Biết rằng ∫ 1 2 ln ( x + 1 ) d x = a ln 3 + b ln 2 + c với a, b, c là các số nguyên. Tính S = a+b+c
A. S = 0
B. S = 1
C. S = 2
D. S = -2
Giải các phương trình sau :
a) \(\ln\left(4x+2\right)-\ln\left(x-1\right)=\ln x\)
b) \(\log_2\left(3x+1\right)\log_3x=2\log_2\left(3x+1\right)\)
c) \(2^{\log_3x^2}.5^{\log_3x}=400\)
d) \(\ln^3x-3\ln^2x-4\ln x+12=0\)
a) Điều kiện: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x+2>0\\x-1>0\\x>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Hay là: \(x>1\)
Khi đó biến đổi pương trình như sau:
\(\ln\dfrac{4x+2}{x-1}=\ln x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x+2}{x-1}=x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+2=x\left(x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{33}}{2}\\x_2=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{33}}{2}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy nghiệm của phương trình là: \(x=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{33}}{2}\)
b) Điều kiện: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x+1>0\\x>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Hay là: \(x>0\)
Biến đổi phương trình như sau:
\(\log_2\left(3x+1\right)\log_3x-2\log_2\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\log_2\left(3x+1\right)\left(\log_3x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\log_2\left(3x+1\right)=0\\\log_3x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+1=2^0\\x=3^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(loại\right)\\x=9\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy nghiệm là x = 9.
c) Điều kiện: x > 0.
Khi đó biến đổi phương trình như sau:
\(2^{\log_3x^2}.5^{\log_3x}=400\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2^{2\log_3x}.5^{\log_3x}=400\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2^2.5\right)^{\log_3x}=400\)
\(\Leftrightarrow20^{\log_3x}=20^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\log_3x=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3^2=9\) (thỏa mãn)
4. Tính đạo hàm của các hàm số sau:
a) \(y = (3x^2-4x+1)^{-4}\)
b) \(y = 3^{x^2-1} + e^{-x+1}\)
c) \(y = \ln (x^2-4x) + \log_{3} (2x-1)\)
d) \(y =x . \ln x + 2^{\frac{x-1}{x+1}}\)
e) \(y = x^{-7} - \ln (x^2-1)\)
`a)TXĐ:R\\{1;1/3}`
`y'=[-4(6x-4)]/[(3x^2-4x+1)^5]`
`b)TXĐ:R`
`y'=2x. 3^[x^2-1] ln 3-e^[-x+1]`
`c)TXĐ: (4;+oo)`
`y'=[2x-4]/[x^2-4x]+2/[(2x-1).ln 3]`
`d)TXĐ:(0;+oo)`
`y'=ln x+2/[(x+1)^2].2^[[x-1]/[x+1]].ln 2`
`e)TXĐ:(-oo;-1)uu(1;+oo)`
`y'=-7x^[-8]-[2x]/[x^2-1]`
Lời giải:
a.
$y'=-4(3x^2-4x+1)^{-5}(3x^2-4x+1)'$
$=-4(3x^2-4x+1)^{-5}(6x-4)$
$=-8(3x-2)(3x^2-4x+1)^{-5}$
b.
$y'=(3^{x^2-1})'+(e^{-x+1})'$
$=(x^2-1)'3^{x^2-1}\ln 3 + (-x+1)'e^{-x+1}$
$=2x.3^{x^2-1}.\ln 3 -e^{-x+1}$
c.
$y'=\frac{(x^2-4x)'}{x^2-4x}+\frac{(2x-1)'}{(2x-1)\ln 3}$
$=\frac{2x-4}{x^2-4x}+\frac{2}{(2x-1)\ln 3}$
d.
\(y'=(x\ln x)'+(2^{\frac{x-1}{x+1}})'=x(\ln x)'+x'\ln x+(\frac{x-1}{x+1})'.2^{\frac{x-1}{x+1}}\ln 2\)
\(=x.\frac{1}{x}+\ln x+\frac{2}{(x+1)^2}.2^{\frac{x-1}{x+1}}\ln 2\\ =1+\ln x+\frac{2^{\frac{2x}{x+1}}\ln 2}{(x+1)^2}\)
e.
\(y'=-7x^{-8}-\frac{(x^2-1)'}{x^2-1}=-7x^{-8}-\frac{2x}{x^2-1}\)
Giải các bất phương trình sau:
a) (2x − 7)ln(x + 1) > 0;
b) (x − 5)(logx + 1) < 0;
c) 2 log 3 2 x + 5 log 2 2 x + log 2 x – 2 ≥ 0
d) ln(3 e x − 2) ≤ 2x
a) Bất phương trình đã cho tương đương với hệ sau:
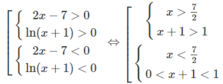
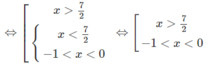
Vậy tập nghiệm là (−1;0) ∪ (7/2; + ∞ )
b) Tương tự câu a), tập nghiệm là (1/10; 5)
c) Đặt t = log 2 x , ta có bất phương trình 2 t 3 + 5 t 2 + t – 2 ≥ 0 hay (t + 2)(2 t 2 + t − 1) ≥ 0 có nghiệm −2 ≤ t ≤ −1 hoặc t ≥ 1/2
Suy ra 1/4 ≤ x ≤ 1/2 hoặc x ≥ 2
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình đã cho là: [1/4; 1/2] ∪ [ 2 ; + ∞ )
d) Bất phương trình đã cho tương đương với hệ:
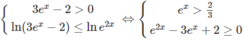
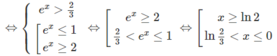
Vậy tập nghiệm là (ln(2/3); 0] ∪ [ln2; + ∞ )
Câu 1: Cho \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow e}\frac{\log_2\left(\ln\left(x\right)\right)}{f\left(x\right)}=\frac{1}{\ln\left(2\right)e}\). Biết \(\ln\left(f\left(0\right)\right)=1\) và \(\int\limits^{5e}_{-e}f\left(2x\right)dx=18e^2\). Tính \(\frac{\ln\left(f\left(1+e\right)\right)}{f\left(1+e\right)^{10}}\) bằng:
a) 0
b) \(\frac{\ln\left(1+e\right)}{\left(1+e\right)^{10}}\)
c) \(1\)
d) \(\frac{\ln\left(1+2e\right)}{\left(1+2e\right)^{10}}\)
Tính các nguyên hàm.
a)\(\int\dfrac{2dx}{x^2-5x}=A\ln\left|x\right|+B\ln\left|x-5\right|+C\) . Tìm 2A-3B.
b)\(\int\dfrac{x^3-1}{x+1}\)dx=\(Ax^3-Bx^2+x+E\ln\left|x+1\right|+C\).Tính A-B+E
a) \(\int\dfrac{2dx}{x^2-5x}=\int\left(\dfrac{-2}{5x}+\dfrac{2}{5\left(x-5\right)}\right)dx=-\dfrac{2}{5}ln\left|x\right|+\dfrac{2}{5}ln\left|x-5\right|+C\)
\(\Rightarrow A=-\dfrac{2}{5};B=\dfrac{2}{5}\Rightarrow2A-3B=-2\)
b) \(\int\dfrac{x^3-1}{x+1}dx=\int\dfrac{x^3+1-2}{x+1}dx=\int\left(x^2-x+1-\dfrac{2}{x+1}\right)dx=\dfrac{1}{3}x^3-\dfrac{1}{2}x^2+x-2ln\left|x+1\right|+C\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{1}{3};B=\dfrac{1}{2};E=-2\Rightarrow A-B+E=-\dfrac{13}{6}\)
Viết mỗi biểu thức sau thành lôgarit của một biểu thức (giả thiết các biểu thức đều có nghĩa):
a) \(A = \ln \left( {\frac{x}{{x - 1}}} \right) + \ln \left( {\frac{{x + 1}}{x}} \right) - \ln \left( {{x^2} - 1} \right);\)
b) \(B = 21{\log _3}\sqrt[3]{x} + {\log _3}\left( {9{x^2}} \right) - {\log _3}9.\)
\(a,A=ln\left(\dfrac{x}{x-1}\right)+ln\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x}\right)-ln\left(x^2-1\right)\\ =ln\left(\dfrac{x}{x-1}\cdot\dfrac{x+1}{x}\right)-ln\left(x^2-1\right)\\ =ln\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}\right)-ln\left(x^2-1\right)\\ =ln\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}\cdot\dfrac{1}{x^2-1}\right)\\ =ln\left[\dfrac{1}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\right]\\ =2ln\left(\dfrac{1}{x-1}\right)\)
\(b,21log_3\sqrt[3]{x}+log_3\left(9x^2\right)-log_3\left(9\right)\\ =7log_3\left(x\right)+log_3x^2+log_39-log_39\\ =7log_3x+2log_3x\\ =9log_3x\)
Viết mỗi biểu thức sau thành lôgarit của một biểu thức (giả thiết các biểu thức đều có nghĩa):
a) \(A = \ln \left( {\frac{x}{{x - 1}}} \right) + \ln \left( {\frac{{x + 1}}{x}} \right) - \ln \left( {{x^2} - 1} \right);\)
b) \(B = 21{\log _3}\sqrt[3]{x} + {\log _3}\left( {9{x^2}} \right) - {\log _3}9.\)
a)
\(\begin{array}{c}A = {\log _{\frac{1}{3}}}5 + 2{\log _9}25 - {\log _{\sqrt 3 }}\frac{1}{5} = {\log _{{3^{ - 1}}}}5 + 2{\log _{{3^2}}}{5^2} - {\log _{{3^{\frac{1}{2}}}}}{5^{ - 1}}\\ = - {\log _3}5 + 2{\log _3}5 + 2{\log _3}5 = 3{\log _3}5\end{array}\)
b) \(B = {\log _a}{M^2} + {\log _{{a^2}}}{M^4} = 2{\log _a}M + \frac{1}{2}.4{\log _a}M = 4{\log _a}M\)
a) Sử dụng giới hạn \(\mathop {\lim }\limits_{t \to 0} \frac{{\ln \left( {1 + t} \right)}}{t} = 1\) và đẳng thức \(\ln \left( {x + h} \right) - \ln x = \ln \left( {\frac{{x + h}}{x}} \right) = \ln \left( {1 + \frac{h}{x}} \right),\) tính đạo hàm của hàm số \(y = \ln x\) tại điểm x > 0 bằng định nghĩa.
b) Sử dụng đẳng thức \({\log _a}x = \frac{{\ln x}}{{\ln a}}\,\,\left( {0 < a \ne 1} \right),\) hãy tính đạo hàm của hàm số \(y = {\log _a}x.\)
a) Với x > 0 bất kì và \(h = x - {x_0}\) ta có
\(\begin{array}{l}f'\left( {{x_0}} \right) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{h \to 0} \frac{{f\left( {{x_0} + h} \right) - f\left( {{x_0}} \right)}}{h} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{h \to 0} \frac{{\ln \left( {{x_0} + h} \right) - \ln {x_0}}}{h}\\ = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{h \to 0} \frac{{\ln \left( {1 + \frac{h}{{{x_0}}}} \right)}}{{\frac{h}{{{x_0}}}.{x_0}}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{h \to 0} \frac{1}{{{x_0}}}.\mathop {\lim }\limits_{h \to 0} \frac{{\ln \left( {1 + \frac{h}{{{x_0}}}} \right)}}{{\frac{h}{{{x_0}}}}} = \frac{1}{{{x_0}}}\end{array}\)
Vậy hàm số \(y = \ln x\) có đạo hàm là hàm số \(y' = \frac{1}{x}\)
b) Ta có \({\log _a}x = \frac{{\ln x}}{{\ln a}}\) nên \(\left( {{{\log }_a}x} \right)' = \left( {\frac{{\ln x}}{{\ln a}}} \right)' = \frac{1}{{x\ln a}}\)
Biết \(\int_1^e\frac{1-\ln x}{\left(x+\ln x\right)^2}dx=\frac{1}{ae+b}\) với a, b\(\in\) Z. Tính \(a^2+b^2\)
\(I=\int\limits^e_1\frac{\frac{1-lnx}{x^2}}{\left(1+\frac{lnx}{x}\right)^2}dx\)
Đặt \(\frac{lnx}{x}=t\Rightarrow\left(\frac{1-lnx}{x^2}\right)dx=dt\)
\(\Rightarrow I=\int\limits^{\frac{1}{e}}_0\frac{dt}{\left(1+t\right)^2}=-\frac{1}{1+t}|^{\frac{1}{e}}_0=\frac{1}{e+1}\)
\(\Rightarrow a=b=1\Rightarrow a^2+b^2=2\)
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) \(\log \left( {x + 1} \right) = 2;\)
b) \(2{\log _4}x + {\log _2}\left( {x - 3} \right) = 2;\)
c) \(\ln x + \ln \left( {x - 1} \right) = \ln 4x;\)
d) \({\log _3}\left( {{x^2} - 3x + 2} \right) = {\log _3}\left( {2x - 4} \right).\)
a, ĐK: \(x+1>0\Leftrightarrow x>-1\)
\(log\left(x+1\right)=2\\ \Leftrightarrow x+1=10^2\\ \Leftrightarrow x+1=100\\ \Leftrightarrow x=99\left(tm\right)\)
b, ĐK: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3>0\\x>0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow x>3\)
\(2log_4x+log_2\left(x-3\right)=2\\ \Leftrightarrow log_2x+log_2\left(x-3\right)=2\\ \Leftrightarrow log_2\left(x^2-3x\right)=2\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-3x=4\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-3x-4=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\left(ktm\right)\\x=4\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
c, ĐK: \(x>1\)
\(lnx+ln\left(x-1\right)=ln4x\\ \Leftrightarrow ln\left[x\left(x-1\right)\right]-ln4x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow ln\left(\dfrac{x-1}{4}\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-1}{4}=1\\ \Leftrightarrow x-1=4\\ \Leftrightarrow x=5\left(tm\right)\)
d, ĐK: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-3x+2>0\\2x-4>0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow x>2\)
\(log_3\left(x^2-3x+2\right)=log_3\left(2x-4\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+2=2x-4\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+6=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\left(ktm\right)\\x=3\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)