Đạo hàm của hàm số y= 4sin 2x + 7cos 3x + 9 là:
A. 8cos 2x - 21sin 3x + 9
B. 8cos 2x - 21sin 3x
C. 4cos 2x - 7sin 3x
D. 4cos 2x + 7sin 3x
Đạo hàm của hàm số \(y=\left(-x^2+3x+7\right)^7\) là:
A. \(y'=7\left(-2x+3\right)\left(-x^2+3x+7\right)^6\)
B. \(y'=7\left(-x^2+3x+7\right)^6\)
C. \(y'=\left(-2x+3\right)\left(-x^2+3x+7\right)^6\)
D. \(y'=7\left(-2x+3\right)\left(-x^2+3x+7\right)^6\)
\(y'=7\left(-x^2+3x+7\right)^6.\left(-x^2+3x+7\right)'\)
\(=7\left(-2x+3\right)\left(-x^2+3x+7\right)^6\)
tính đạo hàm của các hàm số sau
a) \(y=x^2+3x-6x^6+\dfrac{2x-3}{x-1}\)
b) \(y=3x^2-4x+\sqrt{2x^2-3x+1}\)
c) \(y=\sqrt{4x^2-3x+1}-4\)
a: \(y'=\left(x^2\right)'+\left(3x\right)'-\left(6x^6\right)'+\left(\dfrac{2x-3}{x-1}\right)'\)
\(=2x+3-6\cdot6x^5+\dfrac{\left(2x-3\right)'\left(x-1\right)-\left(2x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)'}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
\(=-36x^5+2x+3+\dfrac{2\left(x-1\right)-2x+3}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
\(=-36x^5+2x+3+\dfrac{1}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
b: \(\left(\sqrt{2x^2-3x+1}\right)'=\dfrac{\left(2x^2-3x+1\right)'}{2\sqrt{2x^2-3x+1}}\)
\(=\dfrac{4x-3}{2\sqrt{2x^2-3x+1}}\)
\(y'=3\cdot2x-4+\dfrac{4x-3}{2\sqrt{2x^2-3x+1}}\)
\(=6x-4+\dfrac{4x-3}{2\sqrt{2x^2-3x+1}}\)
c: \(\left(\sqrt{4x^2-3x+1}\right)'=\dfrac{\left(4x^2-3x+1\right)'}{2\sqrt{4x^2-3x+1}}\)
\(=\dfrac{8x-3}{2\sqrt{4x^2-3x+1}}\)
\(y'=\left(\sqrt{4x^2-3x+1}\right)'-4'=\dfrac{8x-3}{2\sqrt{4x^2-3x+1}}\)
Tính đạo hàm của hàm số sau: y = ( 9 − 2 x ) ( 3 x 2 − 3 x + 1 )
A. − 18 x 2 + 46 x − 21
B. − 10 x 2 + 66 x − 19
C. − 18 x 2 + 66 x − 29
D. − 12 x 2 + 48 x − 21
y ' = 9 - 2 x 3 x 2 - 3 x + 1 ' = ( 9 − 2 x ) ' . ( 3 x 2 − 3 x + 1 ) + ( 3 x 2 − 3 x + 1 ) ' . ( 9 − 2 x ) = − 2 ( 3 x 2 − 3 x + 1 ) + ( 6 x − 3 ) ( 9 − 2 x )
= − 6 x 2 + 6 x − 2 + 54 x − 12 x 2 − 27 + 6 x = − 18 x 2 + 66 x − 29
Chọn đáp án C
tìm cực trị của hàm số a)y=x³-3x²+9 b)y=1/3x³-2x²+15x+3
a. TXĐ: D=R
$y'=3x^2-6x=0\Leftrightarrow x=0$ hoặc $x=2$
$y''=6x-6$
$y''(0)=-6<0$ nên hàm số đạt cực đại tại $x=0$, giá trị cực đại tương ứng là $y=9$
$y''(2)=6>0$ nên hàm số đạt cực tiểu tại $x=2$, giá trị cực tiểu tương ứng là $y=5$
b. TXĐ: $D=R$
$y=\frac{1}{3}x^3-2x^2+15x+3$
$y'=x^2-4x+15=(x-2)^2+11>0$ với mọi $x\in D$
Do đó hàm $y$ đồng biến trên toàn tập xác định nên không có cực trị.
1. Tính đạo hàm của các hàm số sau:
a, \(y=\dfrac{2x-1}{x-1}\)
b, \(y=\dfrac{2x+1}{1-3x}\)
c, \(y=\dfrac{x^2+2x+2}{x+1}\)
d, \(y=\dfrac{2x^2}{x^2-2x-3}\)
e, \(y=x+1-\dfrac{2}{x-1}\)
g, \(y=\dfrac{2x^2-4x+5}{2x+1}\)
2. Tính đạo hàm của các hàm số sau:
a, \(y=\left(x^2+x+1\right)^4\)
b, y= (1-2x2)5
c, \(y=\left(\dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}\right)^3\)
d, \(y=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)^3}\)
e, \(y=\dfrac{1}{\left(x^2-2x+5\right)^2}\)
f, \(y=\left(3-2x^2\right)^4\)
a. \(y'=\dfrac{-1}{\left(x-1\right)}\)
b. \(y'=\dfrac{5}{\left(1-3x\right)^2}\)
c. \(y=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2+1}{x+1}=x+1+\dfrac{1}{x+1}\Rightarrow y'=1-\dfrac{1}{\left(x+1\right)^2}=\dfrac{x^2+2x}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
d. \(y'=\dfrac{4x\left(x^2-2x-3\right)-2x^2\left(2x-2\right)}{\left(x^2-2x-3\right)^2}=\dfrac{-4x^2-12x}{\left(x^2-2x-3\right)^2}\)
e. \(y'=1+\dfrac{2}{\left(x-1\right)^2}=\dfrac{x^2-2x+3}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
g. \(y'=\dfrac{\left(4x-4\right)\left(2x+1\right)-2\left(2x^2-4x+5\right)}{\left(2x+1\right)^2}=\dfrac{4x^2+4x-14}{\left(2x+1\right)^2}\)
2.
a. \(y'=4\left(x^2+x+1\right)^3.\left(x^2+x+1\right)'=4\left(x^2+x+1\right)^3\left(2x+1\right)\)
b. \(y'=5\left(1-2x^2\right)^4.\left(1-2x^2\right)'=-20x\left(1-2x^2\right)^4\)
c. \(y'=3\left(\dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}\right)^2.\left(\dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}\right)'=3\left(\dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}\right)^2.\left(\dfrac{-3}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\right)=\dfrac{-9\left(2x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)^4}\)
d. \(y'=\dfrac{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)^3-3\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)^6}=\dfrac{-x^2-6x-5}{\left(x-1\right)^4}\)
e. \(y'=-\dfrac{\left[\left(x^2-2x+5\right)^2\right]'}{\left(x^2-2x+5\right)^4}=-\dfrac{2\left(x^2-2x+5\right)\left(2x-2\right)}{\left(x^2-2x+5\right)^4}=-\dfrac{4\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x^2-2x+5\right)^3}\)
f. \(y'=4\left(3-2x^2\right)^3.\left(3-2x^2\right)'=-16x\left(3-2x^2\right)^3\)
Tính đạo hàm của các hàm số sau:
a) y=\(\dfrac{3x^2-18x-2}{1-2x}-\dfrac{2x-3}{x+4}\)
b) y=\(-\dfrac{\sin x}{3\cos^3x}+\dfrac{4}{3}\tan x\)
Cho hàm số y = x 2 + 2 x - 3 x + 2 . Đạo hàm y' của hàm số là:
A. 1 + 3 x + 2 2
B. x 2 + 6 x - 7 x + 2 2
C. x 2 + 4 x + 5 x + 2 2
D. x 2 + 8 x + 1 x + 2 2
Cách 1:
- Ta có:
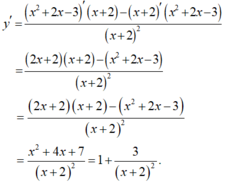
Cách 2:
- Ta có:
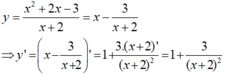
Chọn A.
Cho hàm số y = 3 x + 5 - 1 + 2 x . Đạo hàm y’ của hàm số là:
A. 7 ( 2 x - 1 ) 2
B. 1 ( 2 x - 1 ) 2
C. - 13 ( 2 x - 1 ) 2
D. 13 ( 2 x - 1 ) 2
Cho hàm số y = x 2 + 2 x - 3 x + 2 . Đạo hàm của hàm số là:
A. y ' = x 2 + 6 x + 7 x + 2 2
B. y ' = x 2 + 8 x + 7 x + 2 2
C. y ' = x 2 + 4 x + 7 x + 2 2
D. y ' = x 2 + 6 x + 5 x + 2 2