giải phương trình: 4x2-2\(\sqrt{x+1}\)=x+2

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải phương trình : \(\sqrt{x+1}\) - 4x2 = \(\sqrt{3x}\) -1
\(\sqrt{x+1}-4x^2=\sqrt{3x}-1\left(x\ge0\right)\left(1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x^2+1+\sqrt{x+1}-\dfrac{\sqrt{6}}{2}=\sqrt{3x}-\dfrac{\sqrt{6}}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)+\dfrac{x+1-\dfrac{3}{2}}{\sqrt{x+1}+\dfrac{\sqrt{6}}{2}}=\dfrac{3x-\dfrac{3}{2}}{\sqrt{3x}+\dfrac{\sqrt{6}}{2}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)+\dfrac{x-\dfrac{1}{2}}{\sqrt{x+1}+\dfrac{\sqrt{6}}{2}}-\dfrac{3\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)}{\sqrt{3x}+\dfrac{\sqrt{6}}{2}}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\left[-4\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x+1}+\dfrac{\sqrt{6}}{2}}-\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{3x}+\dfrac{\sqrt{6}}{2}}\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(tm\right)\\-4\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x+1}+\dfrac{\sqrt{6}}{2}}-\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{3x}+\dfrac{\sqrt{6}}{2}}=0\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(x\ge0\right)\Rightarrow\left(2\right)< 0\Rightarrow\left(2\right)vô\) \(nghiệm\)
\(\Rightarrow S=\left\{\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
\(\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình
a) x2-\(4\sqrt{15}\)x+19=0
b) 4x2+4\(\sqrt{5}\)x+5=0
a)
\(x^2-4\sqrt{15}x+19=0\\ < =>x^2-4\sqrt{15}x+60-41=0\\ < =>\left(x-2\sqrt{15}\right)^2-41=0\\ < =>\left(x-2\sqrt{15}-\sqrt{41}\right)\left(x-2\sqrt{15}+\sqrt{41}\right)=0\\ < =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2\sqrt{15}-\sqrt{41}=0\\x-2\sqrt{15}+\sqrt{41}=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ < =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\sqrt{15}+\sqrt{41}\\x=2\sqrt{15}-\sqrt{41}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b)
\(4x^2+4\sqrt{5}x+5=0\\ < =>\left(2x+\sqrt{5}\right)^2=0\\ < =>2x+\sqrt{5}=0\\ < =>2x=-\sqrt{5}\\ < =>-\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a: Δ=(4căn 15)^2-4*1*19=164>0
Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{4\sqrt{5}-2\sqrt{41}}{2}=2\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{41}\\x_2=2\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{41}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x\right)^2+2\cdot2x\cdot\sqrt{5}+5=0\)
=>(2x+căn 5)^2=0
=>2x+căn 5=0
=>x=-1/2*căn 5
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình:
4x2 - 2√3.x = 1 - √3.
4x2 - 2√3 x = 1 - √3.
⇔ 4x2 - 2√3 x – 1 + √3 = 0
Có a = 4; b’ = -√3; c = -1 + √3;
Δ’ = b'2 – ac = (-√3)2 – 4(-1 + √3) = 7 - 4√3 = 4 – 2.2.√3 + (√3)2 = (2 - √3)2.
Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt:
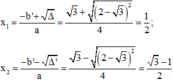
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1: Giải các phương trình dưới đây1) x2 - 9 (x - 3)(5x +2)2) x3 - 1 (x - 1)(x2 - 2x +16)3) 4x2 (x - 1) - x + 1 04) x3 + 4x2 - 9x - 36 05) (3x + 5)2 (x - 1)26) 9 (2x + 1)2 4 (x - 5)27) x2 + 2x 158) x4 + 5x3 + 4x2 09) (x2 - 4) - (x - 2)(3 - 2x) 010) (3x + 2)(x2 - 1) (9x2 - 4) (x + 1)11) (3x - 1)(x2 + 2) (3x - 1)(7x - 10)12) (2x2 + 1) (4x - 3) (x - 12)(2x2 + 1)
Đọc tiếp
Bài 1: Giải các phương trình dưới đây
1) x2 - 9 = (x - 3)(5x +2)
2) x3 - 1 = (x - 1)(x2 - 2x +16)
3) 4x2 (x - 1) - x + 1 = 0
4) x3 + 4x2 - 9x - 36 = 0
5) (3x + 5)2 = (x - 1)2
6) 9 (2x + 1)2 = 4 (x - 5)2
7) x2 + 2x = 15
8) x4 + 5x3 + 4x2 = 0
9) (x2 - 4) - (x - 2)(3 - 2x) = 0
10) (3x + 2)(x2 - 1) = (9x2 - 4) (x + 1)
11) (3x - 1)(x2 + 2) = (3x - 1)(7x - 10)
12) (2x2 + 1) (4x - 3) = (x - 12)(2x2 + 1)
1: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-\left(x-3\right)\left(5x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(-4x+1\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{3;\dfrac{1}{4}\right\}\)
2: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)-\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-2x+16\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1-x^2+2x-16\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(3x-15\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;5\right\}\)
3: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(4x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;\dfrac{1}{2};-\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
4: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+4\right)-9\left(x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+4\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{-4;3;-3\right\}\)
5: \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+5=x-1\\3x+5=1-x\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=-6\\4x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
6: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(6x+3\right)^2-\left(2x-10\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(6x+3-2x+10\right)\left(6x+3+2x-10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x+13\right)\left(8x-7\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{-\dfrac{13}{4};\dfrac{7}{8}\right\}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=\left(x-3\right)\left(5x-2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+3=5x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=5\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
2.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)=\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-2x+16\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x+1=x^2-2x+16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=15\Leftrightarrow x=5\)
3.
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2\left(x-1\right)-\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(4x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=\dfrac{1}{2};x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
7.
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-15=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
8.\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+x^3+4x^3+4x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3\left(x+1\right)+4x^2\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^3+4x^2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=0;x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
9.\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)=\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2=3-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=1\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Trong các phương trình sau,phương trình nào có ít nhất một nghiệm là số nguyên?
A.\(\left(x-\sqrt{5}\right)^2=5\) B.9x2-1=0 C.4x2-4x+1=0 D.x2+x+2=0
Giải phương trình
a
)
2
x
+
3
x
-
4
2
x
-
1
x
+
2
-
27
b
)
x
2
-
4
-
x
+
5...
Đọc tiếp
Giải phương trình
a ) 2 x + 3 x - 4 = 2 x - 1 x + 2 - 27
b ) x 2 - 4 - x + 5 2 - x = 0
c ) x + 2 x - 2 - x - 2 x + 2 = 4 x 2 - 4
d ) x + 1 x - 1 - x + 2 x + 3 + 4 x 2 + 2 x - 3 = 0
a) 2(x + 3)(x – 4) = (2x – 1)(x + 2) – 27
⇔ 2(x2 – 4x + 3x – 12) = 2x2 + 4x – x – 2 – 27
⇔ 2x2 – 2x – 24 = 2x2 + 3x – 29
⇔ -2x – 3x = 24 – 29
⇔ - 5x = - 5 ⇔ x = -5/-5 ⇔ x = 1
Tập nghiệm của phương trình : S = {1}
b) x2 – 4 – (x + 5)(2 – x) = 0
⇔ x2 – 4 + (x + 5)(x – 2) = 0 ⇔ (x – 2)(x + 2 + x + 5) = 0
⇔ (x – 2)(2x + 7) = 0 ⇔ x – 2 = 0 hoặc 2x + 7 = 0
⇔ x = 2 hoặc x = -7/2
Tập nghiệm của phương trình: S = {2; -7/2 }
c) ĐKXĐ : x – 2 ≠ 0 và x + 2 ≠ 0 (khi đó : x2 – 4 = (x – 2)(x + 2) ≠ 0)
⇔ x ≠ 2 và x ≠ -2
Quy đồng mẫu thức hai vế :
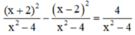
Khử mẫu, ta được : x2 + 4x + 4 – x2 + 4x – 4 = 4
⇔ 8x = 4 ⇔ x = 1/2( thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
Tập nghiệm của phương trình : S = {1/2}
d) ĐKXĐ : x – 1 ≠ 0 và x + 3 ≠ 0 (khi đó : x2 + 2x – 3 = (x – 1)(x + 3) ≠ 0)
⇔ x ≠ 1 và x ≠ -3
Quy đồng mẫu thức hai vế :
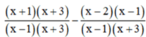
![]()
Khử mẫu, ta được : x2 + 3x + x + 3 – x2 + x – 2x + 2 + 4 = 0
⇔ 3x = -9 ⇔ x = -3 (không thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
Tập nghiệm của phương trình : S = ∅
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(2\left(x+3\right)\left(x-4\right)=\left(2x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)-27\)
\(< =>2\left(x^2-x-12\right)=2x^2+3x-2-27\)
\(< =>2x^2-2x-24=2x^2+3x-2-27\)
\(< =>5x=-24+29=5\)
\(< =>x=\frac{5}{5}=1\)
\(x^2-4-\left(x+5\right)\left(2-x\right)=0\)
\(< =>\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)+\left(x+5\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(< =>\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2+x+5\right)=0\)
\(< =>\left(x-2\right)\left(2x+7\right)=0\)
\(< =>\orbr{\begin{cases}x-2=0\\2x+7=0\end{cases}}< =>\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=-\frac{7}{2}\end{cases}}\)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Giải phương trình 3 + 2 - x = 4 x 2 - x + x - 3
Điều kiện xác định:
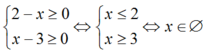
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1. Giải các phương trình sau:
a) |4x2 - 25| = 0
b) |x - 2| = 3
c) |x - 3| = 2x - 1
d) |x - 5| = |3x - 2|
Lời giải:
a) $|4x^2-25|=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 4x^2-25=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (2x-5)(2x+5)=0$
$\Rightarrow x=\pm \frac{5}{2}$
b)
$|x-2|=3$
\(\Rightarrow \left[\begin{matrix} x-2=-3\\ x-2=3\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow \left[\begin{matrix} x=-1\\ x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
c)
\(|x-3|=2x-1\Rightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} 2x-1\geq 0\\ \left[\begin{matrix} x-3=2x-1\\ x-3=1-2x\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} x\geq \frac{1}{2}\\ \left[\begin{matrix} x=-2\\ x=\frac{4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow x=\frac{4}{3}\)
d)
$|x-5|=|3x-2|$
\(\Rightarrow \left[\begin{matrix} x-5=3x-2\\ x-5=2-3x\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left[\begin{matrix} x=\frac{-3}{2}\\ x=\frac{7}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình :
a
)
(
2
x
–
1
)
(
4
x
2
+
2
x
+
1
)
–
4
x
(
2
x
2
–
3
)
23...
Đọc tiếp
Giải phương trình :
a ) ( 2 x – 1 ) ( 4 x 2 + 2 x + 1 ) – 4 x ( 2 x 2 – 3 ) = 23
b ) x + 2 x + 1 - 1 x - 2 = 1 - 3 x 2 - x - 2
a) (2x – 1)(4x2 + 2x + 1) – 4x(2x2 – 3) = 23
⇔ 8x3 – 1 – 8x3 + 12x = 23
⇔ 12x = 24 ⇔ x = 2.
Tập nghiệm của phương trình: S = {2}
b) ĐKXĐ : x + 1 ≠ 0 và x – 2 ≠ 0 (vì vậy x2 – x – 2 = (x + 1)(x – 2) ≠ 0)
⇔ x ≠ -1 và x ≠ 2
Quy đồng mẫu thức hai vế :
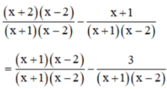
Khử mẫu, ta được : x2 – 4 – x – 1 = x2 – x – 2 – 3 ⇔ 0x = 0
Phương trình này luôn nghiệm đúng với mọi x ≠ -1 và x ≠ 2.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)



















