32x+3x+3=759

Những câu hỏi liên quan
tìm x:
a)(2x-3)+(3x^2+1)-6x*(x^2-x+1)+3x^2-2x=10
b)(3x+1)*(x-2)-x*((3x-5)=-8-5x
c)(4x-3)*(16x^2+12+9)-32x^2*(2x-1)-32x^2+x=20
a: \(\left(2x-3\right)\left(3x^2+1\right)-6x\left(x^2-x+1\right)+3x^2-2x=10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^3+2x-9x^2-3-6x^3+6x^2-6x+3x^2-2x=10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x-3=10\)
=>-6x=13
hay x=-13/6
b: \(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-3x+x-2-3x^2+5x=-8-5x\)
=>3x-2=-5x-8
=>8x=-6
hay x=-3/4
c: \(\Leftrightarrow64x^3-27-64x^3+32x^2-32x^2+x=20\)
=>x-27=20
hay x=47
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
2x^3 + 3X^2 - 32x =48
Ta có: 2x3 + 3x2 - 32x =48
<=> 2x3 + 3x2 - 32x - 48 =0
<=> x2(2x+3) - 16(2x+3) =0
<=> (x2-16)(2x+3) =0
<=> (x-4)(x+4)(2x+3) =0
<=> x-4=0 hoặc x+4=0 hoặc 2x+3=0
<=> x=4 hoặc x=-4 hoặc x= \(\dfrac{-3}{2}\)
Vậy phương trình trên có tập nghiệm là S={4;-4;\(\dfrac{-3}{2}\)}
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
2x3+3x2-32x=48
⇔2x3+3x2-32x-48=0
⇔x2(2x+3)-16(2x+3)=0
⇔(2x+3)(x2-16)=0
⇔(2x+3)(x-4)(x+4)=0
⇔2x+3=0 hoặc x-4=0 hoặc x+4=0
1.2x+3=0⇔2x=-3⇔x=-3/2
2.x-4=0⇔x=4
3.x+4=0⇔x=-4
phương trình có 3 nghiệm:x=-3/2 và x=4 và x=-4
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Ta có: \(2x^3+3x^2-32x=48\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^3+3x^2-32x-48=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(2x+3\right)-16\left(2x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+3\right)\left(x^2-16\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+3=0\\x^2-16=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=-3\\x^2=16\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\\x=4\\x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{3}{2};4;-4\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
2x^3+3x^2-32x=48
Giá trị của x để 3 x + 1 = 3 2 x - 3 là
Giải phương trình:
13
x
-
3
2
x
+
7
+
1
2
x...
Đọc tiếp
Giải phương trình: 13 x - 3 2 x + 7 + 1 2 x + 7 = 6 x - 3 x + 3
Điều kiện xác định: x ≠ ±3; x ≠ -7/2.
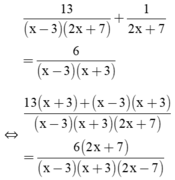
⇒ 13(x + 3) + (x – 3)(x + 3) = 6(2x + 7)
⇔ 13x + 39 + x2 – 9 = 12x + 42
⇔ x2 + x – 12 = 0
⇔ x2 +4x – 3x – 12 = 0
⇔ x(x + 4) – 3(x + 4) = 0
⇔ (x – 3)(x + 4) = 0
⇔ x – 3 = 0 hoặc x + 4 = 0
x – 3 = 0 ⇔ x = 3 (không thỏa mãn đkxđ)
x + 4 = 0 ⇔ x = -4 (thỏa mãn đkxđ).
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {-4}.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cộng các phân thức khác mẫu thức:
3
2
x
+
3
x
-
3
2
x
-
1
+
2
x
2
+
1
4
x
2
-
2
x
Đọc tiếp
Cộng các phân thức khác mẫu thức: 3 2 x + 3 x - 3 2 x - 1 + 2 x 2 + 1 4 x 2 - 2 x
Mẫu thức chung: 4 x 2 - 2 x = 2 x 2 x - 1
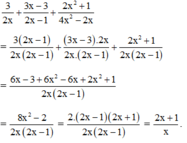
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(2x^3+3x^2-32x=48\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^3+3x^2-32x-48=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(2x+3\right)-16\left(2x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-16\right)\left(2x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)\left(2x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4=0\\x+4=0\\2x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-4\\x=-\frac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(2x^3 + 3x^2 - 32x =48\)
Chứng tỏ cặp phân thức sau bằng nhau:
3
2
x
-
3
và
3
x
+
6
2
x
2
+
x
-...
Đọc tiếp
Chứng tỏ cặp phân thức sau bằng nhau:
3 2 x - 3 và 3 x + 6 2 x 2 + x - 6
- Cách 1: Dùng định nghĩa hai phân thức bằng nhau:
3(2x2 + x – 6) = 6x2 + 3x – 18
(2x – 3)(3x + 6) = 2x.(3x + 6) – 3.(3x + 6) = 6x2 + 12x – 9x – 18 = 6x2 + 3x – 18
⇒ 3(2x2 + x – 6) = (2x – 3)(3x + 6)
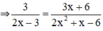
- Cách 2: Rút gọn phân thức:
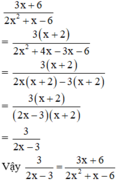
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) x - 5(x - 2) = 6x
b) 23 + 3x2 - 32x = 48
c) (3x + 1)(x - 3)2 = (3x + 1)(2x - 5)2
d) 9x2 - 1 = (3x + 1)(4x + 1)
\(a,x-5\left(x-2\right)=6x\\ \Leftrightarrow x-5x+10-6x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow-10x+10=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=1\\ b,2^3+3x^2-32x=48\\ \Leftrightarrow3x^2-32x+8=48\\ \Leftrightarrow3x^2-32x-40=0\)
Nghiệm xấu lắm bn
\(c,\left(3x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)^2=\left(3x+1\right)\left(2x-5\right)^2\\ \Leftrightarrow c,\left(3x+1\right)\left[\left(2x-5\right)^2-\left(x-3\right)^2\right]\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(2x-5-x+3\right)\left(2x-5+x-3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(3x-8\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=2\\x=\dfrac{8}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(d,9x^2-1=\left(3x+1\right)\left(4x+1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(4x+1\right)-\left(3x-1\right)\left(3x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(4x+1-3x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
\(b,2x^3+3x^2-32x-48=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x^3-8x^2\right)+\left(11x^2-44x\right)+\left(12x-48\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2x^2\left(x-4\right)+11x\left(x-4\right)+12\left(x-4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(2x^2+11x+12\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left[\left(2x^2+8x\right)+\left(3x+12\right)\right]=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left[2x\left(x+4\right)+3\left(x+4\right)\right]=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(2x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\\x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)

















