giải phương trình x^2-2x-3

Những câu hỏi liên quan
3.15 giải các phương trình sau :
a) ( x - 6 ) ( 2x - 5 ) ( 3x + 9 ) = 0
b) 2x( x - 3 ) + 5( x - 3 ) = 0
c) ( x^2 - 4 ) - ( x - 2 ) ( 3 - 2x ) =0
3.16 tìm m để phương trình sau có nghiệm :
x=-7 ( 2m - 5 )x - 2m^2 + 8
3.17 giải các phương trình sau :
a) ( 2x - 1 )^2 - ( 2x + 1 ) = 0
\(a,\left(x-6\right)\left(2x-5\right)\left(3x+9\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-6=0\Leftrightarrow x=6\\2x-5=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\3x+9=0\Leftrightarrow x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,2x\left(x-3\right)+5\left(x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+5\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\Leftrightarrow x=3\\2x+5=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(c,x^2-4-\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)-\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2-3+2x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x=-7\left(2m-5\right)x-2m^2+8\Leftrightarrow x+7\left(2m-5\right)=8-2m^2\Leftrightarrow x\left(14m-34\right)=8-2m^2\)
\(ycđb\Leftrightarrow14m-34\ne0\Leftrightarrow m\ne\dfrac{34}{14}\)\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{8-2m^2}{14m-34}\)
\(3.17\Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x+1-2x-1=0\Leftrightarrow4x^2-6x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(4x-6\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
3.15:
a, \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-6=0\\2x-5=0\\3x+9=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\x=-\dfrac{9}{3}=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b, \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(2x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\2x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c, \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)-\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2-3+2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\3x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
3.16
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2m-5\right).-7-2m^2+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-14m+35-2m^2+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-14m-2m^2+43=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2\left(7m+m^2\right)=-43\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\left(7-m\right)=\dfrac{43}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{m\left(7-m\right)}{1}-\dfrac{43}{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{14m-2m^2}{2}-\dfrac{43}{2}=0\)
pt vô nghiệm
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình ( giải theo trường hợp phương trình chứa biến ở mẫu)
a) 3 phần x-2 = 2x-1 phần x-2 -x
b) x+2 phần x = 2x+3 phần 2x-4
a: \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{x-2}=\dfrac{2x-1}{x-2}-\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{x-2}\)
=>3=2x-1-x^2+2x
=>3=-x^2+4x-1
=>x^2-4x+1+3=0
=>x^2-4x+4=0
=>x=2(loại)
b: =>(x+2)(2x-4)=x(2x+3)
=>2x^2-4x+4x-8=2x^2+3x
=>3x=-8
=>x=-8/3(nhận)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1) Giải các phương trình sau : a) x-3/x=2-x-3/x+3 b) 3x^2-2x-16=0 2) Giải bất phương trình sau: 4x-3/4>3x-5/3-2x-7/12
\(a,\dfrac{x-3}{x}=\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}\)\(\left(đk:x\ne0,-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-3}{x}-\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-x\left(x-3\right)}{x\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9-x^2+3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(n\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(b,\dfrac{4x-3}{4}>\dfrac{3x-5}{3}-\dfrac{2x-7}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x-3}{4}-\dfrac{3x-5}{3}+\dfrac{2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(4x-3\right)-4\left(3x-5\right)+2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-9-12x+20+2x-7>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+4>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x>-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-2\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình và bất phương trình sau:
a
)
|
3
x
|
x
+
6
b
)
x
+
2
x
-
2
-
1
x
2
x...
Đọc tiếp
Giải phương trình và bất phương trình sau:
a ) | 3 x | = x + 6 b ) x + 2 x - 2 - 1 x = 2 x x - 2 c ) ( x + 1 ) ( 2 x – 2 ) – 3 > – 5 x – ( 2 x + 1 ) ( 3 – x )
a) |3x| = x + 6 (1)
Ta có 3x = 3x khi x ≥ 0 và 3x = -3x khi x < 0
Vậy để giải phương trình (1) ta quy về giải hai phương trình sau:
+ ) Phương trình 3x = x + 6 với điều kiện x ≥ 0
Ta có: 3x = x + 6 ⇔ 2x = 6 ⇔ x = 3 (TMĐK)
Do đó x = 3 là nghiệm của phương trình (1).
+ ) Phương trình -3x = x + 6 với điều kiện x < 0
Ta có -3x = x + 6 ⇔ -4x + 6 ⇔ x = -3/2 (TMĐK)
Do đó x = -3/2 là nghiệm của phương trình (1).
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình đã cho S = {3; -3/2}
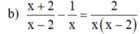
ĐKXĐ: x ≠ 0, x ≠ 2
Quy đồng mẫu hai vễ của phương trình, ta được:
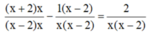
![]()
![]()
![]()
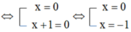
![]()
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S = {-1}
c) (x + 1)(2x – 2) – 3 > –5x – (2x + 1)(3 – x)
⇔ 2x2 – 2x + 2x – 2 – 3 > –5x – (6x – 2x2 + 3 – x)
⇔ 2x2 – 5 ≥ –5x – 6x + 2x2 – 3 + x
⇔ 10x ≥ 2 ⇔ x ≥ 1/5
Tập nghiệm: S = {x | x ≥ 1/5}
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình qui về phương trình tích
a/x\(^2\)+3x=0
b/x-2x\(^2\)=0
c/(x-7)(2x+3)=x(x-7)
d/(x-2)(x+3)=(x-2)(3x-1)
a: =>x(x+3)=0
=>x=0 hoặc x=-3
b: =>x(1-2x)=0
=>x=0 hoặc x=1/2
c: =>(x-7)(2x+3-x)=0
=>(x-7)(x+3)=0
=>x=7 hoặc x=-3
d: =>(x-2)(3x-1-x-3)=0
=>(x-2)(2x-4)=0
=>x=2
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
a)
`x^2 +3x=0`
`<=>x(x+3)=0`
\(< =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ < =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b)
`x-2x^2 =0`
`<=>x(1-2x)=0`
\(< =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\1-2x=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ < =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c)
`(x-7)(2x+3)=x(x-7)`
`<=>(x-7)(2x+3)-x(x-7)=0`
`<=>(x-7)(2x+3-x)=0`
`<=>(x-7)(x+3)=0`
\(< =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-7=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ < =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=7\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
d)
`(x-2)(x+3)=(x-2)(3x-1)`
`<=>(x-2)(x+3)-(x-2)(3x-1)=0`
`<=>(x-2)(x+3-3x+1)=0`
`<=>(x-2)(-2x+4)=0`
\(< =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\-2x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ < =>x=2\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
a)\(x^2+3x=0\)
<=>x(x+3)=0
x=0 hoặc x+3=0
x=0 hoặc x=-3
b)x-2x2=0
x(1-2x)=0
x=0 hoặc 1-2x=0
x=0 hoặc x=0,5
c)(x-7)(2x+3)=4(x-7)
(x-7)(2x+3)-4(x-7)=0
(x-7)(2x+3-4)=0
x-7=0 hoặc 2x+3-4=0
x=7 hoặc x=0,5
d)(x-2)(x+3)=(x-2)(3x-1)
(x-2)(x+3)-(x-2)(3x-1)=0
(x-2)(x+3-3x+1)=0
x-2=0 hoặc x+3-3x+1=0
x=2 hoặc x-3x=-3-1
-2x=-4
x=2
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a) Giải bất phương trình:
\(\sqrt{x^2+2x}+\sqrt{x^2+3x}\) ≥ \(2x\)
b) Giải hệ phương trình
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^3+6x^2y+9xy^2+y^3=0\\\sqrt{x-y}+\sqrt{x+y}=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
a, ĐKXĐ : \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\le-3\\x\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
TH1 : \(x\le-3\) ( LĐ )
TH2 : \(x\ge0\)
BPT \(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+x^2+3x+2\sqrt{\left(x^2+2x\right)\left(x^2+3x\right)}\ge4x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x^2+2x\right)\left(x^2+3x\right)}\ge x^2-\dfrac{5}{2}x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}\ge2x-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< \dfrac{5}{2}\\x\ge-2\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge\dfrac{5}{2}\\4x^2+20x+24\ge4x^2-20x+25\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}0\le x< \dfrac{5}{2}\\x\ge\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge0\)
Vậy \(S=R/\left(-3;0\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình:
Giải các phương trình:
\(x^2-2x+3=\frac{6}{x^2-2x+4}\)
Đặt \(y=x^2-2x+3=\left(x-1\right)^2+2\ge2\), ta có:
\(x^2-2x+3=\frac{6}{x^2-2x+4}\Leftrightarrow y=\frac{6}{y+1}\Leftrightarrow y\left(y+1\right)=6\Leftrightarrow y^2+y-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(y+3\right)\left(y-2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y=2\\y=-3\end{cases}\Rightarrow y=2\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=1}\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{1\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trìnhsau x/2x-6-x/2x+2=2x/(x+1)(x-3) Giải bất phương trình sau 12x+1/12_< 9x+1/3 - 8x+1/4
\(\dfrac{x}{2x-6}-\dfrac{x}{2x+2}=\dfrac{2x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne-1,x\ne3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{2\left(x-3\right)}-\dfrac{x}{2\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}-\dfrac{x\left(x-3\right)}{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{2x\cdot2}{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x+1\right)-x\left(x-3\right)=4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-x^2+3x=4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-x^2+3x-4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x=0\)
Phương trình có vô số nghiệm , trừ x = -1,x = 3
Vậy ...
\(\dfrac{12x+1}{12}< \dfrac{9x+1}{3}-\dfrac{8x+1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12\cdot\dfrac{12x+1}{12}< 12\cdot\dfrac{9x+1}{3}-12\cdot\dfrac{8x+1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x+1< 4\left(9x+1\right)-3\left(8x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x+1< 36x+4-24x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x+1< 12x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-12x< 1-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x< 0\)
Vậy S = {x | x \(\in R\)}
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình x + 2 x = 2 x + 3 2 ( x - 2 )
Bước 1: Điều kiện xác định: x ≠ 0; x ≠ 2.
Bước 2: Quy đồng mẫu hai vế rồi khử mẫu
Ta có: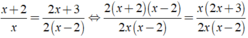
⇒ 2( x - 2 )( x + 2 ) = x( 2x + 3 )
Bước 3: Giải phương trình
Ta có: 2( x - 2 )( x + 2 ) = x( 2x + 3 )
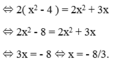
Bước 4: Kết luận
So sánh với ĐKXĐ, ta thấy x = - 8/3 thỏa mãn.
Vậy phương trình đã cho có tập nghiệm S = { - 8/3 }.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 2: giải phương trình sau a) X^4-x^2-20b) (x+1)^4-x^2+2)^20c)3x^2-2x-80Bài 3: giải phương trình sau a) x^3-0,250b) x^4+2x^3+x^20c) x^3-10d) 6x^2-7x+20Mong có người giải giùm xin kẻm ơn :
Đọc tiếp
Bài 2: giải phương trình sau
a) \(X^4\)-\(x^2\)-2=0
b) (x+1)\(^4\)-x\(^2\)+2)\(^2\)=0
c)3x\(^2\)-2x-8=0
Bài 3: giải phương trình sau
a) x\(^3\)-0,25=0
b) x\(^4\)+2x\(^3\)+x\(^2\)=0
c) x\(^3\)-1=0
d) 6x\(^2\)-7x+2=0
Mong có người giải giùm xin kẻm ơn :>
Bài 3:
b: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+1\right)^2=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{0;-1\right\}\)
c: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)=0\)
=>x-1=0
hay x=1
d: \(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-3x-4x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)\left(3x-2\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{\dfrac{1}{2};\dfrac{2}{3}\right\}\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)

























