giải phương trình x2/3+48/x2=10(x/3-4/x)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải phương trình :
1) √x2+x+2 + 1/x= 13-7x/2
2) x2 + 3x = √1-x + 1/4
3) ( x+3)√48-x2-8x= 28-x/ x+3
4) √-x2-2x +48= 28-x/x+3
5) 3x2 + 2(x-1)√2x2-3x +1= 5x + 2
6) 4x2 +(8x - 4)√x -1 = 3x+2√2x2 +5x-3
7) x3/ √16-x2 + x2 -16 = 0
Giải phương trình bằng cách đặt ẩn phụ:
a
)
3.
x
2
+
x
2
−
2
x
2
+
x...
Đọc tiếp
Giải phương trình bằng cách đặt ẩn phụ:
a ) 3. x 2 + x 2 − 2 x 2 + x − 1 = 0 b ) x 2 − 4 x + 2 2 + x 2 − 4 x − 4 = 0 c ) x − x = 5 x + 7 d ) x x + 1 − 10 ⋅ x + 1 x = 3
a)
3 · x 2 + x 2 - 2 x 2 + x - 1 = 0 ( 1 )
Đặt t = x 2 + x ,
Khi đó (1) trở thành : 3 t 2 – 2 t – 1 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2) : Có a = 3 ; b = -2 ; c = -1
⇒ a + b + c = 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm t 1 = 1 ; t 2 = c / a = - 1 / 3 .
+ Với t = 1 ⇒ x 2 + x = 1 ⇔ x 2 + x – 1 = 0 ( * )
Có a = 1; b = 1; c = -1 ⇒ Δ = 1 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 1 ) = 5 > 0
(*) có hai nghiệm
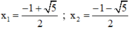
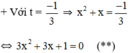
Có a = 3; b = 3; c = 1 ⇒ Δ = 3 2 – 4 . 3 . 1 = - 3 < 0
⇒ (**) vô nghiệm.
Vậy phương trình (1) có tập nghiệm 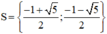
b)
x 2 − 4 x + 2 2 + x 2 − 4 x − 4 = 0 ⇔ x 2 − 4 x + 2 2 + x 2 − 4 x + 2 − 6 = 0 ( 1 )
Đặt x 2 – 4 x + 2 = t ,
Khi đó (1) trở thành: t 2 + t – 6 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2): Có a = 1; b = 1; c = -6
⇒ Δ = 1 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 6 ) = 25 > 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm
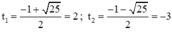
+ Với t = 2 ⇒ x 2 – 4 x + 2 = 2
⇔ x 2 – 4 x = 0
⇔ x(x – 4) = 0
⇔ x = 0 hoặc x = 4.
+ Với t = -3 ⇒ x 2 – 4 x + 2 = - 3
⇔ x2 – 4x + 5 = 0 (*)
Có a = 1; b = -4; c = 5 ⇒ Δ ’ = ( - 2 ) 2 – 1 . 5 = - 1 < 0
⇒ (*) vô nghiệm.
Vậy phương trình ban đầu có tập nghiệm S = {0; 4}.
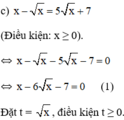
Khi đó (1) trở thành: t 2 – 6 t – 7 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2): Có a = 1; b = -6; c = -7
⇒ a – b + c = 0
⇒ (2) có nghiệm t 1 = - 1 ; t 2 = - c / a = 7 .
Đối chiếu điều kiện chỉ có nghiệm t = 7 thỏa mãn.
+ Với t = 7 ⇒ √x = 7 ⇔ x = 49 (thỏa mãn).
Vậy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm x = 49.
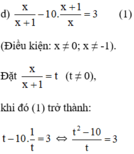
⇔ t 2 – 10 = 3 t ⇔ t 2 – 3 t – 10 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2): Có a = 1; b = -3; c = -10
⇒ Δ = ( - 3 ) 2 - 4 . 1 . ( - 10 ) = 49 > 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm:
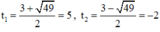
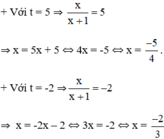
Cả hai nghiệm đều thỏa mãn điều kiện xác định.
Vậy phương trình đã cho có tập nghiệm 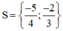
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 2: Giải các phương trình sau:
a. (3x + 2)(x2 – 1) = (9x2 – 4)(x + 1)
b. x(x + 3)(x – 3) – 5(x + 2)(x2 – 2x + 4) = 0
c. x(x + 3)(x – 3) + 5(x – 3) = 0
d. (3x – 1)(x2 + 2) = (3x – 1)(7x – 10)
\(a.\left(3x+2\right)\left(x^2-1\right)=\left(9x^2-4\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)=\left(3x-2\right)\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=3x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
c: =>x-3=0
hay x=3
d: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\cdot\left(x^2+2-7x+10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{\dfrac{1}{3};3;4\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 2: Giải các phương trình sau:
a. (3x + 2)(x2 – 1) = (9x2 – 4)(x + 1)
b. x(x + 3)(x – 3) – 5(x + 2)(x2 – 2x + 4) = 0
c. x(x + 3)(x – 3) + 5(x – 3) = 0
d. (3x – 1)(x2 + 2) = (3x – 1)(7x – 10)
\(\left(3x+2\right)\left(x^2-1\right)=\left(9x^2-4\right)\left(x+1\right).\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)-\left(3x-2\right)\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)=0.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1-3x+2\right)=0.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(-2x+1\right)=0.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+2=0.\\x+1=0.\\-2x+1=0.\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{2}{3}.\\x=-1.\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}.\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
c: =>(x-3)(x2+3x+5)=0
=>x-3=0
hay x=3
d: =>(3x-1)(x2+2-7x+10)=0
=>(3x-1)(x-3)(x-4)=0
hay \(x\in\left\{\dfrac{1}{3};3;4\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:
g/ x(x + 3)(x – 3) – (x + 2)(x2 – 2x + 4) = 0
h/ (3x – 1)(x2 + 2) = (3x – 1)(7x – 10)
i/ (x + 2)(3 – 4x) = x2 + 4x + 4
k/ x(2x – 7) – 4x + 14 = 0
m/ x2 + 6x – 16 = 0
n/ 2x2 + 5x – 3 = 0
\(m,x^2+6x-16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+8x-16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)+8\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+8\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+8=0\\x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-8\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(n,2x^2+5x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-x+6x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(2x-1\right)+3\left(2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left(2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\2x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
\(k,x\left(2x-7\right)-4x+14=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-4x-7x+14=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x-2\right)-7\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-7\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-7=0\\x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{7}{2}\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (1)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
bài 1 giải các bất phương trình sau
a, -x2 +5x-6 ≥ 0
b, x2-12x +36≤0
c, -2x2 +4x-2≤0
d, x2 -2|x-3| +3x ≥ 0
e, x-|x+3| -10 ≤0
bài 2 xét dấu các biểu thức sau
a,<-x2+x-1> <6x2 -5x+1>
b, x2-x-2/ -x2+3x+4
c, x2-5x +2
d, x-< x2-x+6 /-x2 +3x+4 >
Bài 1:
a: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+6< =0\)
=>(x-2)(x-3)<=0
=>2<=x<=3
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right)^2< =0\)
=>x=6
c: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1>=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2>=0\)
hay \(x\in R\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình
1) x2+4-2(x-1) = (x-2)^2
2) x+3/x-3 - x-1/x+3 = x2+4x+6/x2-9
3) 3x-3/x2-9 -1/x-3 = x+1/x+3
Xem chi tiết
1) `x^2+4-2(x-1)=(x-2)^2`
`<=>x^2+4-2x+2=x^2-4x+4`
`<=>-2x+2=-4x`
`<=>2x=-2`
`<=>x=-1`
.
2) ĐKXĐ: `x \ne \pm 3`
`(x+3)/(x-3)-(x-1)/(x+3)=(x^2+4x+6)/(x^2-9)`
`<=>(x+3)^2-(x-1)(x-3)=x^2+4x+6`
`<=>x^2+6x+9-x^2+4x-3=x^2+4x+6`
`<=>10x+6=x^2+4x+6`
`<=>x^2-6x=0`
`<=>x(x-6)=0`
`<=>x=0;x=6`
.
3) ĐKXĐ: `x \ne \pm 3`
`(3x-3)/(x^2-9) -1/(x-3 )= (x+1)/(x+3)`
`<=>(3x-3)-(x+3)=(x+1)(x-3)`
`<=> 2x-6=x^2-2x-3`
`<=>x^2-4x+3=0`
`<=>x^2-x-3x+3=0`
`<=>x(x-1)-3(x-1)=0`
`<=>(x-3)(x-1)=0`
`<=> x=3;x=1`
Vậy...
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
giải các phương trình sau:
a)(x+2)(x2-2x+4)-x(x2-2)=15
b)x(x-5)(x+5)-(x+2)(x2-2x+4)=3
\(a,=>x^3-2x^2+4x+2x^2-4x+8-x^3+2x-15=0\)
\(< =>2x-7=0< =>x=\dfrac{7}{2}\)
b,\(=>x\left(x^2-25\right)-\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)-3=0\)
\(< =>x^3-25x-x^3+2x^2-4x-2x^2+4x-8-3=0\)
\(< =>-25x-11=0\)
\(< =>x=-0,44\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (1)
Giải các bất phương trình sau
a) 4(x-3)2-(2x-1)2<10
b) x(x-5)(x+5)-(x+2)(x2-2x+4)< hoặc = 3
\(a,4\left(x-3\right)^2-\left(2x-1\right)^2< 10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(x^2-6x+9\right)-\left(4x^2-4x+1\right)-10< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-24x+36-4x^2+4x-1-10< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-20x< -25\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>\dfrac{5}{4}\)
\(b,x\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)-\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)\le3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2-25\right)-\left(x^3-2x^2+4x+2x^2-4x+8\right)\le3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-25x-\left(x^3+8\right)\le3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-25x-x^3-8-3\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-25x\le11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge-\dfrac{11}{25}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau: x 2 - 1 ( x + 2 ) ( x - 3 ) = ( x - 1 ) x 2 - 4 ( x + 5 )
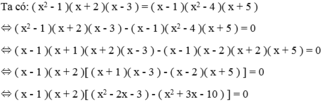
⇔ ( x - 1 )( x + 2 )( 7 - 5x ) = 0
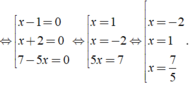
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là S = { - 2; 1; 7/5 }.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)





















