tìm giá trị nguyên của x để A ⋮B
A=10x2-7x-5 và B=2x-3
Tìm các giá trị nguyên của x để phân thức M có giá trị một số nguyên: M = 10 x 2 - 7 x - 5 2 x - 3
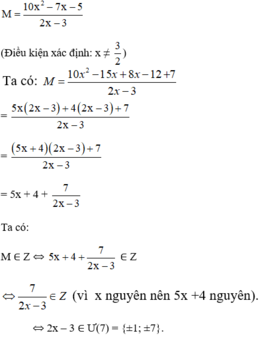
+ 2x – 3 = 1 ⇔ 2x = 4 ⇔ x = 2.
+ 2x – 3 = -1 ⇔ 2x = 2 ⇔ x = 1.
+ 2x – 3 = 7 ⇔ 2x = 10 ⇔ x = 5
+ 2x – 3 = -7 ⇔ 2x = -4 ⇔ x = -2.
Vậy với x ∈ {-2; 1; 2; 5} thì giá trị biểu thức M là một số nguyên.
Tìm giá trị nguyên của \(x\) để \(A⋮B\) biết \(A=10x^2-7x-5\) và \(B=2x-3\)
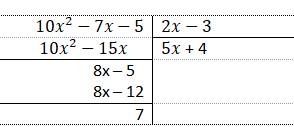
Để \(A⋮B\) thì \(7⋮\left(2x-3\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow2x-3\inƯ\left(7\right)=\left\{-7;-1;1;7\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow2x\in\left\{-4;2;4;10\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{-2;1;2;5\right\}\)
Cho biểu thức : B= \(\dfrac{2x}{x+3}+\dfrac{x+1}{x-3}+\dfrac{7x+3}{9-x^2}\)
a) Rút gọn B.
b) Tính giá trị của biểu thức B tại x thoả mãn: |2x + 1| = 7
c) Tìm x để B = \(-\dfrac{3}{5}\)
d) Tìm x nguyên để biểu thức B nhận giá trị nguyên.
a)B = \(\dfrac{2x}{x+3}+\dfrac{x+1}{x-3}+\dfrac{7x+3}{9-x^2}\left(ĐK:x\ne\pm3\right)\)
= \(\dfrac{2x}{x+3}+\dfrac{x+1}{x-3}-\dfrac{7x+3}{x^2-9}\)
= \(\dfrac{2x\left(x-3\right)+\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)-7x-3}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
= \(\dfrac{3x^2-9x}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{3x}{x+3}\)
b) \(\left|2x+1\right|=7< =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=7< =>x=3\left(L\right)\\2x+1=-7< =>x=-4\left(C\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay x = -4 vào B, ta có:
B = \(\dfrac{-4.3}{-4+3}=12\)
c) Để B = \(\dfrac{-3}{5}\)
<=> \(\dfrac{3x}{x+3}=\dfrac{-3}{5}< =>\dfrac{3x}{x+3}+\dfrac{3}{5}=0\)
<=> \(\dfrac{15x+3x+9}{5\left(x+3\right)}=0< =>x=\dfrac{-1}{2}\left(TM\right)\)
d) Để B nguyên <=> \(\dfrac{3x}{x+3}\) nguyên
<=> \(3-\dfrac{9}{x+3}\) nguyên <=> \(9⋮x+3\)
| x+3 | -9 | -3 | -1 | 1 | 3 | 9 |
| x | -12(C) | -6(C) | -4(C) | -2(C) | 0(C) | 6(C) |
Tìm x thuộc Z để biểu thức có giá trị nguyên
a) A=\(\dfrac{3x+21}{x+4}\)
b) B=\(\dfrac{2x^3-7x^2+7x+5}{2x-1}\)
a)
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne-4\)
Để A nguyên thì \(3x+21⋮x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x+12+9⋮x+4\)
mà \(3x+12⋮x+4\)
nên \(9⋮x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+4\inƯ\left(9\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+4\in\left\{1;-1;3;-3;9;-9\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-3;-5;-1;-7;5;-13\right\}\)(nhận)
Vậy: Để A nguyên thì \(x\in\left\{-3;-5;-1;-7;5;-13\right\}\)
b) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Để B nguyên thì \(2x^3-7x^2+7x+5⋮2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^3-x^2-6x^2+3x+4x-2+7⋮2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(2x-1\right)-3x\left(2x-1\right)+2\left(2x-1\right)+7⋮2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)\left(x^2-3x+2\right)+7⋮2x-1\)
mà \(\left(2x-1\right)\left(x^2-3x+2\right)⋮2x-1\)
nên \(7⋮2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-1\inƯ\left(7\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-1\in\left\{1;-1;7;-7\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\in\left\{2;0;8;-6\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;0;4;-3\right\}\)(nhận)
Vậy: \(x\in\left\{1;0;4;-3\right\}\)
a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{3;-3;-2\right\}\)
Ta có: \(P=\left(\dfrac{2x-1}{x+3}-\dfrac{x}{3-x}-\dfrac{3-10x}{x^2-9}\right):\dfrac{x+2}{x-3}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{\left(2x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}+\dfrac{x\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}-\dfrac{3-10x}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\right):\dfrac{x+2}{x-3}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2-6x-x+3+x^2+3x-3+10x}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}:\dfrac{x+2}{x-3}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x^2+6x}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}:\dfrac{x+2}{x-3}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x-3}{x+2}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x}{x+3}\)
b) Ta có: \(x^2-7x+12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x-4x+12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)-4\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\x-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\left(loại\right)\\x=4\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay x=4 vào biểu thức \(P=\dfrac{3x}{x+3}\), ta được:
\(P=\dfrac{3\cdot4}{4+3}=\dfrac{12}{7}\)
Vậy: Khi \(x^2-7x+12=0\) thì \(P=\dfrac{12}{7}\)
Tìm các giá trị nguyên của x để thương có giá trị nguyên.
a ) ( 3x3 + 13x2 - 7x + 5 ) : ( 3x - 2 )
b) ( 2x5 + 4x4 - 7x3 - 44 ) : ( 2x2 - 7 )
a) Ta thực hiện phép chia \(3x^3+13x^2-7x+5\) cho \(3x-2\). Khi đó ta có:
\(A=\frac{3x^3+13x^2-7x+5}{3x-2}=3x^2+5x+1+\frac{7}{3x-2}\)
Nếu x nguyên thì \(3x^2+5x+1\in\text{Z}\) nên để A nguyên thì \(\frac{7}{3x-2}\in Z\)
\(\Rightarrow3x-2\in\left\{-7;-1;1;7\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{1;3\right\}\)
b) Ta có: \(B=\frac{2x^5+4x^4-7x^3-44}{2x^2-7}=\left(x^3+2x^2+7\right)+\frac{5}{2x^2-7}\)
Để B nguyên thì \(\frac{5}{2x^2-7}\in Z\Rightarrow2x^2-7\in\left\{-5;-1;1;5\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{-1;1;2;-2\right\}\)
Cho biểu thức P=(2x-1 phần x+3-x phần 3-x-3-10x phần x^2-9):x+2 phần x-3 a)Rút gọn P và tìm đkxd của P b)tính giá trị của P khi x^2-7x+12=0 c)tính giá trị nguyên của x để P có giá trị nguyên
\(a,P=\left(\dfrac{2x-1}{x+3}-\dfrac{x}{3-x}-\dfrac{3-10x}{x^2-9}\right):\dfrac{x+2}{x-3}\left(x\ne\pm3;x\ne-2\right)\\ P=\dfrac{2x^2-7x+3+x^2+3x-3+10x}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x-3}{x+2}\\ P=\dfrac{3x^2+6x}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{3x\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{3x}{x-3}\\ b,x^2-7x+12=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=4\left(x\ne3\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow A=\dfrac{3\cdot4}{4-3}=12\\ c,P=\dfrac{3\left(x-3\right)+9}{x-3}=3+\dfrac{9}{x-3}\in Z\\ \Leftrightarrow x-3\inƯ\left(9\right)=\left\{-9;-3;-1;1;3;9\right\}\\ \Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-6;0;2;4;6;12\right\}\)
Tìm x thuộc Z để thương có giá trị nguyên:
a/ 3x^3+13x^2-7x+5 : 3x-2
b/ 2x^5+4x^4-7x^3-44 : 2x^2-7
a: \(\Leftrightarrow3x^3-2x^2+15x^2-10x+3x-2+7⋮3x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-2\in\left\{1;-1;7;-7\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{3;1\right\}\)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow2x^5-7x^3+4x^4-14x^2+14x^2-49x+49x-44⋮2x^2-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2401x^2-1936⋮2x^2-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4802x^2-3872⋮2x^2-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-7\inƯ\left(12935\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-7\in\left\{1;5;13;65;199;995;2587;12935;-1;-5\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2\in\left\{8;72;2\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{2;-2;6;-6;1;-1\right\}\)
tìm giá trị nguyên của x để A \(⋮\)B biết:
\(A=10x^2-7x-5\)và\(B=2x-3\)
\(A=10x^2-7x-5=\left(10x^2-15x\right)+8x-12+7=5x\left(2x-3\right)+4\left(2x-3\right)+7\)
\(A⋮B\Leftrightarrow7⋮2x+3\)
Rồi xét từng ước và tìm x
Xét \(\frac{A}{B}=\frac{10x^2-7x-5}{2x-3}=5x+4+\frac{7}{2x-3}\)
Với \(x\inℤ\)thì\(A⋮B\)thì \(\frac{7}{2x-3}\inℤ\Rightarrow7⋮\left(2x-3\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow(2x-3)\in u\left(7\right)=\left\{1;-1;7;-7\right\}\)
Lập bảng:
| \(2x-3\) | \(1\) | \(-1\) | \(7\) | \(-7\) |
| \(x\) | \(2\) | \(1\) | \(5\) | \(-2\) |
Vậy x \(\in\)\(\left\{1;2;-2;5\right\}\)