Giải phương trình:
\(\sin3x-\sin4x+\sin5x=0\).
Số nghiệm nằm trong đoạn − π 2 ; π 2 của phương trình sin 5 x + sin 3 x = sin 4 x là
A. 5.
B. 7.
C. 9.
D. 3.
Đáp án B
PT: sin 5 x + sin 3 x = sin 4 x
⇔ 2 sin 4 x cos x − sin 4 x = 0 ⇔ sin 4 x 2 cos x − 1 = 0
⇔ sin 4 x = 0 cos x = 1 2 ⇔ x = k π 4 1 x = − π 3 + 2 k π 2 x = π 3 + 2 k π 3
Trong đoạn − π 2 ; π 2 thì số nghiệm của (1) là 5 ứng với k ∈ 0 ; ± 1 ; ± 2 , (2) là 1 ứng với k = 0 , (3) là 1 ứng với k=0.
Như vậy PT đã cho có 7 nghiệm trong đoạn − π 2 ; π 2 .
Giải các phương trình sin3x + sin5x = 0
sin3x + sin5x = 0
⇔ 2sin4x. cosx = 0
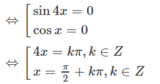
Vậy nghiệm của phương trình là:

Giải phương trình: sin5x-sin3x=0
\(\sin4x\sin5x+\sin4x\sin3x-\sin2x\sin x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin4x\left(sin5x+sin3x\right)-sin2x.sinx=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2sin^24x.cosx-2sin^2x.cosx=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx\left(2sin^24x-2sin^2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx\left(1-cos8x-1+cos2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx\left(cos2x-cos8x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cosx=0\\cos8x=cos2x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\\8x=2x+k2\pi\\8x=-2x+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\\x=\frac{k\pi}{3}\\x=\frac{k\pi}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
sin5x+sin3x+2cos2=1+sin4x
\(\sin\left(5x\right)+\sin\left(3x\right)+2\cos\left(x\right)=1+\sin\left(4x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\sin\left(4x\right)\cos\left(x\right)-\sin\left(4x\right)+2\cos\left(x\right)-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sin\left(4x\right)(2\cos\left(x\right)-1)+(2\cos\left(x\right)-1)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow(2\cos\left(x\right)-1)(\sin\left(4x\right)+1)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\cos\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\\\sin\left(4x\right)=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\pm\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\\4x=\dfrac{-\pi}{2}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\pm\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\\x=\dfrac{-\pi}{8}+k\dfrac{\pi}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Giải các phương trình sau :
a) \(\sin x+2\sin3x=-\sin5x\)
b) \(\cos5x\cos x=\cos4x\)
c) \(\sin x\sin2x\sin3x=\dfrac{1}{4}\sin4x\)
d) \(\sin^4x+\cos^4x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\cos^22x\)
Rút gọn:
A=(2sin2x-sin4x)/(2sin2x+sin4x) B=(sin5x-sin3x)/(2cos4x) C=tanx((1+cos²x)/(sinx)-sinx)\(A=\frac{2sin2x-2sin2x.cos2x}{2sin2x+2sin2x.cos2x}=\frac{1-cos2x}{1+cos2x}=\frac{2sin^2x}{2cos^2x}=tan^2x\)
\(B=\frac{2cos4x.sinx}{2cos4x}=sinx\)
Câu C ko dịch được đề
Giải phương trình sau :
\(4\sin3x+\sin5x-2\sin x\cos2x=0\)
\(4\sin3x+\sin5x-2\sin x\cos2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(4\sin3x+\sin5x-\sin3x+\sin x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\sin3x+\sin5x+\sin x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\sin3x+2\sin3x\cos2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sin3x\left(3+2\cos2x\right)=0\)
Đáp số : \(x=k\dfrac{\pi}{3},k\in\mathbb{Z}\)
Nghiệm của phương trình s i n 4 x + c o s 4 x + c o s x - π 4 . s i n 3 x - π 4 - 3 2 = 0 là
A. x = π 3 + k π , k ∈ ℤ
B. x = π 3 + k 2 π , k ∈ ℤ
C. x = π 4 + k 2 π , k ∈ ℤ
D. x = π 4 + k π , k ∈ ℤ