Phương trình 3 ln x = 4 ln 4 tương đương với bất phương trình nào dưới đây?
A. ln x 3 = ln y 4
B. ln x 4 = ln y 3
C. ln x ln 3 = ln y ln 4
D. ln x ln 4 = ln y ln 3
Giải các bất phương trình lôgarit sau: ln|x - 2| + ln|x + 4| ≤ 3ln2
ln|(x − 2)(x + 4)| ≤ ln8
⇔| x 2 + 2x − 8| ≤ 8
⇔ −8 ≤ x 2 + 2x – 8 ≤ 8
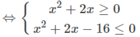
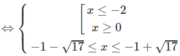
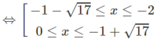
Vậy tập nghiệm là
![]()
Đề bài
Giải mỗi bất phương trình sau:
a) \({5^x} < 0,125\)
b) \({\left( {\frac{1}{3}} \right)^{2x + 1}} \ge 3\)
c) \({\log _{0,3}}x > 0\)
d) \(\ln (x + 4) > \ln (2x - 3)\)
\(a,5^x< 0,125\\ \Leftrightarrow x< -1,292\\ b,\left(\dfrac{1}{3}\right)^{2x+1}\ge3\\ \Leftrightarrow2x+1\le-1\\ \Leftrightarrow2x\le-2\\ \Leftrightarrow x\le-1\)
c, Điều kiện: x > 0
\(log_{0,3}x>0\\ \Leftrightarrow x>1\)
d, Điều kiện: \(x>\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(ln\left(x+4\right)>ln\left(2x-3\right)\\ \Rightarrow x+4>2x-3\\ \Leftrightarrow x< 7\)
Vậy \(\dfrac{3}{2}< x< 7\)
Giải các phương trình sau :
a) \(\ln\left(4x+2\right)-\ln\left(x-1\right)=\ln x\)
b) \(\log_2\left(3x+1\right)\log_3x=2\log_2\left(3x+1\right)\)
c) \(2^{\log_3x^2}.5^{\log_3x}=400\)
d) \(\ln^3x-3\ln^2x-4\ln x+12=0\)
a) Điều kiện: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x+2>0\\x-1>0\\x>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Hay là: \(x>1\)
Khi đó biến đổi pương trình như sau:
\(\ln\dfrac{4x+2}{x-1}=\ln x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x+2}{x-1}=x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+2=x\left(x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{33}}{2}\\x_2=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{33}}{2}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy nghiệm của phương trình là: \(x=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{33}}{2}\)
b) Điều kiện: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x+1>0\\x>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Hay là: \(x>0\)
Biến đổi phương trình như sau:
\(\log_2\left(3x+1\right)\log_3x-2\log_2\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\log_2\left(3x+1\right)\left(\log_3x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\log_2\left(3x+1\right)=0\\\log_3x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+1=2^0\\x=3^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(loại\right)\\x=9\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy nghiệm là x = 9.
c) Điều kiện: x > 0.
Khi đó biến đổi phương trình như sau:
\(2^{\log_3x^2}.5^{\log_3x}=400\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2^{2\log_3x}.5^{\log_3x}=400\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2^2.5\right)^{\log_3x}=400\)
\(\Leftrightarrow20^{\log_3x}=20^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\log_3x=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3^2=9\) (thỏa mãn)
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) \(\log \left( {x + 1} \right) = 2;\)
b) \(2{\log _4}x + {\log _2}\left( {x - 3} \right) = 2;\)
c) \(\ln x + \ln \left( {x - 1} \right) = \ln 4x;\)
d) \({\log _3}\left( {{x^2} - 3x + 2} \right) = {\log _3}\left( {2x - 4} \right).\)
a, ĐK: \(x+1>0\Leftrightarrow x>-1\)
\(log\left(x+1\right)=2\\ \Leftrightarrow x+1=10^2\\ \Leftrightarrow x+1=100\\ \Leftrightarrow x=99\left(tm\right)\)
b, ĐK: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3>0\\x>0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow x>3\)
\(2log_4x+log_2\left(x-3\right)=2\\ \Leftrightarrow log_2x+log_2\left(x-3\right)=2\\ \Leftrightarrow log_2\left(x^2-3x\right)=2\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-3x=4\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-3x-4=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\left(ktm\right)\\x=4\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
c, ĐK: \(x>1\)
\(lnx+ln\left(x-1\right)=ln4x\\ \Leftrightarrow ln\left[x\left(x-1\right)\right]-ln4x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow ln\left(\dfrac{x-1}{4}\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-1}{4}=1\\ \Leftrightarrow x-1=4\\ \Leftrightarrow x=5\left(tm\right)\)
d, ĐK: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-3x+2>0\\2x-4>0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow x>2\)
\(log_3\left(x^2-3x+2\right)=log_3\left(2x-4\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+2=2x-4\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+6=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\left(ktm\right)\\x=3\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
giải các phương trình sau
a) \(\log_5\left(4x-3\right)=2\)
b) \(\log_2x^2=2\)
c) \(\log_5\left(2x+1\right)=\log_5\left(-2x+3\right)\)
d) \(\ln\left(x^2-6x+7\right)=\ln\left(x-3\right)\)
e) \(\log\left(5x-1\right)=log\left(4-2x\right)\)
a: ĐKXĐ: \(4x-3>0\)
=>x>3/4
\(log_5\left(4x-3\right)=2\)
=>\(log_5\left(4x-3\right)=log_525\)
=>4x-3=25
=>4x=28
=>x=7(nhận)
b: ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne0\)
\(log_2x^2=2\)
=>\(log_2x^2=log_24\)
=>\(x^2=4\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\left(nhận\right)\\x=-2\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2};\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
\(\log_52x+1=\log_5-2x+3\)
=>2x+1=-2x+3
=>4x=2
=>\(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(nhận\right)\)
d: ĐKXD: \(x\notin\left\{3\right\}\)
\(ln\left(x^2-6x+7\right)=ln\left(x-3\right)\)
=>\(x^2-6x+7=x-3\)
=>\(x^2-7x+10=0\)
=>(x-2)(x-5)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\left(nhận\right)\\x=5\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
e: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{\dfrac{1}{5};2\right\}\)
\(log\left(5x-1\right)=log\left(4-2x\right)\)
=>5x-1=4-2x
=>7x=5
=>\(x=\dfrac{5}{7}\left(nhận\right)\)
Bất phương trình ln(2x2 + 3) > ln(x2 + ax + 1) nghiệm đúng với mọi số thực x khi:
A. - 2 2 < a < 2 2
B. 0 < a < 2 2
C. 0 < a < 2
D. - 2 < a < 2
Đáp án D
Ta có ln(2x2 + 3) > ln(x2 + ax + 1)
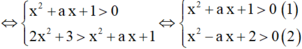
Giải (1), ta có x2 + ax + 1 > 0
∀ x ∈ ℝ ⇔ ∆ = a 2 - 4 < 0 ⇔ - 2 < a < 2 .
Giải (2), ta có x2 + ax + 2 > 0
∀ x ∈ ℝ ⇔ ∆ = - a 2 - 8 < 0 ⇔ - 2 2 < a < a 2 .
Vậy a thuộc (–2;2) là giá trị cần tìm.
Giải các phương trình sau :
a) \(e^{2+\ln x}=x+3\)
b) \(e^{4-\ln x}=x\)
c) \(\left(5-x\right)\log\left(x-3\right)=0\)
giải phương trình
a) \(logx=2\)
b) \(log_45x=log_4\left(2x-3\right)\)
c) \(log7x=4\)
d) \(ln\left(x^2+5\right)=ln6x\)
a.
ĐKXĐ: \(x>0\)
\(logx=2\Rightarrow x=10^2=100\)
b.
ĐKXĐ: \(x>\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(log_45x=log_4\left(2x-3\right)\Rightarrow5x=2x-3\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-1\) (ktm ĐKXĐ)
Vậy pt vô nghiệm
c.
ĐKXĐ: \(x>0\)
\(log7x=4\Rightarrow7x=10^4\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{10^4}{7}\)
d.
ĐKXĐ: \(x>0\)
\(ln\left(x^2+5\right)=ln\left(6x\right)\Rightarrow x^2+5=6x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-6x+5=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Giải các bất phương trình lôgarit sau :
a) \(\dfrac{\ln x+2}{\ln x-1}< 0\)
b) \(\log^2_{0,2}x-\log_{0,2}x-6\le0\)
c) \(\log\left(x^2-x-2\right)< 2\log\left(3-x\right)\)
d) \(\ln\left|x-2\right|+\ln\left|x+4\right|\le3\ln2\)
Tìm số nghiệm của phương trình ln ( x ) + ln ( 2 x - 1 ) = 0
A. 2
B. 4
C. 1
D. 0