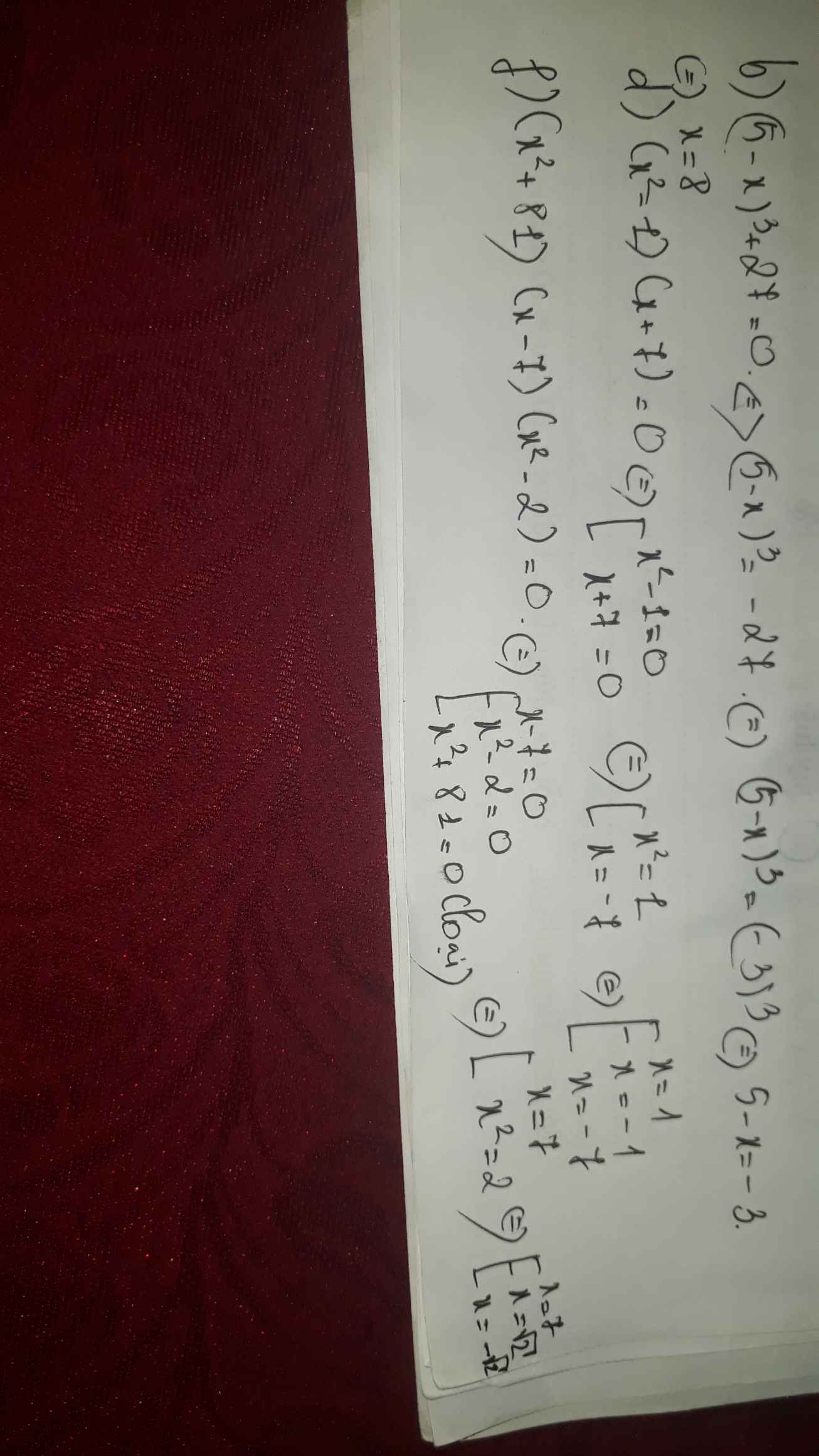7-5\(\left|2-x\right|\)=0

Những câu hỏi liên quan
\(Bài\) \(2:\) \(Tìm\) \(x:\)
b) \(\left(5-x\right)^3+27=0\)
d) \(\left(x^2-1\right).\left(x+7\right)=0\)
f) \(\left(x^2+81\right).\left(x-7\right).\left(x^2-2\right)=0\)
b) Ta có: \(\left(5-x\right)^3+27=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(5-x\right)^3=-27\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5-x=-3\)
hay x=8
d) Ta có: \(\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x+7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x+7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-1\\x=-7\end{matrix}\right.\)
f) Ta có: \(\left(x^2+81\right)\left(x-7\right)\left(x^2-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-7\right)\left(x+\sqrt{2}\right)\left(x-\sqrt{2}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=7\\x=\sqrt{2}\\x=-\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
Giải các PT:
a) \(\left(3x-2\right).\left(4x+5\right)=0\)
b) \(\left(2,3x-6,9\right).\left(0,1x+2\right)=0\)
c) \(\left(4x+2\right).\left(x^2+1\right)=0\)
d) \(\left(2x+7\right).\left(x-5\right).\left(5x+1\right)=0\)
Áp dụng công thức: \(A\left(x\right).B\left(x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}A\left(x\right)=0\\B\left(x\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
a) \(PT\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-2=0\\4x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\x=-\dfrac{5}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{2}{3};-\dfrac{5}{4}\right\}\)
b) \(PT\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2,3x-6,9=0\\0,1x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-20\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{3;20\right\}\)
c) Vì \(x^2+1\ge1>0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow4x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
d) \(PT\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+7=0\\x-5=0\\5x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{7}{2}\\x=5\\x=-\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{7}{2};5;-\dfrac{1}{5}\right\}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
a: =>3x-2=0 hoặc 4x+5=0
=>x=2/3 hoặc x=-5/4
b: =>(x-3)(x+20)=0
=>x=3 hoặc x=-20
c: =>4x+2=0
hay x=-1/2
d: =>2x+7=0 hoặc x-5=0 hoặc 5x+1=0
=>x=-7/2 hoặc x=5 hoặc x=-1/5
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1.Cho x+y+z0. CMR:a) 5left(x^3+y^3+z^3right)left(x^2+y^2+z^2right)6left(x^5+y^5+z^5right)b) x^7+y^7+z^77xyzleft(x^2y^2+y^2z^2+z^2x^2right)c) 10left(x^7+y^7+z^7right)7left(x^2+y^2+z^2right)left(x^5+y^5+z^5right)d) 2left(x^5+y^5+z^5right)5xyzleft(x^2+y^2+z^2right)2. Tìm n∈ N để biểu thức sau là số nguyên tố a) An^3-4n^2-4n-1b) Bn^3-6n^2+9n-2c) Cn^{1975}+n^{1973}+1
Đọc tiếp
1.Cho x+y+z=0. CMR:
a) \(5\left(x^3+y^3+z^3\right)\left(x^2+y^2+z^2\right)=6\left(x^5+y^5+z^5\right)\)
b) \(x^7+y^7+z^7=7xyz\left(x^2y^2+y^2z^2+z^2x^2\right)\)
c) \(10\left(x^7+y^7+z^7\right)=7\left(x^2+y^2+z^2\right)\left(x^5+y^5+z^5\right)\)
d) \(2\left(x^5+y^5+z^5\right)=5xyz\left(x^2+y^2+z^2\right)\)
2. Tìm n∈ N để biểu thức sau là số nguyên tố
a) \(A=n^3-4n^2-4n-1\)
b) \(B=n^3-6n^2+9n-2\)
c) \(C=n^{1975}+n^{1973}+1\)
Vì bài dài nên mình sẽ tách ra nhé.
1a. Ta có:
$x^2+y^2+z^2=(x+y+z)^2-2(xy+yz+xz)=-2(xy+yz+xz)$
$x^3+y^3+z^3=(x+y+z)^3-3(x+y)(y+z)(x+z)=-3(x+y)(y+z)(x+z)$
$=-3(-z)(-x)(-y)=3xyz$
$\Rightarrow \text{VT}=-30xyz(xy+yz+xz)(1)$
------------------------
$x^5+y^5=(x^2+y^2)(x^3+y^3)-x^2y^2(x+y)$
$=[(x+y)^2-2xy][(x+y)^3-3xy(x+y)]-x^2y^2(x+y)$
$=(z^2-2xy)(-z^3+3xyz)+x^2y^2z$
$=-z^5+3xyz^3+2xyz^3-6x^2y^2z+x^2y^2z$
$=-z^5+5xyz^3-5x^2y^2z$
$\Rightarrow 6(x^5+y^5+z^5)=6(5xyz^3-5x^2y^2z)$
$=30xyz(z^2-xy)=30xyz[z(-x-y)-xy]=-30xyz(xy+yz+xz)(2)$
Từ $(1);(2)$ ta có đpcm.
Đúng 14
Bình luận (0)
1b.
$x^4+y^4=(x^2+y^2)^2-2x^2y^2=[(x+y)^2-2xy]^2-2x^2y^2$
$=(z^2-2xy)^2-2x^2y^2=z^4+2x^2y^2-4xyz^2$
$x^3+y^3=(x+y)^3-3xy(x+y)=-z^3+3xyz$
Do đó:
$x^7+y^7=(x^4+y^4)(x^3+y^3)-x^3y^3(x+y)$
$=(z^4+2x^2y^2-4xyz^2)(-z^3+3xyz)+x^3y^3z$
$=7x^3y^3z-14x^2y^2z^3+7xyz^5-z^7$
$\Rightarrow \text{VT}=7x^3y^3z-14x^2y^2z^3+7xyz^5$
$=7xyz(x^2y^2-2xyz^2+z^4)$
$=7xyz(xy-z^2)$
$=7xyz[xy+z(x+y)]^2=7xyz(xy+yz+xz)^2$
$=7xyz[x^2y^2+y^2z^2+z^2x^2+2xyz(x+y+z)]$
$=7xyz(x^2y^2+y^2z^2+z^2x^2)$ (đpcm)
Đúng 9
Bình luận (0)
1c. Sử dụng kq phần a,b:
\(10(x^7+y^7+z^7)=70xyz(xy+yz+xz)^2\)
\(=-35xyz(xy+yz+xz).-2(xy+yz+xz)=-35xyz(x+y+z)(x^2+y^2+z^2)\)
\(=\frac{7}{6}.-30xyz(xy+yz+xz)(x^2+y^2+z^2)=\frac{7}{6}.6(x^5+y^5+z^5).(x^2+y^2+z^2)\)
\(=7(x^5+y^5+z^5)(x^2+y^2+z^5)\)
(đpcm)
1d. Áp dụng kq phần a
$6(x^5+y^5+z^5)=-30xyz(xy+y+xz)=15xyz.-2(xy+yz+xz)=15xyz(x^2+y^2+z^2)$
$\Rightarrow 2(x^5+y^5+z^5)=5xyz(x^2+y^2+z^2)$ (đpcm)
Đúng 13
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Tìm x :
1) \(\left(-0,75x+\dfrac{5}{2}\right).\dfrac{4}{7}-\left(-\dfrac{1}{3}\right)=-\dfrac{5}{6}\)
2) \(\left(4x-9\right)\left(2,5+\dfrac{-7}{3}x\right)=0\)
3) \(\left|x-\dfrac{3}{4}\right|-\dfrac{1}{2}=0\)
4)\(\left(\dfrac{3}{5}-\dfrac{2}{3}x\right)^3=\dfrac{-64}{125}\)
3: \(\left|x-\dfrac{3}{4}\right|-\dfrac{1}{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x-\dfrac{3}{4}\right|=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-\dfrac{3}{4}=\dfrac{1}{2}\\x-\dfrac{3}{4}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{4}\\x=\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2\left(x+y\right)^2-5\left(x+y\right)-7=0\\x-y-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Lời giải:
$x-y-5=0\Leftrightarrow x-y=5$
$2(x+y)^2-5(x+y)-7=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 2(x+y)^2+2(x+y)-[7(x+y)+7]=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 2(x+y)(x+y+1)-7(x+y+1)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+y+1)(2x+2y-7)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x+y=-1$ hoặc $x+y=\frac{7}{2}$
Nếu $x+y=-1$. Kê hợp với $x-y=5$ thì:
$(x+y)+(x-y)=-1+5=4$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x=4\Leftrightarrow x=2$
$y=-1-x=-1-2=-3$
Nếu $x+y=\frac{7}{2}=3,5$. Kết hợp với $x-y=5$ thì:
$(x+y)+(x-y)=3,5+5=8,5$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x=8,5\Leftrightarrow x=4,25$
$y=x-5=4,25-5=-0,75$
Vậy...............
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
BÀI 6 tìm x1,2xleft(x-5right)-left(3x+2x^2right)0 2,xleft(5-2xright)+2xleft(x-1right)133,2x^3left(2x-3right)-x^2left(4x^2-6x+2right)0 4,5xleft(x-1right)-left(x+2right)left(5x-7right)65,6x^2-left(2x-3right)left(3x+2right)1 6,2xleft(1-xright)+59-2x^2
Đọc tiếp
BÀI 6 tìm x
1,\(2x\left(x-5\right)-\left(3x+2x^2\right)=0\) 2,\(x\left(5-2x\right)+2x\left(x-1\right)=13\)
3,\(2x^3\left(2x-3\right)-x^2\left(4x^2-6x+2\right)=0\) 4,\(5x\left(x-1\right)-\left(x+2\right)\left(5x-7\right)=6\)
5,\(6x^2-\left(2x-3\right)\left(3x+2\right)=1\) 6,\(2x\left(1-x\right)+5=9-2x^2\)
1: \(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-10x-3x-2x^2=0\)
=>-13x=0
=>x=0
2: \(\Leftrightarrow5x-2x^2+2x^2-2x=13\)
=>3x=13
=>x=13/3
3: \(\Leftrightarrow4x^4-6x^3-4x^3+6x^3-2x^2=0\)
=>-2x^2=0
=>x=0
4: \(\Leftrightarrow5x^2-5x-5x^2+7x-10x+14=6\)
=>-8x=6-14=-8
=>x=1
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
`1)2x(x-5)-(3x+2x^2)=0`
`<=>2x^2-10x-3x-2x^2=0`
`<=>-13x=0`
`<=>x=0`
___________________________________________________
`2)x(5-2x)+2x(x-1)=13`
`<=>5x-2x^2+2x^2-2x=13`
`<=>3x=13<=>x=13/3`
___________________________________________________
`3)2x^3(2x-3)-x^2(4x^2-6x+2)=0`
`<=>4x^4-6x^3-4x^4+6x^3-2x^2=0`
`<=>x=0`
___________________________________________________
`4)5x(x-1)-(x+2)(5x-7)=0`
`<=>5x^2-5x-5x^2+7x-10x+14=0`
`<=>-8x=-14`
`<=>x=7/4`
___________________________________________________
`5)6x^2-(2x-3)(3x+2)=1`
`<=>6x^2-6x^2-4x+9x+6=1`
`<=>5x=-5<=>x=-1`
___________________________________________________
`6)2x(1-x)+5=9-2x^2`
`<=>2x-2x^2+5=9-2x^2`
`<=>2x=4<=>x=2`
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải các PT sau
a)\(\left(3\left(x+1\right)-2\left(x+3\right)\right)^3+\left(2\left(x+3\right)-x+5\right)^3+\left(x-5-3\left(x+1\right)\right)^3=0\)
b)\(\left(x-2\right)^3+\left(x-4\right)^3+\left(x-7\right)^3+3\left(x-2\right)\left(x-4\right)\left(x-7\right)=0\)
Tìm x,biết:
\(\left(2x-1\right)^2+\left(x+3\right)^2-5\left(x+7\right)\left(x-7\right)=0\)0
( 2x - 1 )2 + ( x + 3 )2 - 5( x + 7 )( x - 7 ) = 0
<=> ( 2x - 1 )2 + ( x + 3 )2 - 5( x2 - 72 ) = 0
<=> 4x2 - 4x + 1 + x2 + 6x + 9 - 5x2 + 245 = 0
<=> 2x + 255 = 0
<=> 2x = -255
<=> x = -255/2
\(pt< =>4x^2-4x+1+x^2+6x+9-5x^2+5.49=0\)
\(< =>2x+255=0< =>x=-\frac{255}{2}\)
\(\left(2x-1\right)^2+\left(x+3\right)^2-5\left(x+7\right)\left(x-7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x^2-4x+1\right)+\left(x^2+6x+9\right)-5\left(x^2-49\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x+1+x^2+6x+9-5x^2+245=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+255=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=-255\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-255}{2}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là: \(S=\left\{\frac{-255}{2}\right\}\)
A)left(2x-7right)^2-6left(2x-7right)left(x-3right)0B) x^3+1+left(x^2-x+1right)0C) left(3x+1right)^2-x^2+8x-160D)left(x+1right)left(x-1right)^2left(x+1right)left(x-2right)^20E) left(3x+1right)left(x-3right)^2left(3x+1right)left(2x-5right)^2F) left(x+5right)left(3x+2right)^2x^2left(x+5right)
Đọc tiếp
A)\(\left(2x-7\right)^2-6\left(2x-7\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
B) \(x^3+1+\left(x^2-x+1\right)=0\)
C) \(\left(3x+1\right)^2-x^2+8x-16=0\)
D)\(\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)^2=0\)
E) \(\left(3x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)^2=\left(3x+1\right)\left(2x-5\right)^2\)
F) \(\left(x+5\right)\left(3x+2\right)^2=x^2\left(x+5\right)\)
1) \(\left(3-x^2\right)+6-2x=0\)
2) \(5\left(2x-1\right)+7=4\left(2-x\right)+2\)
3) \(x^2-6x+4\left(x-6\right)=0\)
4) \(\left(x+1\right)\left(2x-3\right)=x\left(x+1\right)\)
1) Ta có: \(\left(3-x^2\right)+6-2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3-x^2+6-2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x^2-2x+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+1=10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2=10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=\sqrt{10}\\x+1=-\sqrt{10}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{10}-1\\x=-\sqrt{10}-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\sqrt{10}-1;-\sqrt{10}-1\right\}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
2) Ta có: \(5\left(2x-1\right)+7=4\left(2-x\right)+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow10x-5+7=8-4x+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow10x+4x=8+2+5-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow14x=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{4}{7}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{4}{7}\right\}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
3) Ta có: \(x^2-6x+4\left(x-6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-6\right)+4\left(x-6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right)\left(x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-6=0\\x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={6;-4}
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời