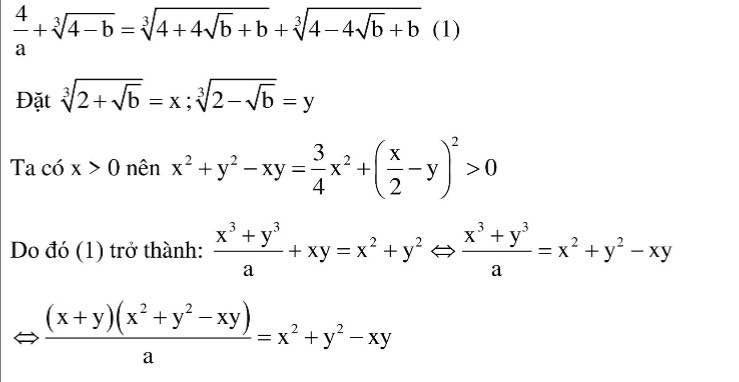Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên \(3\sqrt{x}+4\sqrt{y}\)\(=\sqrt[]{320}\)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
1. Tìm các số nguyên dương a; b sao cho:dfrac{4}{a} + 3sqrt{4-b} 3sqrt{4+4sqrt{b}+b} + 3sqrt{4-4sqrt{b}+b}2. Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyênx^3-y^3-6x^2+12x27
Đọc tiếp
1. Tìm các số nguyên dương a; b sao cho:
\(\dfrac{4}{a}\) \(+\) 3\(\sqrt{4-b}\) \(=\) 3\(\sqrt{4+4\sqrt{b}+b}\) \(+\) 3\(\sqrt{4-4\sqrt{b}+b}\)
2. Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên
\(x^3-y^3-6x^2+12x=27\)
đăng câu hỏi kiểu j mà đặng đc lên như thế này đấy
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1.
Đặt \(\sqrt[3]{2+\sqrt{b}}=x;\sqrt[3]{2-\sqrt{b}}=y\)
Do \(x>0\Rightarrow x^2+y^2-xy=\dfrac{3}{4}x^2+\left(\dfrac{1}{2}x-y\right)^2>0\)
\(PT\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^3+y^3}{a}+xy=x^2+y^2\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x+y\right)\left(x^2-xy+y^2\right)}{a}=x^2-xy+y^2\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-xy+y^2\right)\left(\dfrac{x+y}{a}-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x+y}{a}=1\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt[3]{2+\sqrt{b}}+\sqrt[3]{2-\sqrt{b}}=a\left(1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt[3]{2+\sqrt{b}}+\sqrt[3]{2-\sqrt{b}}\right)^3=a^3\\ \Leftrightarrow4+3a\sqrt[3]{4-b}=a^3\left(2\right)\\ \Rightarrow4-b=\left(\dfrac{a^3-4}{3a}\right)^3\)
Mặt khác \(b\in \mathbb{Z^+}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(a^3-4\right)⋮3a\Rightarrow\left(a^3-4\right)⋮a\\ \Rightarrow4⋮a\Rightarrow a\in\left\{1;2;4\right\}\)
Với \(a=1\Rightarrow4-b=1\Rightarrow b=5\)
Với \(a=2;a=4\Rightarrow b\notin \mathbb{Z}\)
Vậy \(\left(a;b\right)=\left(1;5\right)\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Bài 1:a) Chứng minh rằng không tồn tại các cặp số x,y thỏa mãn:
8x2+26xy+29y2=10001
b) Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên 2xy-2y+x^2-4x+2=0
c) Giải phương trình 4+2\(\sqrt{2-2x^2}\)=3\(\sqrt{x}+3\sqrt{2-x}\)
a) Tìm nghiệm nguyên của phương trình: \(2y^2-x+2xy=y+4\)
b) Giải phương trình : ( \(1+x\sqrt{x^2+1}\))(\(\sqrt{x^2+1}-x\)) = 1
\(\left(1+x\sqrt{x^2+1}\right)\left(\sqrt{x^2+1}-x\right)=1\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1+x\sqrt{x^2+1}}{\sqrt{x^2+1}+x}=1\)
\(\Rightarrow1+x\sqrt{x^2+1}=\sqrt{x^2+1}+x\)
\(\Rightarrow1+x\sqrt{x^2+1}-\sqrt{x^2+1}-x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow-\left(x-1\right)+\left(x-1\right)\sqrt{x^2+1}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x^2+1}-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\\sqrt{x^2+1}-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\\sqrt{x^2+1}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x^2+1=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(a,2y^2-x+2xy=y+4\\ \Leftrightarrow2y\left(x+y\right)-\left(x+y\right)=4\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2y-1\right)\left(x+y\right)=4=4\cdot1=\left(-4\right)\left(-1\right)=\left(-2\right)\left(-2\right)=2\cdot2\)
Vì \(x,y\in Z\Leftrightarrow2y-1\) lẻ
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2y-1=1\\x+y=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2y-1=-1\\x+y=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy PT có nghiệm \(\left(x;y\right)=\left\{\left(3;1\right);\left(4;0\right)\right\}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên sau
\(\sqrt[3]{x}+\sqrt[3]{y}=\sqrt[3]{1984}\)
Gọi 1/4 số a là 0,25 . Ta có :
a . 3 - a . 0,25 = 147,07
a . (3 - 0,25) = 147,07 ( 1 số nhân 1 hiệu )
a . 2,75 = 147,07
a = 147,07 : 2,75
a = 53,48
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Gọi 1/4 số a là 0,25 . Ta có :
a . 3 - a . 0,25 = 147,07
a . (3 - 0,25) = 147,07 ( 1 số nhân 1 hiệu )
a . 2,75 = 147,07
a = 147,07 : 2,75
a = 53,48
mình nha
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Đặt căn bậc 3 của x=a;căn bậc 3 của y=b>>>a+b=4 căn bậc 3 của 31
>>>a^3+b^3+3ab(a+b)=1984>>>Dễ chứng minh ab31 là lập phương của một số tự nhiên >>>ab=961x^3>>>tự giải nha bn
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên \(\sqrt{2x-1}+2\sqrt{2y-2}+3\sqrt{4z-3}=x+y+2z+4\)
Điều kiện xác định : \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ge\frac{1}{2}\\y\ge1\\z\ge\frac{3}{4}\end{cases}}\)
Ta có : \(\sqrt{2x-1}+2\sqrt{2y-2}+3\sqrt{4z-3}=x+y+2z+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{2x-1}+4\sqrt{2y-2}+6\sqrt{4z-3}=2x+2y+4z+8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1-2\sqrt{2x-1}+1\right)+\left(2y-2-4\sqrt{2y-2}+4\right)+\left(4z-3+6\sqrt{4z-3}+9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{2x-1}-1\right)^2+\left(\sqrt{2y-2}-2\right)^2+\left(\sqrt{4z-3}-3\right)^2=0\)
Mà ta luôn có \(\left(\sqrt{2x-1}-1\right)^2\ge0\), \(\left(\sqrt{2y-2}-2\right)^2\ge0\), \(\left(\sqrt{4z-3}-3\right)^2\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(\sqrt{2x-1}-1\right)^2+\left(\sqrt{2y-2}-2\right)^2+\left(\sqrt{4z-3}-3\right)^2\ge0\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(\hept{\begin{cases}\sqrt{2x-1}-1=0\\\sqrt{2y-2}-2=0\\\sqrt{4z-3}-3=0\end{cases}}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=1\\y=3\\z=3\end{cases}}\) (TMDK)
Vậy (x;y;z) = (1;3;3)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm nghiệm nguyên của phương trình \(\sqrt{x+y+3}\)+1=\(\sqrt{x}\)+\(\sqrt{y}\)
Lời giải:
PT $\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{x+y+3}=\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}-1$
$\Rightarrow x+y+3=(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}-1)^2$
$\Leftrightarrow x+y+3=x+y+1-2(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}-\sqrt{xy})$
$\Leftrightarrow 1+\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}-\sqrt{xy}=0(*)$
$\Rightarrow (\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y})^2=(\sqrt{xy}-1)^2$
$\Rightarrow 4\sqrt{xy}=xy+1-x-y\in\mathbb{Z}$
Ta có nhận xét sau: Với số không âm $a$ bất kỳ thì khi $\sqrt{a}$ là số hữu tỉ thì $\sqrt{a}$ cũng là số chính phương.
Do đó: $\sqrt{xy}$ là scp
Kết hợp $(*)$ suy ra $\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\in\mathbb{Z}$
$\sqrt{x}(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y})=x+\sqrt{xy}\in\mathbb{Z}$
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{x}=\frac{x+\sqrt{xy}}{\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}}\in\mathbb{Q}$
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{x}$ là scp. Kéo theo $\sqrt{y}$ là scp.
Từ $(*)$ ta cũng có $(\sqrt{x}-1)(1-\sqrt{y})=-2$
Đến đây thì với $\sqrt{x}, \sqrt{y}\in\mathbb{Z}$ ta có pt tích khá đơn giản.
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải Phương Trình Nghiệm nguyên:
\(\sqrt{x+\sqrt{x+\sqrt{x+\sqrt{x}}}}=y\)
Bình phương hai vế ta có:
\(x+\sqrt{x+\sqrt{x+\sqrt{x}}}=y^2\Rightarrow\sqrt{x+\sqrt{x+\sqrt{x}}}=y^2-x=t\)
Tiếp túc bình phương và chuyển vế, ta có:
\(\sqrt{x+\sqrt{x}}=t^2-x=u\)
\(x+\sqrt{x}=u^2\)
Do y nguyên, x nguyên nên t nguyên, suy ra u nguyên, suy ra u2 nguyên, vậy thì \(\sqrt{x}\) nguyên.
Ta có \(\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)=u^2\). Hai số tự nhiên liên tiếp có tích là số chính phương u2 nên \(\sqrt{x}=0\Rightarrow x=0.\)
Từ đó suy ra y = 0.
Vậy nghiệm của phương trình là (x; y) = (0; 0).
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm nghiệm nguyên dương của phương trình \(\sqrt{x+y+3}+1=\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\).
\(\sqrt{x+y+3}+1=\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\)
Bình phương 2 vế, ta có:
\(x+y+3+1=x+y\)
\(x+y+3+1-x-y=0\)
\(4=0\) (vô lý)
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm
-Chúc bạn học tốt-
Đúng 0
Bình luận (3)
(x,y) hoán vị của (4,9) . có vẻ hoạt động
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên: \(13\sqrt{x}-7\sqrt{y}=\sqrt{2000}\)