6/x +1/2 =2
tìm x
1. Tìm các số tự nhiên x và y sao cho:
a) x/3 - 4/y = 1/5
b) 4/x + y/3 = 5/6 .
2Tìm các số nguyên x và y sao cho:
a) 5/x - y/3 = 1/6
b) x/6 - 2/y = 1/30
2:
a: 5/x-y/3=1/6
=>\(\dfrac{15-xy}{3x}=\dfrac{1}{6}\)
=>\(\dfrac{30-2xy}{6x}=\dfrac{x}{6x}\)
=>30-2xy=x
=>x(2y+1)=30
=>(x;2y+1) thuộc {(30;1); (-30;-1); (10;3); (-10;-3); (6;5); (-6;-5)}
=>(x,y) thuộc {(30;0); (-30;-1); (10;1); (-10;-2); (6;2); (-6;-3)}
b: x/6-2/y=1/30
=>\(\dfrac{xy-12}{6y}=\dfrac{1}{30}\)
=>\(\dfrac{5xy-60}{30y}=\dfrac{y}{30y}\)
=>5xy-60=y
=>y(5x-1)=60
=>(5x-1;y) thuộc {(-1;-60); (4;15); (-6;-10)}(Vì x,y là số nguyên)
=>(x,y) thuộc {(0;-60); (1;15); (-1;-10)}
cho các đa thức P (x) =-5x^3+3x^2+2x+5
Q(x)= -5x^3+6x^2+2x+5
tính giá trị đa thức P(x)+Q(x) tại x =1/2
tìm x để Q(x)-P(x)= 6
\(P\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)+Q\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=-5.\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^3+3\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{2}{2}+5-5\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^3+6\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{2}{2}+5\)
\(P\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)+Q\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=-\dfrac{5.1}{8}+\dfrac{3.1}{4}+6-\dfrac{5.1}{8}+\dfrac{6.1}{4}+6\)
\(P\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)+Q\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=-\dfrac{5}{8}+\dfrac{3}{4}+6-\dfrac{5}{8}+\dfrac{3}{2}+6\)
\(P\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)+Q\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=13\)
\(Q\left(x\right)-P\left(x\right)=6\)
\(-5x^3+6x^2+2x+5+5x^3-3x^2-2x-5=6\)
\(3x^2=6\)
\(x^2=2\)
\(=>x=\pm\sqrt{2}\)
Tìm x
\(\left(3x+1\right)^2=9\left(x-2\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2+6x+1=9\left(x^2-4x+4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2+6x+1=9x^2-36x+36\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2+6x+1-9x^2+36x-36=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow42x-35=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow42x=35\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{35}{42}=\dfrac{5}{6}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{5}{6}\right\}\)
Phân tích thành nhân tử
(3x+2)^2-(x-6)^2
Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất
A= x^2+2y^2+2xy-2y+2021
1) \(\left(3x+2\right)^2-\left(x-6\right)^2=\left(3x+2-x+6\right)\left(3x+2+x-6\right)=\left(2x+8\right)\left(4x-4\right)=8\left(x+4\right)\left(x-1\right)\)
2) \(A=x^2+2y^2+2xy-2y+2021=\left(x^2+2xy+y^2\right)+\left(y^2-2y+1\right)+2020=\left(x+y\right)^2+\left(y-1\right)^2+2020\ge2020\)
\(minA=2020\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(3x+2\right)^2-\left(x-6\right)^2=\left(3x+2-x+6\right)\left(3x+2+x-6\right)=\left(2x+8\right)\left(4x-4\right)=2.\left(x+4\right).4\left(x-1\right)=8\left(x-1\right)\left(x+4\right)\)
Bài 1:
Ta có: \(\left(3x+2\right)^2-\left(x-6\right)^2\)
\(=\left(3x+2-x+6\right)\left(3x+2+x-6\right)\)
\(=\left(2x+8\right)\left(4x-4\right)\)
\(=8\left(x+4\right)\left(x-1\right)\)
a x 1/5 + a x 2/3 = 2 2/13 : 2
Tìm a nhé
\(\Leftrightarrow a\cdot\dfrac{13}{15}=\dfrac{28}{13}:2=\dfrac{14}{13}\)
=>\(a=\dfrac{14}{13}:\dfrac{13}{15}=\dfrac{210}{169}\)
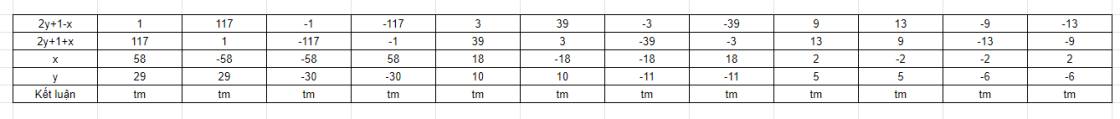
x^2+117=(2y+1)^2
tìm các cặp số nguyên (x;y)
Lời giải:
$117=(2y+1)^2-x^2=(2y+1-x)(2y+1+x)$
Vì $x,y$ nguyên nên $2y+1-x, 2y+1+x$ nguyên. Do đó ta có bảng sau:
a) 5(k+3x)(x+1)-4(1+2x)=80 x\(_0\)=2Tìm gt của kb) x+1=xc) x+2=0d) x+5=0e) (x+1)(2x-3)-3(x-2)=2(x-1)\(^2\)f) (x+1)(x\(^2\)-x+1)-2x=x(x-1)(x+1)g)\(\dfrac{x}{3}\)-\(\dfrac{5x}{6}\)-\(\dfrac{15x}{12}\)=\(\dfrac{x}{4}\)-5h) \(\dfrac{x-1}{2}\)-\(\dfrac{x+1}{15}\)-\(\dfrac{2x-13}{6}\)=0i) \(\dfrac{3\left(5x-2\right)}{4}\)-2=\(\dfrac{7x}{3}\)-5(x-7)
j) \(\dfrac{x-3}{11}\)+\(\dfrac{x+1}{3}\)=\(\dfrac{x+7}{9}\)-1k)\(\dfrac{3x-0,4}{2}\)+\(\dfrac{1,5-2x}{3}\)=\(\dfrac{x+0,5}{5}\)l) \(\dfrac{x-4}{5}\)+\(\dfrac{3x-2}{10}\)-x=\(\dfrac{2x-5}{3}\)-\(\dfrac{7x+2}{6}\)m) \(\dfrac{\left(2x-3\right)\left(2x+3\right)}{8}\)=\(\dfrac{\left(x-4\right)^{^2}}{6}\)+\(\dfrac{\left(x-2^{ }\right)^2}{3}\)n) \(\dfrac{7x^2-14x-5}{15}\)=\(\dfrac{\left(2x+1\right)^2}{5}\)-\(\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{3}\)o) \(\dfrac{\left(7x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}{10}\)+\(\dfrac{2}{5}\)=\(\dfrac{\left(x-2^{ }\right)^2}{5}\)+\(\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)}{10}\)
Chia câu hỏi ra cho thành nhiều phần cho dễ trả lời á bạn
x(x-1)+(x+1)(3-x)=2
tìm x
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-x^2+2x+3=2\)
=>x=-1
h(x)=4x^2-2x^3-2x+2x^3-(-x)+x+(-5x)+1+4x^2
tìm nghiệm đa thức