Tính đạo hàm của hàm số sau: f x = ln x 2 + 1
A. f ' ( x ) = ln ( x 2 + 1 )
B. f ' x = ln 2 x
C. f ' x = 1 x 2 + 1
D. f ' x = 2 x x 2 + 1
Tính đạo hàm của hàm số f(x)=ln x
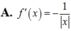
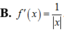
![]()
![]()
Tính đạo hàm của các hàm số sau:
g) \(y = \ln (x^2+x+1)\)
l) \(y = \dfrac{\ln x}{x+1}\)
g: \(y=ln\left(x^2+x+1\right)\)
=>\(y'=\dfrac{\left(x^2+x+1\right)'}{x^2+x+1}=\dfrac{2x+1}{x^2+x+1}\)
l: \(y=\dfrac{lnx}{x+1}\)
=>\(y'=\dfrac{\left(lnx\right)'\cdot\left(x+1\right)-\left(x+1\right)'\left(lnx\right)}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
=>\(y'=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{x}\left(x+1\right)-lnx}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y'=\dfrac{\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)}{x}-lnx}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
Tính đạo hàm cấp hai của mỗi hàm số sau:
a) \(y = 2{x^4} - 3{x^3} + 5{x^2}\)
b) \(y = \frac{2}{{3 - x}}\)
c) \(y = \sin 2x\cos x\)
d) \(y = {e^{ - 2x + 3}}\)
e) \(y = \ln (x + 1)\)
f) \(y = \ln ({e^x} + 1)\)
\(a,y'=8x^3-9x^2+10x\\ \Rightarrow y''=24x^2-18x+10\\ b,y'=\dfrac{2}{\left(3-x\right)^2}\\ \Rightarrow y''=\dfrac{4}{\left(3-x\right)^3}\)
\(c,y'=2cos2xcosx-sin2xsinx\\ \Rightarrow y''=-5sin\left(2x\right)cos\left(x\right)-4cos\left(2x\right)sin\left(x\right)\\ d,y'=-2e^{-2x+3}\\ \Rightarrow y''=4e^{-2x+3}\)
e,
\(y = \ln (x + 1) \Rightarrow y' = \frac{1}{{x + 1}} \Rightarrow y'' = - \frac{1}{{{{\left( {x + 1} \right)}^2}}}\)
f,
\(y = \ln ({e^x} + 1) \Rightarrow y' = \frac{{{e^x}}}{{{e^x} + 1}} \Rightarrow y'' = - \frac{{{e^x}.{e^x}}}{{{{\left( {{e^x} + 1} \right)}^2}}} = - \frac{{{e^{2x}}}}{{{{\left( {{e^x} + 1} \right)}^2}}}\)
Tìm đạo hàm của các hàm số sau:
1, \(y=3^{(\dfrac{x}{\ln(x)})}\)
2, \(y=\dfrac{1}{2}tan^2(x)+\ln(tan(x))\)
3, \(y=\sqrt[3]{ln^2(2x)}\)
1.
\(y'=\left(\dfrac{x}{lnx}\right)'.3^{\dfrac{x}{lnx}}.ln3=\dfrac{lnx-1}{ln^2x}.3^{\dfrac{x}{lnx}}.ln3\)
2.
\(y'=\left(tanx\right)'.tanx+\left(tanx\right)'.\dfrac{1}{tanx}=\dfrac{tanx}{cos^2x}+\dfrac{1}{tanx.cos^2x}\)
3.
\(y=\left(ln2x\right)^{\dfrac{2}{3}}\Rightarrow y'=\left(ln2x\right)'.\dfrac{2}{3}.\left(ln2x\right)^{-\dfrac{1}{3}}=\dfrac{1}{3x\sqrt[3]{ln2x}}\)
Đạo hàm của hàm số f ( x ) = l n ( x 2 - x ) là
A. 2 x - 1 x 2 - x
B. x 2 - x 2 x + 1
C. x 2 - x 2 x - 1
D. 2 x + 1 x 2 - x
Tính đạo hàm của hàm số :
\(y=\frac{\ln x}{x}+\frac{1+\ln x}{1-\ln x}\)
\(y'=\frac{\frac{1}{x}x-\ln x}{x^2}+\frac{-\frac{1}{x}\left(x+\ln x\right)-\frac{1}{x}\left(x-\ln x\right)}{\left(1+\ln_{ }x\right)^2}=\frac{1-\ln x}{x^2}+\frac{-2}{x\left(1+\ln_{ }x\right)^2}\)
Biết hàm số f ( x ) - f ( 2 x ) có đạo hàm bằng 5 tại x = 1 và đạo hàm bằng 7 tại x = 2 Tính đạo hàm của hàm số f ( x ) - f ( 4 x ) tại x = 1.
A. 8.
B. 12.
C. 16.
D. 19.
Bài 1: Xét tính đơn điệu của hàm số \(y=f(x)\) khi biết đạo hàm của hàm số là:
a) \(f'(x)=(x+1)(1-x^2)(2x-1)^3\)
b) \(f'(x)=(x+2)(x-3)^2(x-4)^3\)
Bài 2: Cho hàm số \(y=f(x)\) có đạo hàm \(f'(x)=x(x+1)(x-2)\). Xét tính biến thiên của hàm số:
a) \(y=f(2-3x)\)
b) \(y=f(x^2+1)\)
c) \(y=f(3x+1)\)
Tính đạo hàm của hàm số y = ln ( x + x 2 + 1 )
A. y ' = 1 x + x 2 + 1
B. y ' = 1 x 2 + 1
C. y ' = x + x 2 + 1
d. y ' = x x + x 2 + 1
Tính đạo hàm của hàm số y = ln ( x 2 + 1 - x )
A. y ' = - 1 x 2 + 1 - x
B. y ' = - 1 x 2 + 1
C. y ' = 1 x 2 + 1
D. y ' = x x 2 + 1