2x+1)2-2x-1=2
\(< =>4x^2+4x+1-2x-1=2\)
\(< =>4x^2+2x-2=0\)
\(< =>4x^2+4x-2x-2=0\)
\(< =>\left(4x^2+4x\right)-\left(2x+2\right)=0\)
\(< =>4x\left(x+1\right)-2\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(< =>\left(x+1\right)\left(4x-2\right)=0\)
\(=>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0=>x=-1\\4x-2=0=>x=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy....
Đúng 0
Bình luận (2)
b) (2x+1)2-2x-1=2
<=>4x2+4x+1−2x−1=2
<=>4x2+2x−2=0
<=>4x2+4x−2x−2=0
<=>(4x2+4x)−(2x+2)=0
<=>4x(x+1)−2(x+1)=0
<=>(x+1)(4x−2)=0
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1) Giải phương trình: x(x-3)-(x+2)(x-1)=3 ta được nghiệm
2) Phương trình nào sau đây có 1 nghiệm
a) x(x-1)=0 b) (x+2)(x2+1)=0
c) x2-3x=0 d) x2-2x+3=0
1. x(x-3)-(x+2)(x-1)=3 <=> x2 - 3x - x2 - x + 2 = 3 => 4x = -1 => x = 1/4
2.
a) x = 0, x=1 (2 nghiệm, loại)
b) x2 + 1 > 0 => x = - 2 (1 nghiệm, chọn b)
c) <=> x(x-3) = 0 => x = 0, x=3 (2 nghiệm, loại)
d) (x-1)2 + 2 > 0 => Vô nghiệm (loại)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải bất phương trình
x2-2x+1<9
(x-1)(4-x2)≥0
\(\dfrac{x+2}{x-5}\)<0
\(x^2-2x+1< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1< 3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< 4\)
\(\left(x-1\right)\left(4-x^2\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2-x\right)\left(2+x\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\2-x=0\\2+x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=2\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{x+2}{x-5}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< -2\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a)\(x^2-2x+1< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2-9< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1-3\right)\left(x-1+3\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x+2\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4< 0\\x+2>0\end{matrix}\right.hay\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4>0\\x+2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< 4\\x>-2\end{matrix}\right.hay\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>4\\x< -2\end{matrix}\right.\)(vô lý)
-Vậy nghiệm của BĐT là \(-2< x< 4\).
b) \(\left(x-1\right)\left(4-x^2\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2-x\right)\left(x+2\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1< 0\\x-2>0\\x+2>0\end{matrix}\right.\) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1>0\\x-2< 0\\x+2>0\end{matrix}\right.\) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1>0\\x-2 >0\\x+2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1< 0\\x-2< 0\\x+2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< 1\\x>2\\x>-2\end{matrix}\right.\) (vô lí) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>1\\x< 2\\x>-2\end{matrix}\right.\) (có thể xảy ra) hay
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>1\\x>2\\x< -2\end{matrix}\right.\) (vô lí) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< 1\\x< 2\\x< -2\end{matrix}\right.\) (có thể xảy ra)
-Vậy nghiệm của BĐT là \(x< -2\) hay \(1< x< 2\).
c) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne5\)
\(\dfrac{x+2}{x-5}< 0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2< 0\\x-5>0\end{matrix}\right.hay\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2>0\\x-5< 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< -2\\x>5\end{matrix}\right.\)(vô lí) hay
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>-2\\x< 5\end{matrix}\right.\) (có thể xảy ra)
-Vậy nghiệm của BĐT là \(-2< x< 5\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
Giải các phương trình sau trên tập số phức:
a) 2x2 + 3x + 4 = 0
b) 3x2 + 2x + 7 = 0
c) 2x4 + 3x2 – 5 = 0
Giải các phương trình sau:a)
2
x
−
1
2
x
−
5
;
b)
7
−
x
−
2
−
3
x
0
;
c)...
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) 2 x − 1 = 2 x − 5 ; b) 7 − x − 2 − 3 x = 0 ;
c) x − 4 + x 2 − 5 x + 4 = 0 ; d) x 2 − x − 2 x + 1 − x = 0 .
Giải các phương trình sau:a)
2
x
+
1
2
−
2
x
−
1
2
;
b)
x
2
−
3
x
2
+
5
x...
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) 2 x + 1 2 − 2 x − 1 = 2 ;
b) x 2 − 3 x 2 + 5 x 2 − 3 x + 6 = 0 ;
c) x 2 − x − 1 x 2 − x − 2 = 0 .