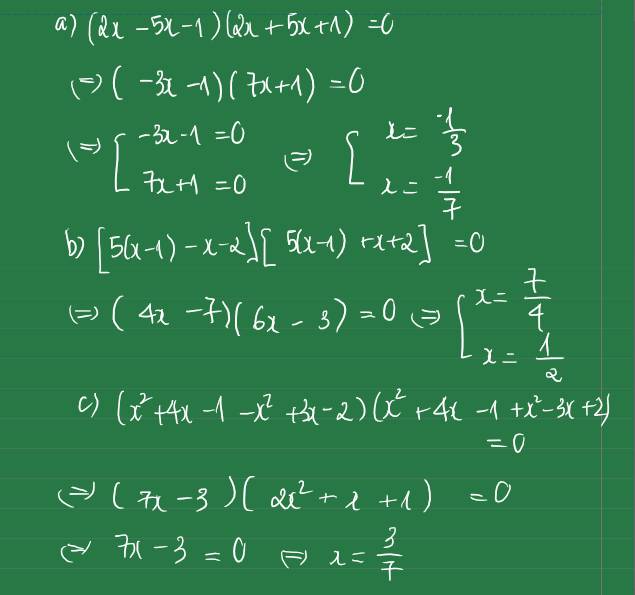Giải phương trình ( x2 - 25)2 - ( x - 5 )2 = 0

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải các phương trình sau:a)
x
2
–l0x -25; b) 4
x
2
- 4x -1;c)
(
1
-
2
x
)
2
(
3
x
-
2...
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) x 2 –l0x = -25; b) 4 x 2 - 4x = -1;
c) ( 1 - 2 x ) 2 = ( 3 x - 2 ) 2 ; d) ( x - 2 ) 3 + ( 5 - 2 x ) 3 =0.
a) x = 5. b) x = 1 2 .
c) x = 3 5 hoặc x = 1. d) x = 3.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(a,x^2-10x=-25\)
\(< =>x^2-10x+25=0\)
\(< =>\left(x-5\right)^2=0< =>x=5\)
b, \(4x^2-4x=-1\)
\(< =>4x^2-4x+1=0\)
\(< =>\left(2x-1\right)^2=0< =>x=\frac{1}{2}\)
c,\(\left(1-2x\right)^2=\left(3x-2\right)^2\)
\(< =>\left(1-2x\right)^2-\left(3x-2\right)^2=0\)
\(< =>\left(1-2x-3x+2\right)\left(1-2x+3x-2\right)=0\)
\(< =>\left(-5x+3\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(< =>\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{3}{5}\\x=1\end{cases}}\)
d, \(\left(x-2\right)^3+\left(5-2x\right)^3=0\)
\(< =>\left(x-2+5-2x\right)\left(x^2-4x+4+5x-2x^2-10+4x+25-20x+4x^2\right)=0\)
\(< =>\left(3-x\right)\left(-5x^2-15x+19\right)=0\)
\(< =>\left(x-3\right)\left(5x^2+15x-19=0\right)\)
\(< =>\orbr{\begin{cases}x=3\\x^2+3x-\frac{19}{5}=0\end{cases}}\)
Xét phương trình \(x^2+3x-\frac{19}{5}=0< =>\left(x^2+2.x.\frac{3}{2}+\frac{9}{4}\right)-\left(\frac{19}{5}+\frac{9}{4}\right)=0\)
\(< =>\left(x+\frac{3}{2}\right)^2=\frac{29}{5}+\frac{1}{4}\)
\(< =>\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\sqrt{\frac{29}{5}+\frac{1}{4}}-\frac{3}{2}\\x=-\sqrt{\frac{29}{5}+\frac{1}{4}}-\frac{3}{2}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy .........
Xem thêm câu trả lời
giải các phương trình sau:
a. x2-25=8(5-x)
b.x-2/ x+2 - 2(x-11)/x2-4 =3/x-2
a.\(x^2-25=8\left(5-x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)-8\left(5-x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)+8\left(x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(x+13\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=-13\end{matrix}\right.\)
b.\(\dfrac{x-2}{x+2}-\dfrac{2\left(x-11\right)}{x^2-4}=\dfrac{3}{x-2}\) ; \(ĐK:x\ne\pm2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-2\right)-2\left(x-11\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{3\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2-2\left(x-11\right)=3\left(x+2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+4-2x+22=3x+6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9x+20=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\left(tm\right)\\x=4\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình tích :
a) ( 2x - 10 ) ( 5x + 25) = 0
b) ( x + 15) ( x - 2 ) = 0
c) x2 - 7x =0
a: (2x-10)(5x+25)=0
=>2x-10=0 hoặc 5x+25=0
=>x=5 hoặc x=-5
b: (x+15)(x-2)=0
=>x+15=0 hoặc x-2=0
=>x=-15 hoặc x=2
c: =>x(x-7)=0
=>x=0 hoặc x=7
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a, (2x - 10) (5x + 25) = 0
⇒ 2x - 10 = 0 hoặc 5x + 25 = 0
⇒ x = 5 hoặc x = -5
b, (x + 15) (x - 2) = 0
⇒ x + 15 = 0 hoặc x - 2 = 0
⇒ x = -15 hoặc x = 2
c: =>x(x-7)=0
=>x=0 hoặc x=7
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau
a) 4x2-(5x+1)2=0
b) 25(x-1)2-(x+2)2=0
c) (x2+4x-1)2-(x2-3x+2)20
a: =>(2x-5x-1)(2x+5x+1)=0
=>(-3x-1)(7x+1)=0
=>x=-1/3 hoặc x=-1/7
b: =>(5x-5)^2-(x+2)^2=0
=>(5x-5-x-2)(5x-5+x+2)=0
=>(4x-7)(6x-3)=0
=>x=1/2 hoặc x=7/4
c: =>(x^2+4x-1-x^2+3x-2)(x^2+4x-1+x^2-3x+2)=0
=>(7x-3)(2x^2+x+1)=0
=>7x-3=0
=>x=3/7
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho phương trình x^2-2x-5=0 có 2 nghiệm x1,x2. Không giải phương trình, hãy tính giá trị của các biểu thức : B=x1^2+x2^2 ; C=x1^5+x2^5
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x_1+x_2=2\\x_1.x_2=-5\end{cases}}\)
\(B=x_1^2+x_2^2=\left(x_2+x_2\right)^2-2x_1.x_2=2^2+2.5=14\)
Câu C phân tích tương tự
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho phương trình: 5 x^2-2\sqrt{5}x+1 = 05x2−25x+1=0.
Điền số thích hợp vào ô trống:
Biệt thức \Delta=Δ=
×
.
Nghiệm x=x=
Giải bất phương trình
x2-2x+1<9
(x-1)(4-x2)≥0
\(\dfrac{x+2}{x-5}\)<0
\(x^2-2x+1< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1< 3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< 4\)
\(\left(x-1\right)\left(4-x^2\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2-x\right)\left(2+x\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\2-x=0\\2+x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=2\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{x+2}{x-5}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< -2\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a)\(x^2-2x+1< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2-9< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1-3\right)\left(x-1+3\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x+2\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4< 0\\x+2>0\end{matrix}\right.hay\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4>0\\x+2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< 4\\x>-2\end{matrix}\right.hay\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>4\\x< -2\end{matrix}\right.\)(vô lý)
-Vậy nghiệm của BĐT là \(-2< x< 4\).
b) \(\left(x-1\right)\left(4-x^2\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2-x\right)\left(x+2\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1< 0\\x-2>0\\x+2>0\end{matrix}\right.\) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1>0\\x-2< 0\\x+2>0\end{matrix}\right.\) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1>0\\x-2 >0\\x+2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1< 0\\x-2< 0\\x+2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< 1\\x>2\\x>-2\end{matrix}\right.\) (vô lí) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>1\\x< 2\\x>-2\end{matrix}\right.\) (có thể xảy ra) hay
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>1\\x>2\\x< -2\end{matrix}\right.\) (vô lí) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< 1\\x< 2\\x< -2\end{matrix}\right.\) (có thể xảy ra)
-Vậy nghiệm của BĐT là \(x< -2\) hay \(1< x< 2\).
c) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne5\)
\(\dfrac{x+2}{x-5}< 0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2< 0\\x-5>0\end{matrix}\right.hay\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2>0\\x-5< 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< -2\\x>5\end{matrix}\right.\)(vô lí) hay
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>-2\\x< 5\end{matrix}\right.\) (có thể xảy ra)
-Vậy nghiệm của BĐT là \(-2< x< 5\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
giải phương trình:
11/x2 - 25/(x+5)2 = 1
giải giúp em với ạ!
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\left\{0;-5\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{11}{x^2}-\left[1-\dfrac{10}{x+5}+\left(\dfrac{5}{x+5}\right)^2+\dfrac{10}{x+5}\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{11}{x^2}-\left[\left(1-\dfrac{5}{x+5}\right)^2+\dfrac{10}{x+5}\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{11}{x^2}-\dfrac{10}{x+5}-\left(\dfrac{x}{x+5}\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{x}{x+5}\right)\left(\dfrac{11}{x}+\dfrac{x}{x+5}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{x}{x+5}=0\\\dfrac{11}{x}+\dfrac{x}{x+5}=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-x-5=0\\x^2+11x+55=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\) (bấm máy)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (3)
Giải các phương trình sau:
a
)
x
2
–
5
0
;
b
)
x
2
–
2
√
11
x
+
11
0
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình sau:
a ) x 2 – 5 = 0 ; b ) x 2 – 2 √ 11 x + 11 = 0
a ) x 2 – 5 = 0 ⇔ x 2 = 5 ⇔ x 1 = √ 5 ; x 2 = - √ 5
Vậy phương trình có hai nghiệm x 1 = √ 5 ; x 2 = - √ 5
Cách khác:
x 2 – 5 = 0 ⇔ x 2 – ( √ 5 ) 2 = 0
⇔ (x - √5)(x + √5) = 0
hoặc x - √5 = 0 ⇔ x = √5
hoặc x + √5 = 0 ⇔ x = -√5
b)
x 2 – 2 √ 11 x + 11 = 0 ⇔ x 2 – 2 √ 11 x + ( √ 11 ) 2 = 0 ⇔ ( x - √ 11 ) 2 = 0
⇔ x - √11 = 0 ⇔ x = √11
Vậy phương trình có một nghiệm là x = √11
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 2: Cho phương trình x2- 2(m+2)x – 2m - 5 = 0 (1) a) Giải phương trình (1) khi m=2 b) Tìm m để phương trình (1) có hai nghiệm phân biệt x1, X2 thoả mãn: |x1-x2| = 2
a: Khi m=2 thì pt sẽ là \(x^2-8x-9=0\)
=>x=9 hoặc x=-1
b: \(\text{Δ}=\left(2m+4\right)^2-4\left(-2m-5\right)\)
\(=4m^2+16m+16+8m+20=4m^2+24m+36\)
\(=4\left(m^2+6m+9\right)=4\left(m+3\right)^2>=0\)
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì m+3<>0
hay m<>-3
Theo đề, ta có: \(\sqrt{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(2m+4\right)^2-4\left(-2m-5\right)}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{4m^2+16m+16+8m+20}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2+24m+36=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2+6m+9=1\)
=>m+3=1 hoặc m+3=-1
=>m=-2 hoặc m=-4
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
giải các phương trình sau bằng cách đưa về phương trình tích
a) x^2+10x+25-4x(x+5)=0
b) (4x-5)^2-2(16x^2-25)=0
Tham khảo bài này :
(3x+1)(7x+3)=(5x-7)(3x+1)
<=> (3x+1)(7x+3)-(5x-7)(3x+1)=0
<=> (3x+1)(7x+3-5x+7)=0
<=> (3x+1)(2x+10)=0
<=> 2(3x+1)(x+5)=0
=> 3x+1=0 hoặc x+5=0
=> x= -1/3 hoặc x=-5
Vậy x = -1/3 hoặc x = -5
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(a,x^2+10x+25-4x\left(x+5\right)=0.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)^2-4x\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)\left(5-3x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+5=0\\5-3x=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-5\\x=\frac{5}{3}\end{cases}}}\)
\(b,\left(4x-5\right)^2-2\left(16x^2-25\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x-5\right)^2-2\left(4x+5\right)\left(4x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(4x-5\right)\left(4x+15\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}4x-5=0\\4x+15=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{4}\\x=-\frac{15}{4}\end{cases}}}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)