Giải bất phương trình: |2x - 7| < x2 + 2x + 2
Giải bất phương trình: - 2x + 2 - 3 0 trên tập số thực
Bài 1: Giải các bất phương trình sau
a) x+1/x+3 > 1
b) 2x-1/x-3 ≤ 2
c) x2+2x+2/x2+3 ≥ 1
d) 2x+1/x2+2 ≥ 1
a, \(\dfrac{x+1}{x+3}>1\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x+1}{x+3}-1>0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x+1-x-3}{x+3}>0\)
\(\Rightarrow x+3< 0\)do -2 < 0
\(\Rightarrow x< -3\)Vậy tập nghiệm BFT là S = { x | x < -3 }
b, \(\dfrac{2x-1}{x-3}\le2\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x-1}{x-3}-2\le0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x-1-2x+6}{x-3}\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow x-3\le0\)do 5 > 0
\(\Rightarrow x\le3\)Vậy tập nghiệm BFT là S = { x | x \(\le\)3 }
c, \(\dfrac{x^2+2x+2}{x^2+3}\ge1\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2+2x+2}{x^2+3}-1\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2+2x+2-x^2-3}{x^2+3}\ge0\Rightarrow2x-1\ge0\)do x^2 + 3 > 0
\(\Rightarrow x\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\)Vậy tập nghiệm BFT là S = { x | x \(\ge\)1/2 }
mình ko chắc nên mình đăng sau :>
d, \(\dfrac{2x+1}{x^2+2}\ge1\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x+1}{x^2+2}-1\ge0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x+1-x^2-2}{x^2+2}\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow-x^2+2x-1\ge0\Rightarrow-\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0\)vô lí
Giải bất phương trình l o g ( x 2 - 2 x - 2 ) ≤ 0
A. [-1; 3]
B. ( 1 - 3 ; 1 + 3 )
C. [ - 1 ; 1 - 3 ) ∪ ( 1 + 3 ; 3 ]
D. (-∞; -1) ∪ (3; +∞)
Chọn C
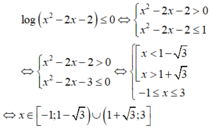
⇒ [ - 1 ; 1 - 3 ) ∪ ( 1 + 3 ; 3 ]
Giải bất phương trình l o g ( x 2 - 2 x - 2 ) ≤ 0
A. [-1; 3]
B. ( 1 - 3 ; 1 + 3 )
C. [ - 1 ; 1 - 3 ) ∪ ( 1 + 3 ; 3 ]
D. (-∞; -1) ∪ (3; +∞)
Giải bất phương trình sau
(x+2)(x2-2x+4)-x(x2+2)> hoặc = 5
=>x^3+8-x^3-2x>=5
=>-2x>=-3
=>x<=3/2
giải các bất phương trình sau và biểu diễn tập nghiệp trên trục số
1, 6+2x ≥ 3-x
2, 2x+7 > 16-x
3, x-5<3x+1
1.
\(6+2x\ge3-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\ge-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge-1\)
2.
\(2x+7>16-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x>23\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>\dfrac{23}{3}\)
3.
\(x-5< 3x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x>-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-3\)
Mik chưa học đến lớp 8 nên ko bt biểu diễn trên trục số nên chỉ tìm dc x thôi nha:
1. 6 + 2x \(\ge\) 3 - x
<=> 6 - 3 \(\ge\) -x - 2x
<=> 3 \(\ge\) -3x
<=> 3 : (-3) \(\ge\) -3x : (-3)
<=> -1 \(\le\) x
<=> x \(\ge\) -1
2. 2x + 7 > 16 - x
<=> 2x + x > 16 - 7
<=> 3x > 9
<=> 3x : 3 > 9 : 3
<=> x > 3
3. x - 5 < 3x + 1
<=> -5 - 1 < 3x - x
<=> -6 < 2x
<=> -6 : 2 < 2x : 2
<=> -3 < x
<=> x > (-3)
1: Ta có: \(2x+6\ge3-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\ge-3\)
hay \(x\ge-1\)
2: ta có: \(2x+7>16-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x>9\)
hay x>3
3: Ta có: \(x-5< 3x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x< 6\)
hay x>-3
Giải bất phương trình
x2-2x+1<9
(x-1)(4-x2)≥0
\(\dfrac{x+2}{x-5}\)<0
\(x^2-2x+1< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1< 3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< 4\)
\(\left(x-1\right)\left(4-x^2\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2-x\right)\left(2+x\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\2-x=0\\2+x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=2\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{x+2}{x-5}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< -2\)
a)\(x^2-2x+1< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2-9< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1-3\right)\left(x-1+3\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x+2\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4< 0\\x+2>0\end{matrix}\right.hay\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4>0\\x+2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< 4\\x>-2\end{matrix}\right.hay\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>4\\x< -2\end{matrix}\right.\)(vô lý)
-Vậy nghiệm của BĐT là \(-2< x< 4\).
b) \(\left(x-1\right)\left(4-x^2\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2-x\right)\left(x+2\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1< 0\\x-2>0\\x+2>0\end{matrix}\right.\) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1>0\\x-2< 0\\x+2>0\end{matrix}\right.\) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1>0\\x-2 >0\\x+2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1< 0\\x-2< 0\\x+2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< 1\\x>2\\x>-2\end{matrix}\right.\) (vô lí) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>1\\x< 2\\x>-2\end{matrix}\right.\) (có thể xảy ra) hay
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>1\\x>2\\x< -2\end{matrix}\right.\) (vô lí) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< 1\\x< 2\\x< -2\end{matrix}\right.\) (có thể xảy ra)
-Vậy nghiệm của BĐT là \(x< -2\) hay \(1< x< 2\).
c) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne5\)
\(\dfrac{x+2}{x-5}< 0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2< 0\\x-5>0\end{matrix}\right.hay\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2>0\\x-5< 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< -2\\x>5\end{matrix}\right.\)(vô lí) hay
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>-2\\x< 5\end{matrix}\right.\) (có thể xảy ra)
-Vậy nghiệm của BĐT là \(-2< x< 5\)
Kiểm tra xem -2 là nghiệm của bất phương trình nào trong các bất phương trình sau:
a) -3x + 2 > -5 ; b) 10 - 2x < 2
c) x2 - 5 < 1 ; d) |x| < 3
e) |x| > 2 ; f) x + 1 > 7 - 2x
Lần lượt thay x = -2 vào từng bất phương trình:
a) -3x + 2 = -3.(-2) + 2 = 8
Vì 8 > -5 nên x = -2 là nghiệm của bất phương trình -3x + 2 > -5.
b) 10 – 2x = 10 – 2.(-2) = 10 + 4 = 14
Vì 14 > 2 nên x = -2 không phải nghiệm của bất phương trình 10 – 2x < 2.
c) x2 – 5 = (-2)2 – 5 = 4 – 5 = -1
Vì -1 < 1 nên x = -2 là nghiệm của bất phương trình x2 – 5 < 1.
d) |x| = |-2| = 2
Vì 2 < 3 nên x = -2 là nghiệm của bất phương trình |x| < 3.
e) |x| = |-2| = 2
Vì 2 = 2 nên x = -2 không phải nghiệm của bất phương trình |x| > 2.
f) x + 1 = -2 + 1 = -1.
7 – 2x = 7 – 2.(-2) = 7 + 4 = 11
Vì -1 < 11 nên x = -2 không phải nghiệm của bất phương trình x + 1 > 7 – 2x.
|2x-3| ≤ -x2+3x-1 giải bất phương trình
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-3\ge0\\2x-3\le-x^2+3x-1\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-3< 0\\3-2x\le-x^2+3x-1\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge\dfrac{3}{2}\\x^2-x-2\le0\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< \dfrac{3}{2}\\x^2-5x+4\le0\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge\dfrac{3}{2}\\-1\le x\le2\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< \dfrac{3}{2}\\1\le x\le4\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{2}\le x\le2\\1\le x< \dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow1\le x\le2\)