Đưa về phương trình tích:
a) 3.(x - 1).(2x - 1) = 5.(x+8).(x-1)
b) 2x3 + 3x2 - 32x = 48
Giải phương trình bằng cách đưa về phương trình tích:
a ) 3 x 2 − 7 x − 10 ⋅ 2 x 2 + ( 1 − 5 ) x + 5 − 3 = 0 b ) x 3 + 3 x 2 − 2 x − 6 = 0 c ) x 2 − 1 ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) = 0 , 6 x 2 + x d ) x 2 + 2 x − 5 2 = x 2 − x + 5 2
a) 3 x 2 − 7 x − 10 ⋅ 2 x 2 + ( 1 − 5 ) x + 5 − 3 = 0
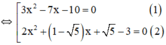
+ Giải (1):
3 x 2 – 7 x – 10 = 0
Có a = 3; b = -7; c = -10
⇒ a – b + c = 0
⇒ (1) có hai nghiệm x 1 = - 1 v à x 2 = - c / a = 10 / 3 .
+ Giải (2):
2 x 2 + ( 1 - √ 5 ) x + √ 5 - 3 = 0
Có a = 2; b = 1 - √5; c = √5 - 3
⇒ a + b + c = 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm:
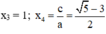
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 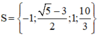
b)
x 3 + 3 x 2 - 2 x - 6 = 0 ⇔ x 3 + 3 x 2 - ( 2 x + 6 ) = 0 ⇔ x 2 ( x + 3 ) - 2 ( x + 3 ) = 0 ⇔ x 2 - 2 ( x + 3 ) = 0
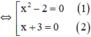
+ Giải (1): x 2 – 2 = 0 ⇔ x 2 = 2 ⇔ x = √2 hoặc x = -√2.
+ Giải (2): x + 3 = 0 ⇔ x = -3.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {-3; -√2; √2}
c)
x 2 − 1 ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) = 0 , 6 x 2 + x ⇔ x 2 − 1 ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) = x ⋅ ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) ⇔ x 2 − 1 ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) − x ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) = 0 ⇔ ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) x 2 − 1 − x = 0
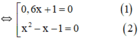
+ Giải (1): 0,6x + 1 = 0 ⇔ 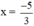
+ Giải (2):
x 2 – x – 1 = 0
Có a = 1; b = -1; c = -1
⇒ Δ = ( - 1 ) 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 1 ) = 5 > 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm 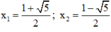
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 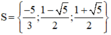
d)
x 2 + 2 x − 5 2 = x 2 − x + 5 2 ⇔ x 2 + 2 x − 5 2 − x 2 − x + 5 2 = 0 ⇔ x 2 + 2 x − 5 − x 2 − x + 5 ⋅ x 2 + 2 x − 5 + x 2 − x + 5 = 0 ⇔ ( 3 x − 10 ) 2 x 2 + x = 0
⇔ (3x-10).x.(2x+1)=0
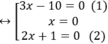
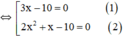
+ Giải (1): 3x – 10 = 0 ⇔ 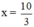
+ Giải (2):
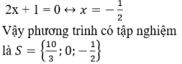
1) (1-x)(5x+3)=(3x-7)(x-1)
2) (x-2)(x+1)=x2-4
3) 2x3+3x2-32x=48
4) x2+2x-15=0
5) 2x(2x-3)=(3-2x)(2-5x)
6) x3-5x2+6x=0
7) (x2-5)(x+3)=0
8) (x+7)(3x-1)=49-x2
\(\left(1-x\right)\left(5x+3\right)=\left(3x-7\right)\left(x-1\right)\)
\(< =>\left(1-x\right)\left(5x+3+3x-7\right)=0\)
\(< =>\left(1-x\right)\left(8x-4\right)=0\)
\(< =>\orbr{\begin{cases}1-x=0\\8x-4=0\end{cases}< =>\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=\frac{1}{2}\end{cases}}}\)
\(\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)=x^2-4\)
\(< =>\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)=\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\)
\(< =>\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1-x-2\right)=0\)
\(< =>-1\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(< =>2-x=0< =>x=2\)
\(2x^3+3x^2-32x=48\)
\(< =>x^2\left(2x+3\right)-16\left(2x+3\right)=0\)
\(< =>\left(x^2-16\right)\left(2x+3\right)=0\)
\(< =>\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)\left(2x+3\right)=0\)
\(< =>\hept{\begin{cases}x=4\\x=-4\\x=-\frac{3}{2}\end{cases}}\)
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) x - 5(x - 2) = 6x
b) 23 + 3x2 - 32x = 48
c) (3x + 1)(x - 3)2 = (3x + 1)(2x - 5)2
d) 9x2 - 1 = (3x + 1)(4x + 1)
\(a,x-5\left(x-2\right)=6x\\ \Leftrightarrow x-5x+10-6x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow-10x+10=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=1\\ b,2^3+3x^2-32x=48\\ \Leftrightarrow3x^2-32x+8=48\\ \Leftrightarrow3x^2-32x-40=0\)
Nghiệm xấu lắm bn
\(c,\left(3x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)^2=\left(3x+1\right)\left(2x-5\right)^2\\ \Leftrightarrow c,\left(3x+1\right)\left[\left(2x-5\right)^2-\left(x-3\right)^2\right]\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(2x-5-x+3\right)\left(2x-5+x-3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(3x-8\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=2\\x=\dfrac{8}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(d,9x^2-1=\left(3x+1\right)\left(4x+1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(4x+1\right)-\left(3x-1\right)\left(3x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(4x+1-3x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,2x^3+3x^2-32x-48=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x^3-8x^2\right)+\left(11x^2-44x\right)+\left(12x-48\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2x^2\left(x-4\right)+11x\left(x-4\right)+12\left(x-4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(2x^2+11x+12\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left[\left(2x^2+8x\right)+\left(3x+12\right)\right]=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left[2x\left(x+4\right)+3\left(x+4\right)\right]=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(2x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\\x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
1. giải phương trình tích:
a) \(\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2+2021\right)=0\)
\(\)2. giải các phương trình sau bằng cách đưa về phương trình tích:
b) \(x\left(x-3\right)+3\left(x-3\right)=0\)
c) \(\left(x^2-9\right)+\left(x+3\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\)
d) \(3x^2+3x=0\)
e) \(x^2-4x+4=4\)
`a,(x+3)(x^2+2021)=0`
`x^2+2021>=2021>0`
`=>x+3=0`
`=>x=-3`
`2,x(x-3)+3(x-3)=0`
`=>(x-3)(x+3)=0`
`=>x=+-3`
`b,x^2-9+(x+3)(3-2x)=0`
`=>(x-3)(x+3)+(x+3)(3-2x)=0`
`=>(x+3)(-x)=0`
`=>` $\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=0\\x=-3\end{array} \right.$
`d,3x^2+3x=0`
`=>3x(x+1)=0`
`=>` $\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=0\\x=-1\end{array} \right.$
`e,x^2-4x+4=4`
`=>x^2-4x=0`
`=>x(x-4)=0`
`=>` $\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=0\\x=4\end{array} \right.$
1) a) \(\left(x+3\right).\left(x^2+2021\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\x^2+2021=0\end{matrix}\right.\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\left(nhận\right)\\x^2=-2021\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right. \)
=> S={-3}
Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2+2021\right)=0\)
mà \(x^2+2021>0\forall x\)
nên x+3=0
hay x=-3
Vậy: S={-3}
Bài 2:
b) Ta có: \(x\left(x-3\right)+3\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={3;-3}
1)giải phương trình sau bằng cách đưa về phương trình tích.
A) 3(x-1)(2x-1)=5(x+8)(x-1)
B) 9x2-1=(3x+1)(4x+1)
C) (x+7)(3x-1)=49-x2
D) x3-5x2+6x=0
E) 2x3+3x2-32x=48
Giúp mình với đang cần gấp lắm ạ
Lời giải:
a)
$3(x-1)(2x-1)=5(x+8)(x-1)$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-1)[3(2x-1)-5(x+8)]=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-1)(x-43)=0$
$\Rightarrow x-1=0$ hoặc $x-43=0$
$\Rightarrow x=1$ hoặc $x=43$
b)
$9x^2-1=(3x+1)(4x+1)$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x+1)(3x-1)=(3x+1)(4x+1)$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x+1)(4x+1)-(3x+1)(3x-1)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x+1)[(4x+1)-(3x-1)]=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x+1)(x+2)=0$
$\Rightarrow 3x+1=0$ hoặc $x+2=0$
$\Rightarrow x=\frac{-1}{3}$ hoặc $x=-2$
c)
$(x+7)(3x-1)=49-x^2=(7-x)(7+x)$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+7)(3x-1)-(7-x)(7+x)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+7)(3x-1-7+x)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+7)(4x-8)=0$
$\Rightarrow x+7=0$ hoặc $4x-8=0$
$\Rightarrow x=-7$ hoặc $x=2$
d)
$x^3-5x^2+6x=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x(x^2-5x+6)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x(x-2)(x-3)=0$
$\Rightarrow x=0; x-2=0$ hoặc $x-3=0$
$\Rightarrow x=0; x=2$ hoặc $x=3$
e)
$2x^3+3x^2-32x=48$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x^3+3x^2-32x-48=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x^2(x-4)+11x(x-4)+12(x-4)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-4)(2x^2+11x+12)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-4)[2x(x+4)+3(x+2)]=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-4)(x+4)(2x+3)=0$
$\Rightarrow x-4=0; x+4=0$ hoặc $2x+3=0$
$\Rightarrow x=4; x=-4$ hoặc $x=-\frac{3}{2}$
Lời giải:
a)
$3(x-1)(2x-1)=5(x+8)(x-1)$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-1)[3(2x-1)-5(x+8)]=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-1)(x-43)=0$
$\Rightarrow x-1=0$ hoặc $x-43=0$
$\Rightarrow x=1$ hoặc $x=43$
b)
$9x^2-1=(3x+1)(4x+1)$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x+1)(3x-1)=(3x+1)(4x+1)$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x+1)(4x+1)-(3x+1)(3x-1)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x+1)[(4x+1)-(3x-1)]=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x+1)(x+2)=0$
$\Rightarrow 3x+1=0$ hoặc $x+2=0$
$\Rightarrow x=\frac{-1}{3}$ hoặc $x=-2$
c)
$(x+7)(3x-1)=49-x^2=(7-x)(7+x)$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+7)(3x-1)-(7-x)(7+x)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+7)(3x-1-7+x)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+7)(4x-8)=0$
$\Rightarrow x+7=0$ hoặc $4x-8=0$
$\Rightarrow x=-7$ hoặc $x=2$
d)
$x^3-5x^2+6x=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x(x^2-5x+6)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x(x-2)(x-3)=0$
$\Rightarrow x=0; x-2=0$ hoặc $x-3=0$
$\Rightarrow x=0; x=2$ hoặc $x=3$
e)
$2x^3+3x^2-32x=48$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x^3+3x^2-32x-48=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x^2(x-4)+11x(x-4)+12(x-4)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-4)(2x^2+11x+12)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-4)[2x(x+4)+3(x+2)]=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-4)(x+4)(2x+3)=0$
$\Rightarrow x-4=0; x+4=0$ hoặc $2x+3=0$
$\Rightarrow x=4; x=-4$ hoặc $x=-\frac{3}{2}$
Giải các phương trình sau bằng cách đưa về phương trình tích
a) 2x(x-5)+4(x-5)=0
b) 3x-15=2x(x-5)
c) (2x+1)(3x-2)=(5x-8)(2x+1)
d) (4x^2-1+(2x+1)(3x-5)
\(a,2x\left(x-5\right)+4\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(2x+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\2x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\2x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{5;-2\right\}\)
\(b,3x-15=2x\left(x-5\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow3\left(x-5\right)-2x\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(-2x+3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\-2x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\2x=3\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{5;\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
\(c,\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)=\left(5x-8\right)\left(2x+1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)-\left(5x-8\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2-5x+8\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(-2x+6\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=0\\-2x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=-1\\2x=6\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2};3\right\}\)
Câu d xem lại đề
Đưa các phương trình sau về dạng a x 2 + 2 b ' x + c = 0 và giải chúng. Sau đó, dùng bảng số hoặc máy tính để viết gần đúng nghiệm tìm được (làm tròn kết quả đến chữ số thập phân thứ hai):
a ) 3 x 2 − 2 x = x 2 + 3 b ( 2 x - 2 ) − 1 = ( x + 1 ) ( x − 1 ) c ) 3 x 2 + 3 = 2 ( x + 1 ) d ) 0 , 5 x ( x + 1 ) = x - 1 2
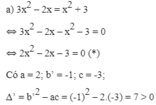
Phương trình (*) có hai nghiệm phân biệt:
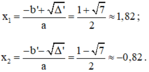

Có: a = 3; b’ = -2√2; c = 2;
Δ ’ = b ’ 2 – a c = ( - 2 √ 2 ) 2 – 3 . 2 = 2 > 0
Vì Δ’ > 0 nên phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
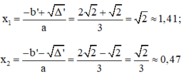
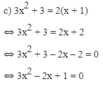
Phương trình có a = 3; b’ = -1; c = 1;
Δ ’ = b ’ 2 – a c = ( - 1 ) 2 – 3 . 1 = - 2 < 0
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm.
d)
0 , 5 x ( x + 1 ) = ( x – 1 ) 2 ⇔ 0 , 5 x 2 + 0 , 5 x = x 2 – 2 x + 1 ⇔ x 2 – 2 x + 1 – 0 , 5 x 2 – 0 , 5 x = 0 ⇔ 0 , 5 x 2 – 2 , 5 x + 1 = 0 ⇔ x 2 – 5 x + 2 = 0
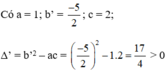
Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt:
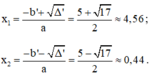
a, \(2x^3+3x^2-32x=48\)
b, \(\dfrac{3}{5x-1}+\dfrac{2}{3-5x}=\dfrac{4}{\left(1-5x\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
giải phương trình giúp mik nhanh nhé
a)(-3x2+5x2-9x+15):(-3x+5)
b)(x4-2x3+2x-1):(x2-1)
c)(5x4+9x3-2x2-4x-8):(x-1)
d)(5x3+14x2+12x+8):(x+2)
b: \(\dfrac{\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)-2x\left(x^2-1\right)}{x^2-1}\)
\(=x^2-2x+1\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)^2\)
c: \(=\dfrac{5x^4-5x^3+14x^3-14x^2+12x^2-12x+8x-8}{x-1}\)
\(=5x^3+14x^2+12x+8\)