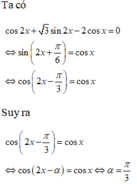giải phương trình sau : \(\cos^2x\cos2x=0\)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải phương trình lượng giác: \(\cos^23x.\cos2x-\cos^2x=0\)
Giải phương trình :
\(2^{\cos2x}\cos x+2\cos^2x=2^{\cos2x-1}+4\cos^3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2^{\cos2x-1}\left(2\cos x-1\right)=2\cos^2x\left(2\cos x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2\cos x-1\right)\left(2^{\cos2x}-2\cos^2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}\cos x=\frac{1}{2}\\2^{\cos2x}=\cos2x+1\end{array}\right.\)
* Với \(\cos x=\frac{1}{2}\) ta có \(x=\frac{\pi}{3}=k2\pi,k\in Z\)
* Với \(2^{\cos2x}=\cos2x+1\) (*), đặt \(t=\cos2x;t\in\left[-1;1\right]\)
Phương trình trở thành \(2^t-t-1=0\)
Xét hàm số \(f\left(t\right)=2^t-t-1,t\in\left[-1;1\right]\)
Có \(f'\left(t\right)=2^t\ln2-1,t\in\left[-1;1\right];f'\left(t\right)=0\) có đúng 1 nghiệm nên phương trình \(f\left(t\right)=0\) có tối đa 2 nghiệm. Mà \(f\left(0\right)=f\left(1\right)=0\) nên \(t=0;t=1\) là tất cả các nghiệm của phương trình \(f\left(t\right)=0\)
Do đó phương trình (*) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}\cos2x=0\\\cos2x=1\end{array}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}x=\frac{\pi}{4}+k\frac{\pi}{2}\\x=k\pi\end{array}\right.\) \(k\in Z\)
Vậy phương trình đã cho có 3 nghiệm là :
\(x=\frac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi;x=\frac{\pi}{4}+k\frac{\pi}{2};x=k\pi;k\in Z\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình lượng giác sau:1) a/ cosleft(10x+12right)+4sqrt{2}sinleft(5x+6right)-40 b/ cosleft(4x+2right)+3sinleft(2x+1right)22) a/ cos2x+sin^2x+2cosx+10 b/ 4sin^22x-8cos^2x+ 30 c/ 4cos2x+4sin^2x+4sinx13) a/ tanx+cotx2 b/ 2tanx-2cotx34) a/ 2sin2x+8tanx9sqrt{3} b/ 2cos2x+tan^2x55) a/ left(3+cotxright)^25left(3+cotxright) b/ 4left(sin^2x+dfrac{1}{sin^2x}right)-4left(sinx+dfrac{1}{sinx}right)7
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình lượng giác sau:
1) a/ \(cos\left(10x+12\right)+4\sqrt{2}sin\left(5x+6\right)-4=0\)
b/ \(cos\left(4x+2\right)+3sin\left(2x+1\right)=2\)
2) a/ \(cos2x+sin^2x+2cosx+1=0\)
b/ \(4sin^22x-8cos^2x+ 3=0\)
c/ \(4cos2x+4sin^2x+4sinx=1\)
3) a/ \(tanx+cotx=2\)
b/ \(2tanx-2cotx=3\)
4) a/ \(2sin2x+8tanx=9\sqrt{3}\)
b/ \(2cos2x+tan^2x=5\)
5) a/ \(\left(3+cotx\right)^2=5\left(3+cotx\right)\)
b/ \(4\left(sin^2x+\dfrac{1}{sin^2x}\right)-4\left(sinx+\dfrac{1}{sinx}\right)=7\)
1a.
Đặt \(5x+6=u\)
\(cos2u+4\sqrt{2}sinu-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1-2sin^2u+4\sqrt{2}sinu-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2sin^2u-4\sqrt{2}sinu+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sinu=\dfrac{3\sqrt{2}}{2}>1\left(loại\right)\\sinu=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow sin\left(5x+6\right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}5x+6=\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k2\pi\\5x+6=\dfrac{3\pi}{4}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{6}{5}+\dfrac{\pi}{20}+\dfrac{k2\pi}{5}\\x=-\dfrac{6}{5}+\dfrac{3\pi}{20}+\dfrac{k2\pi}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1b.
Đặt \(2x+1=u\)
\(cos2u+3sinu=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1-2sin^2u+3sinu=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2sin^2u-3sinu+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sinu=1\\sinu=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sin\left(2x+1\right)=1\\sin\left(2x+1\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\\2x+1=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k2\pi\\2x+1=\dfrac{5\pi}{6}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{\pi}{12}+k\pi\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{5\pi}{12}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
2a.
\(cos^2x-sin^2x+sin^2x+2cosx+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos^2x+2cosx+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(cosx+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\pi+k2\pi\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Giải các phương trình sau:
\(a,cos2x+4cosx+1=0\)
\(b,cos^22x=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
a, \(cos2x+4cosx+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2cos^2x+4cosx=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2cosx\left(cosx+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
b, \(cos^22x=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4cos^22x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2cosx-1\right)\left(2cosx+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx=\pm\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k\pi\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:
1) \(2\cos4x-3=0\)
2) \(cos5x+2=0\)
3) \(cos2x+0,7=0\)
4) \(cos^22x-\dfrac{1}{4}=0\)
1.
\(2cos4x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos4x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
Mà \(cos4x\in\left[-1;1\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow\) phương trình vô nghiệm.
2.
\(cos5x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos5x=-2\)
Mà \(cos5x\in\left[-1;1\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow\) phương trình vô nghiệm.
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
3.
\(cos2x+0,7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos2x=-\dfrac{7}{10}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=\pm arccos\left(-\dfrac{7}{10}\right)+k2\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\dfrac{arccos\left(-\dfrac{7}{10}\right)}{2}+k\pi\)
4.
\(cos^22x-\dfrac{1}{4}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos^22x=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cos2x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\cos2x=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=\pm\dfrac{2\pi}{3}+k2\pi\\2x=\pm\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\pm\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k\pi\\x=\pm\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình:
\(\dfrac{1+cos2x\times cosx}{cos^2x}+2\left(sin^4x+cos^4x\right)=3\)
Giải phương trình:
\(Tan\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2}+x\right)-3Tan^2x=\dfrac{Cos2x-1}{Cos^2x}\)
Lời giải:
$\tan (\frac{\pi}{2}+x)-3\tan ^2x=\frac{\cos 2x-1}{\cos ^2x}=\frac{2\cos ^2x-2}{\cos ^2x}=\frac{2(\cos ^2x-1)}{\cos ^2x}$
$=\frac{-2\sin ^2x}{\cos ^2x}=-2\tan ^2x$
$\Leftrightarrow \tan (x+\frac{\pi}{2})=\tan ^2x$
Dễ thấy $\tan x=0$ không thỏa mãn nên $\tan x\neq 0$. Do đó pt $\Leftrightarrow \tan ^2x=\tan [\pi +(x-\frac{\pi}{2})]=\tan (x-\frac{\pi}{2})=-\tan (\frac{\pi}{2}-x)=-\cot x =\frac{-1}{\tan x}$
$\Rightarrow \tan ^3x=-1$
$\Rightarrow \tan x=-1$
$\Rightarrow x=\frac{-\pi}{4}+k\pi$ với $k$ nguyên.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm góc
a
∈
π
6
;
π
4
;
π
3
;
π
2
để phương trình cos2x+
3
sin2x-2cosx 0 tương đương với phương trình c...
Đọc tiếp
Tìm góc a ∈ π 6 ; π 4 ; π 3 ; π 2 để phương trình cos2x+ 3 sin2x-2cosx= 0 tương đương với phương trình cos(2x- α )=cosx
A. α = π 3
B. α = π 4
C. α = π 6
![]()
Có bao nhiêu giá trị nguyên của tham số m để phương trình
sin
2
x
+
cos
2
x
+
|
sin
x
+
cos
x
|
-
cos
2
x
+
m
-
m
0
có nghiệm thực? A. 9 B. 2 C. 3 D. 5
Đọc tiếp
Có bao nhiêu giá trị nguyên của tham số m để phương trình sin 2 x + cos 2 x + | sin x + cos x | - cos 2 x + m - m = 0 có nghiệm thực?
A. 9
B. 2
C. 3
D. 5
Đáp án C
Sử dụng tính đơn điệu của hàm số, đánh giá số nghiệm của phương trình.
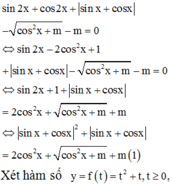
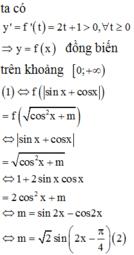

Vậy, có 3 giá trị nguyên của m thỏa mãn yêu cầu đề bài.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)