cíu mình vssss =(((((
cíu mình vssss =(((((

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Mình cần gấp, giúp mình vssss
A=1/2! + 1/3! + 1/4! +...+ 1/100!
Tính A giúp mình vssss
cíu mình 
Cíu mình
Cíu mình vớiiiiii
bạn tham khảo ở đây nghe
https://hoc24.vn/cau-hoi/.1003659772279
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
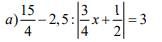 Cíu mình với=(((
Cíu mình với=(((
a, \(\dfrac{15}{4}\) - 2,5 : |\(\dfrac{3}{4}\)\(x\) + \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)| = 3
3,75 - 2,5:|\(\dfrac{3}{4}\)\(x\) + \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)| = 3
2,5:|\(\dfrac{3}{4}\)\(x\) + \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)| = 3,75 - 3
2,5 : |\(\dfrac{3}{4}\)\(x\) + \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)| = 0,75
|\(\dfrac{3}{4}\)\(x\) + \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)| = 2,5 : 0,75
|\(\dfrac{3}{4}\)\(x\) + \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)| = \(\dfrac{10}{3}\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{4}x+\dfrac{1}{2}=-\dfrac{10}{3}\\\dfrac{3}{4}x+\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{10}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{4}x=-\dfrac{10}{3}-\dfrac{1}{2}\\\dfrac{3}{4}x=\dfrac{10}{3}-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{4}x=-\dfrac{26}{3}\\\dfrac{3}{4}x=\dfrac{17}{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{46}{9}\\x=\dfrac{34}{9}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Mình cần gấp cíu
Bài 2:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long a,b;
int main()
{
cin>>a>>b;
cout<<a+b;
return 0;
}
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Cíu mình với ạ
a. Ta có: $\sin x\in [-1;1]$ nên $|\sin x|\in [0;1]$
$\Rightarrow 1\leq 3-2|\sin x|\leq 3$
Vậy $y_{\min}=1; y_{\max}=3$
b.
$y=\frac{1-\cos 2x}{2}-\frac{3}{2}\sin 2x+1$
$2y=3-\cos 2x-3\sin 2x$
$3-2y=\cos 2x+3\sin x$
Áp dụng định lý Bunhiacopxky:
$(3-2y)^2\leq (\cos ^22x+\sin ^22x)(1+3^2)=10$
$\Rightarrow -\sqrt{10}\leq 3-2y\leq \sqrt{10}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{3-\sqrt{10}}{2}\leq y\leq \frac{3+\sqrt{10}}{2}$
Vậy $y_{\max}=\frac{1+\sqrt{10}}{2}; y_{\min}=\frac{1-\sqrt{10}}{2}$
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
c.
\(y=\sqrt{5-\frac{1}{4}(2\sin x\cos x)^2}=\sqrt{5-\frac{1}{2}\sin ^22x}\)
Vì $\sin 2x\in [-1;1]$
$\Rightarrow \sin ^22x\in [0;1]$
$\Rightarrow \frac{3\sqrt{2}}{2}\leq \sqrt{5-\frac{1}{2}\sin ^22x}\leq \sqrt{5}$
d.
$\cos (x+\frac{\pi}{3})\in [-1;1]$
$\Rightarrow 2(-1)+3\leq 2\cos (x+\frac{\pi}{3})+3\leq 2.1+3$
$\Rightarrow 1\leq y\leq 5$
$\Rightarrow y_{\min}=1; y_{\max}=5$
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
e.
\(y=2\sin ^2x-\cos 2x=1-\cos 2x-\cos 2x=1-2\cos 2x\)
Vì $\cos 2x\in [-1;1]$ nên:
$-1\leq 1-2\cos 2x\leq 3$
Vậy $y_{\min}=-1; y_{\max}=3$
f.
$y=(\sin ^2x+\cos ^2x)^2-2(\sin x\cos x)^2$
$=1-\frac{1}{2}\sin ^22x$
Vì $-1\leq \sin 2x\leq 1\Rightarrow 0\leq \sin ^22x\leq 1$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{2}\leq y\leq 1$
Vậy $y_{\min}=\frac{1}{2};y_{\max}=1$
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
.cíu mình với mn