Giải các phương trình sau: 2 tan 2 x + 3 tan x + 2 c o t 2 x + 3 c o t x + 2 = 0

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải các phương trình sau :
a) \(2\tan x-3\cot x-2=0\)
b) \(\cos^2=3\sin2x+3\)
c) \(\cot x-\cot2x=\tan x+1\)
1/ Giải phương trình sau:
\(tan^2\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)+\left(\sqrt{3}-1\right)tan\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)-\sqrt{3}=0\)
Đặt \(tan\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=t\)
\(\Rightarrow t^2+\left(\sqrt{3}-1\right)t-\sqrt{3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t\left(t-1\right)+\sqrt{3}\left(t-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=1\\t=-\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}tan\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=1\\tan\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=-\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}=\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}=-\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{\pi}{12}+k\pi\\x=-\dfrac{2\pi}{3}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải các phương trình sau : a) \(\left(\tan x+\cot x\right)^2-\left(\tan x+\cot x\right)=2\) ; b) \(\sin x+\sin^2\frac{x}{2}=0,5\)
tham khảogiúp mình nhé: (tanx + cotx)^2 - (tanx + cotx) = 2? | Yahoo Hỏi & Đáp
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình sau :
\(2\tan^2x-3\tan x+2\cot^2x+3\cot x-3=0\)
Giải các phương trình sau :
a) \(\sin^2\dfrac{x}{2}-2\cos\dfrac{x}{2}+2=0\)
b) \(8\cos^2x+2\sin x-7=0\)
c) \(2\tan^2c+3\tan x+1=0\)
d) \(\tan x-2\cos x+1=0\)
a) Đặt t = cos![]() , t ∈ [-1 ; 1] thì phương trình trở thành
, t ∈ [-1 ; 1] thì phương trình trở thành
(1 - t2) - 2t + 2 = 0 ⇔ t2 + 2t -3 = 0 ⇔ ![]()
Phương trình đã cho tương đương với
cos![]() = 1 ⇔
= 1 ⇔ ![]() = k2π ⇔ x = 4kπ, k ∈ Z.
= k2π ⇔ x = 4kπ, k ∈ Z.
b) Đặt t = sinx, t ∈ [-1 ; 1] thì phương trình trở thành
8(1 - t2) + 2t - 7 = 0 ⇔ 8t2 - 2t - 1 = 0 ⇔ t ∈ {![]() }.
}.
Các nghiệm của phương trình đã cho là nghiệm của hai phương trình sau :
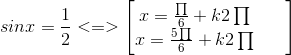
và ![]()
Đáp số : x = ![]() + k2π; x =
+ k2π; x = ![]() + k2π;
+ k2π;
x = arcsin(![]() ) + k2π; x = π - arcsin(
) + k2π; x = π - arcsin(![]() ) + k2π, k ∈ Z.
) + k2π, k ∈ Z.
c) Đặt t = tanx thì phương trình trở thành 2t2 + 3t + 1 = 0 ⇔ t ∈ {-1 ; ![]() }.
}.
Vậy ![]()
d) Đặt t = tanx thì phương trình trở thành
t - ![]() + 1 = 0 ⇔ t2 + t - 2 = 0 ⇔ t ∈ {1 ; -2}.
+ 1 = 0 ⇔ t2 + t - 2 = 0 ⇔ t ∈ {1 ; -2}.
Vậy ![]()
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình sau:
\(\tan\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)+\cot\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2}-3x\right)=0\)
Pt \(\Leftrightarrow\)\(tan\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)\)=\(-cot\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2}-3x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(tan\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)\)=\(tan\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2}+\dfrac{\pi}{2}-3x\right)\)=\(tan\left(\pi-3x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}=\pi-3x+k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)4\(x\)=\(\dfrac{4}{3}\pi+k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x=\) \(\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k\dfrac{\pi}{4}\)(\(k\in Z\))
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(pt\Leftrightarrow tan\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=-cot\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2}-3x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow tan\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=cot\left(-\dfrac{\pi}{2}+3x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow tan\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=tan\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2}+\dfrac{\pi}{2}-3x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow tan\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=tan\left(\pi-3x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}=\pi-3x+k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=\dfrac{2\pi}{3}+k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+\dfrac{k\pi}{4}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình: \(\tan\left(\dfrac{3}{2}-x\right)+\dfrac{\sin x}{1+\cos x}=2\)
1/ Giải phương trình sau:tan^2left(x+dfrac{pi}{3}right)+left(sqrt{3}-1right)tanleft(x+dfrac{pi}{3}right)-sqrt{3}02/ Tìm hệ số của số hạng chứa x^{26} trong khai triển left(dfrac{1}{x^4}+x^7right)^n . Biết C^2_{n+2}-4C^n_{n+1}2left(n+1right) (n ∈ N* ; x 0)
Đọc tiếp
1/ Giải phương trình sau:
\(tan^2\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)+\left(\sqrt{3}-1\right)tan\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)-\sqrt{3}=0\)
2/ Tìm hệ số của số hạng chứa \(x^{26}\) trong khai triển \(\left(\dfrac{1}{x^4}+x^7\right)^n\) . Biết \(C^2_{n+2}-4C^n_{n+1}=2\left(n+1\right)\) (n ∈ N* ; x > 0)
Câu 2:
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(n+2\right)!}{2!\cdot n!}-4\cdot\dfrac{\left(n+1\right)!}{n!\cdot1!}=2\left(n+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(n+1\right)\left(n+2\right)}{2}-4\cdot\dfrac{n+1}{1}=2\left(n+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(n+1\right)\left(n+2\right)-8\left(n+1\right)=4\left(n+1\right)\)
=>(n+1)(n+2-8-4)=0
=>n=-1(loại) hoặc n=10
=>\(A=\left(\dfrac{1}{x^4}+x^7\right)^{10}\)
SHTQ là: \(C^k_{10}\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{x^4}\right)^{10-k}\cdot x^{7k}=C^k_{10}\cdot1\cdot x^{11k-40}\)
Số hạng chứa x^26 tương ứng với 11k-40=26
=>k=6
=>Số hạng cần tìm là: \(210x^{26}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình sau: \(\cot x-1=\dfrac{\cos2x}{1+\tan x}+\sin^2x-\dfrac{1}{2}\sin2x\)
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{cosx}{sinx}-1=\dfrac{cos^2x-sin^2x}{1+\dfrac{sinx}{cosx}}+sin^2x-sinx.cosx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{cosx-sinx}{sinx}=cosx\left(cosx-sinx\right)-sinx\left(cosx-sinx\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(cosx-sinx\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{sinx}-cosx+sinx\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(cosx-sinx\right)\left(1-sinx.cosx+sin^2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(cosx-sinx\right)\left(3-sin2x-cos2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(cosx-sinx\right)\left(3-\sqrt{2}sin\left(2x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\right)=0\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) \(\sin x = \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\);
b) \(2\cos x = - \sqrt 2 \);
c) \(\sqrt 3 \tan \left( {\frac{x}{2} + {{15}^0}} \right) = 1\);
d) \(\cot \left( {2x - 1} \right) = \cot \frac{\pi }{5}\)
a) \(\sin x = \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\;\; \Leftrightarrow \sin x = \sin \frac{\pi }{3}\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{x = \frac{\pi }{3} + k2\pi }\\{x = \pi - \frac{\pi }{3} + k2\pi }\end{array}} \right.\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{x = \frac{\pi }{3} + k2\pi }\\{x = \frac{{2\pi }}{3} + k2\pi \;}\end{array}\;} \right.\left( {k \in \mathbb{Z}} \right)\)
b) \(2\cos x = - \sqrt 2 \;\; \Leftrightarrow \cos x = - \frac{{\sqrt 2 }}{2}\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow \cos x = \cos \frac{{3\pi }}{4}\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{x = \frac{{3\pi }}{4} + k2\pi }\\{x = - \frac{{3\pi }}{4} + k2\pi }\end{array}\;\;\left( {k \in \mathbb{Z}} \right)} \right.\)
c) \(\sqrt 3 \;\left( {\tan \frac{x}{2} + {{15}^0}} \right) = 1\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow \tan \left( {\frac{x}{2} + \frac{\pi }{{12}}} \right) = \frac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\;\; \Leftrightarrow \tan \left( {\frac{x}{2} + \frac{\pi }{{12}}} \right) = \tan \frac{\pi }{6}\)
\( \Leftrightarrow \frac{x}{2} + \frac{\pi }{{12}} = \frac{\pi }{6} + k\pi \;\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow \frac{x}{2} = \frac{\pi }{{12}} + k\pi \;\;\; \Leftrightarrow x = \frac{\pi }{6} + k\pi \;\left( {k \in \mathbb{Z}} \right)\)
d) \(\cot \left( {2x - 1} \right) = \cot \frac{\pi }{5}\;\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow 2x - 1 = \frac{\pi }{5} + k\pi \;\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow 2x = \frac{\pi }{5} + 1 + k\pi \;\; \Leftrightarrow x = \frac{\pi }{{10}} + \frac{1}{2} + \frac{{k\pi }}{2}\;\;\left( {k \in \mathbb{Z}} \right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)

























