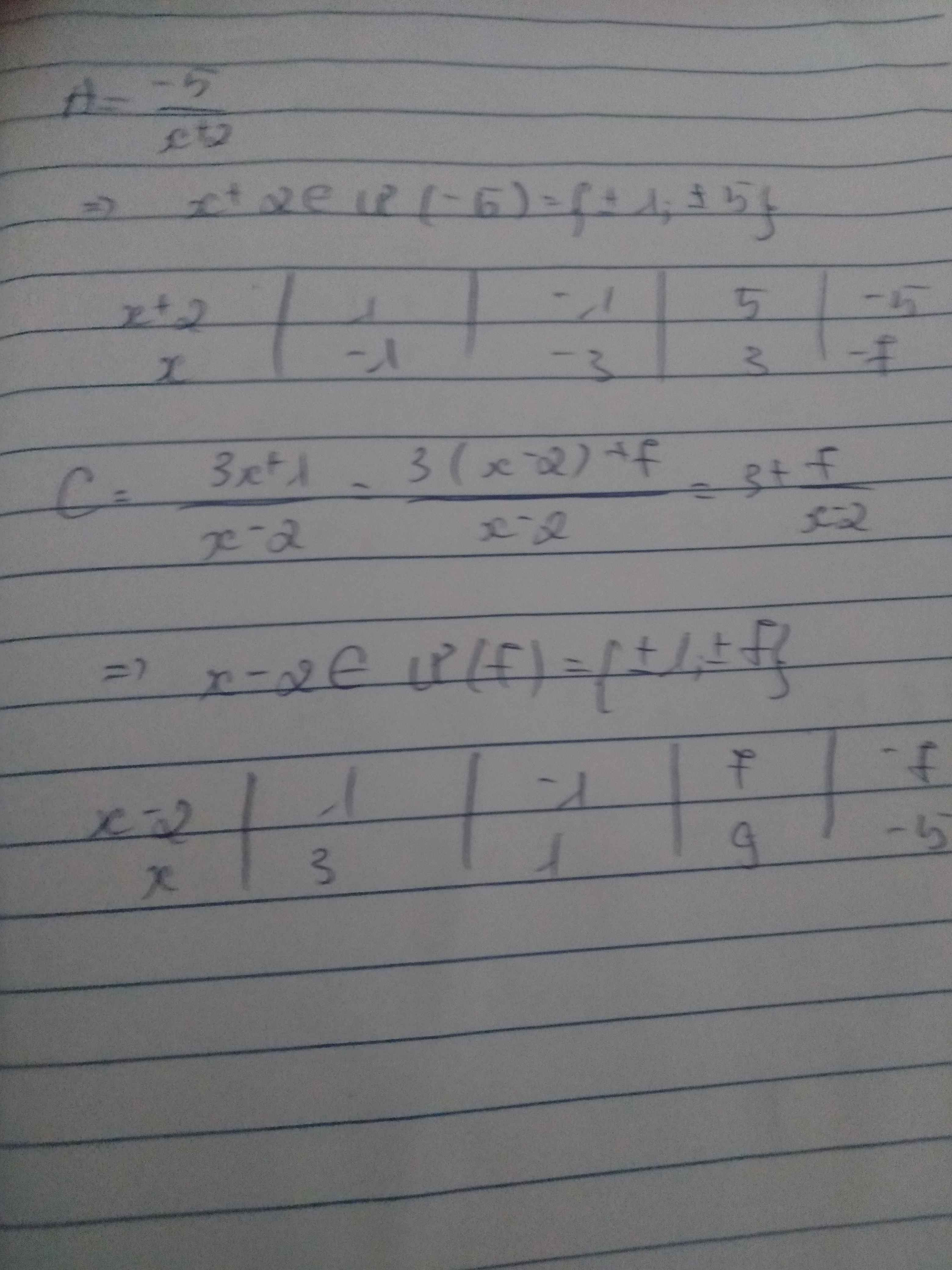Tìm các số nguyên x để: \(\dfrac{x+4}{x-2}\) + \(\dfrac{2x+5}{x-2}\)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
A= \(\dfrac{x-2}{x}\)+\(\dfrac{x-1}{3-x}\)+\(\dfrac{2x^2-6}{x^2-3x}\) và x ≠ 3; 𝑥 ≠ 0
a) Rút gọn A. Tính A khi |x-4|=1
b) Tìm x để A= \(\dfrac{x-4}{2x-3}\) với x ≠ 3/2
c) Tìm x là số nguyên để A nhận giá trị nguyên .
d) Tìm x để A <2
a: \(A=\dfrac{x^2-5x+6-x^2+x+2x^2-6}{x\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{2x^2-4x}{x\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{2x}{x-3}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
. tìm x nguyên để các phân số sau nhận giá rị nguyên
a) \(\dfrac{2}{x-1}\)
b)\(\dfrac{4}{2x-1}\)
c*)\(\dfrac{x+3}{x-1}\)
a, `2/(x-1) in ZZ`.
`=> 2 vdots x - 1`
`=> x-1 in Ư(2)`
`=> x - 1 in {+-1, +-2}`.
`=> x - 1 = 1 => x = 2`.
`=> x - 1 = -1 => x = 0`.
`=> x - 1 = -2 => x = -1`.
`=> x - 1 = 2 => x = 3`.
Vậy `x = 2, 0, - 1, 3`.
b, `4/(2x-1) in ZZ`
`=> 4 vdots 2x - 1`.
`=> 2x - 1 in Ư(4)`
Vì `2x vdots 2 => 2x - 1 cancel vdots 2`
`=> 2x - 1 in {+-1}`
`=> 2x - 1 = -1 => x = 0`.
`=> 2x - 1 = 1 => x = 1`
Vậy `x = 0,1`.
c, `(x+3)/(x-1) in ZZ`.
`=> x + 3 vdots x - 1`
`=> x - 1 + 4 vdots x - 1`.
`=> 4 vdots x-1`
`=> x -1 in Ư(4)`
`=> x - 1 in{+-1, +-2, +-4}`
`x - 1 = 1 => x = 2`.
`x - 1 = -1 => x = 0`.
`x - 1 = 2 =>x = 3`.
`x - 1 = -2 => x = -1`.
`x - 1 = 4 => x = 5`.
`x - 1 = -4 => x = -3`.
Vậy `x = 2, 0 , +-1, 5, -3`.
Đúng 8
Bình luận (2)
Tìm tất cả các số nguyên x,y
a)\(\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{5} mà x+y=35\)
b)\(\dfrac{x+2}{y+10}=\dfrac{1}{5} và y-3x=2\)
c)\(\dfrac{x}{4}=\dfrac{y}{5} và 2x-y=15\)
\(a.\)
\(\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{5}\)
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau :
\(\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{5}=\dfrac{x+y}{2+5}=\dfrac{35}{7}=5\)
\(\Rightarrow x=5\cdot2=10\\ y=5\cdot5=25\)
\(b.\)
\(\dfrac{x+2}{y+10}=\dfrac{1}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x+2}{1}=\dfrac{y+10}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3x+6}{3}=\dfrac{y+10}{5}\)
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau :
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3x+6}{3}=\dfrac{y+10}{5}=\dfrac{y+10-3x-6}{5-3}=\dfrac{2-4}{2}=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x+6=-3\\y+10=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\y=-15\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(c.\)
\(\dfrac{x}{4}=\dfrac{y}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x}{8}=\dfrac{y}{5}\)
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau :
\(\dfrac{2x}{8}=\dfrac{y}{5}=\dfrac{2x-y}{8-5}=\dfrac{15}{3}=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x=5\cdot8\\y=5\cdot5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=20\\y=25\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a) Ta có: \(\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{5}\)
mà x+y=35
nên Áp dụng tính chất của dãy tỉ số bằng nhau, ta được:
\(\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{5}=\dfrac{x+y}{2+5}=\dfrac{35}{7}=5\)
Do đó:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{x}{2}=5\\\dfrac{y}{5}=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=10\\y=25\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: (x,y)=(10;25)
b) Ta có: \(\dfrac{x+2}{y+10}=\dfrac{1}{5}\)
nên \(\dfrac{x+2}{1}=\dfrac{y+10}{5}\)
hay \(\dfrac{3x+6}{3}=\dfrac{y+10}{5}\)
mà y-3x=2
nên Áp dụng tính chất của dãy tỉ số bằng nhau, ta được:
\(\dfrac{3x+6}{3}=\dfrac{y+10}{5}=\dfrac{y-3x+10-6}{5-3}=\dfrac{2+4}{2}=3\)
Do đó:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3x+6}{3}=3\\\dfrac{y+10}{5}=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x+6=9\\y+10=15\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x=3\\y=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: (x,y)=(1;5)
c) Ta có: \(\dfrac{x}{4}=\dfrac{y}{5}\)
nên \(\dfrac{2x}{8}=\dfrac{y}{5}\)
mà 2x-y=15
nên Áp dụng tính chất của dãy tỉ số bằng nhau, ta được:
\(\dfrac{2x}{8}=\dfrac{y}{5}=\dfrac{2x-y}{8-5}=\dfrac{15}{3}=5\)
Do đó:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{x}{4}=5\\\dfrac{y}{5}=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=20\\y=25\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: (x,y)=(20;25)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Cho các biểu thức:\(A=\dfrac{2x}{x+3}+\dfrac{x+1}{x-3}+\dfrac{3-11x}{9-x^2};B=\dfrac{x-3}{x+1}\) \(\left(0\le x,x\ne9\right)\) a, Rút gọn A
b, Với P = A.B ,tìm x để P = \(\dfrac{9}{2}\)
c, Tìm x để B < 1
d, Tìm số nguyên x để P là số nguyên
a) Ta có: \(A=\dfrac{2x}{x+3}+\dfrac{x+1}{x-3}+\dfrac{3-11x}{9-x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}+\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\dfrac{11x-3}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2-6x+x^2+4x+3+11x-3}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x^2+9x}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{3x}{x-3}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
b)
ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{3;-3;-1\right\}\)
Ta có: P=AB
\(=\dfrac{3x}{x-3}\cdot\dfrac{x-3}{x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x}{x+1}\)
Để \(P=\dfrac{9}{2}\) thì \(\dfrac{3x}{x+1}=\dfrac{9}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9\left(x+1\right)=6x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x-6x=-9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=-9\)
hay x=-3(loại)
Vậy: Không có giá trị nào của x để \(P=\dfrac{9}{2}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm các số nguyên x,y biết:a)dfrac{6}{2x+1}dfrac{2}{7}b) dfrac{24}{7x-3}dfrac{-4}{25}c) dfrac{4}{x-6}dfrac{y}{24}dfrac{-12}{18}d) dfrac{-1}{5}ledfrac{x}{8}ledfrac{1}{4}e) dfrac{x+46}{20}xdfrac{2}{5}f) ydfrac{5}{y}dfrac{86}{y} ( xdfrac{2}{5};ydfrac{5}{y} là các hỗn số)
Đọc tiếp
Tìm các số nguyên x,y biết:
a)\(\dfrac{6}{2x+1}=\dfrac{2}{7}\)
b) \(\dfrac{24}{7x-3}=\dfrac{-4}{25}\)
c) \(\dfrac{4}{x-6}=\dfrac{y}{24}=\dfrac{-12}{18}\)
d) \(\dfrac{-1}{5}\le\dfrac{x}{8}\le\dfrac{1}{4}\)
e) \(\dfrac{x+46}{20}=x\dfrac{2}{5}\)
f) \(y\dfrac{5}{y}=\dfrac{86}{y}\) ( \(x\dfrac{2}{5};y\dfrac{5}{y}\) là các hỗn số)
a,\(\dfrac{6}{2x+1}=\dfrac{2}{7}\)
⇒\(\dfrac{6}{2x+1}=\dfrac{6}{21}\)
⇒\(2x+1=21\)
\(2x=21-1\)
\(2x=20\)
⇒\(x=10\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
a) Tìm số tự nhiên x sao cho: 2x+2x+3=72
b)Tìm x nguyên để số hữu tỉ \(\dfrac{x-2}{x+1}\) có giá trị nguyên
c) Tìm GTNN của biểu thức: P=|2x+7|+\(\dfrac{2}{5}\)
a) 2ˣ + 2ˣ⁺³ = 72
2ˣ.(1 + 2³) = 72
2ˣ.9 = 72
2ˣ = 72 : 9
2ˣ = 8
2ˣ = 2³
x = 3
b) Để số đã cho là số nguyên thì (x - 2) ⋮ (x + 1)
Ta có:
x - 2 = x + 1 - 3
Để (x - 2) ⋮ (x + 1) thì 3 ⋮ (x + 1)
⇒ x + 1 ∈ Ư(3) = {-3; -1; 1; 3}
⇒ x ∈ {-4; -2; 0; 2}
Vậy x ∈ {-4; -2; 0; 2} thì số đã cho là số nguyên
c) P = |2x + 7| + 2/5
Ta có:
|2x + 7| ≥ 0 với mọi x ∈ R
|2x + 7| + 2/5 ≥ 2/5 với mọi x ∈ R
Vậy GTNN của P là 2/5 khi x = -7/2
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1)Tìm các số nguyên x để các phân số sau có giá trị là số nguyên:
A=\(\dfrac{x+3}{x-2}\)
C=\(\dfrac{2x+3}{x-2}\)
2)
(x - 2)2=25
Tìm x nguyên để các biểu thức sau nguyên:
a) D= \(\dfrac{5}{x-3}\) (với x≠3)
b) E= \(\dfrac{4x-5}{2x+1}\) (với x≠\(-\dfrac{1}{2}\))
a: Để D là số nguyên thì \(x-3\in\left\{1;-1;5;-5\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{4;2;8;-2\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}-\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}\right):\dfrac{2x}{5x-5}-\dfrac{x^2-1}{x^2+2x+1}\left(x\ne\pm1;x\ne0\right)\)
a) Rút gọn A
b)Tìm x để A=2
c)Tìm giá trị nguyên của x để A nguyên
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\pm1;x\ne0\)
a)\(\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}-\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}\right):\dfrac{2x}{5x-5}-\dfrac{x^2-1}{x^2+2x+1}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\right):\dfrac{2x}{5x-5}-\dfrac{x^2-1}{x^2+2x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+2x+1-\left(x^2-2x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}:\dfrac{2x}{5x-5}-\dfrac{x^2-1}{x^2+2x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{4x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}:\dfrac{2x}{5x-5}-\dfrac{x^2-1}{x^2+2x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{4x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}.\dfrac{5\left(x-1\right)}{2x}-\dfrac{x^2-1}{x^2+2x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{10}{x+1}-\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{10}{x+1}-\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{11-x}{x+1}\)
b) \(A=\dfrac{11-x}{x+1}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow11-x=2\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow11-x=2x+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x-2x=2-11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3x=-9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(nhận\right)\)
c) -Để \(A=\dfrac{11-x}{x+1}\in Z\) thì:
\(\left(11-x\right)⋮\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(12-x-1\right)⋮\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow12⋮\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+1\right)\inƯ\left(12\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+1\right)\in\left\{1;2;3;4;6;12;-1;-2;-3;-4;-6;-12\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{2;3;5;11;-2;-3;-4;-5;-7;-13\right\}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
Tìm số nguyên x:
1) A=\(\dfrac{-5}{x+2}\)
2) B=\(\dfrac{x+1
}{x-3}\)
3) C=\(\dfrac{3x+1}{x-2}\)
4) D=\(\dfrac{2x-1}{x+2}\)