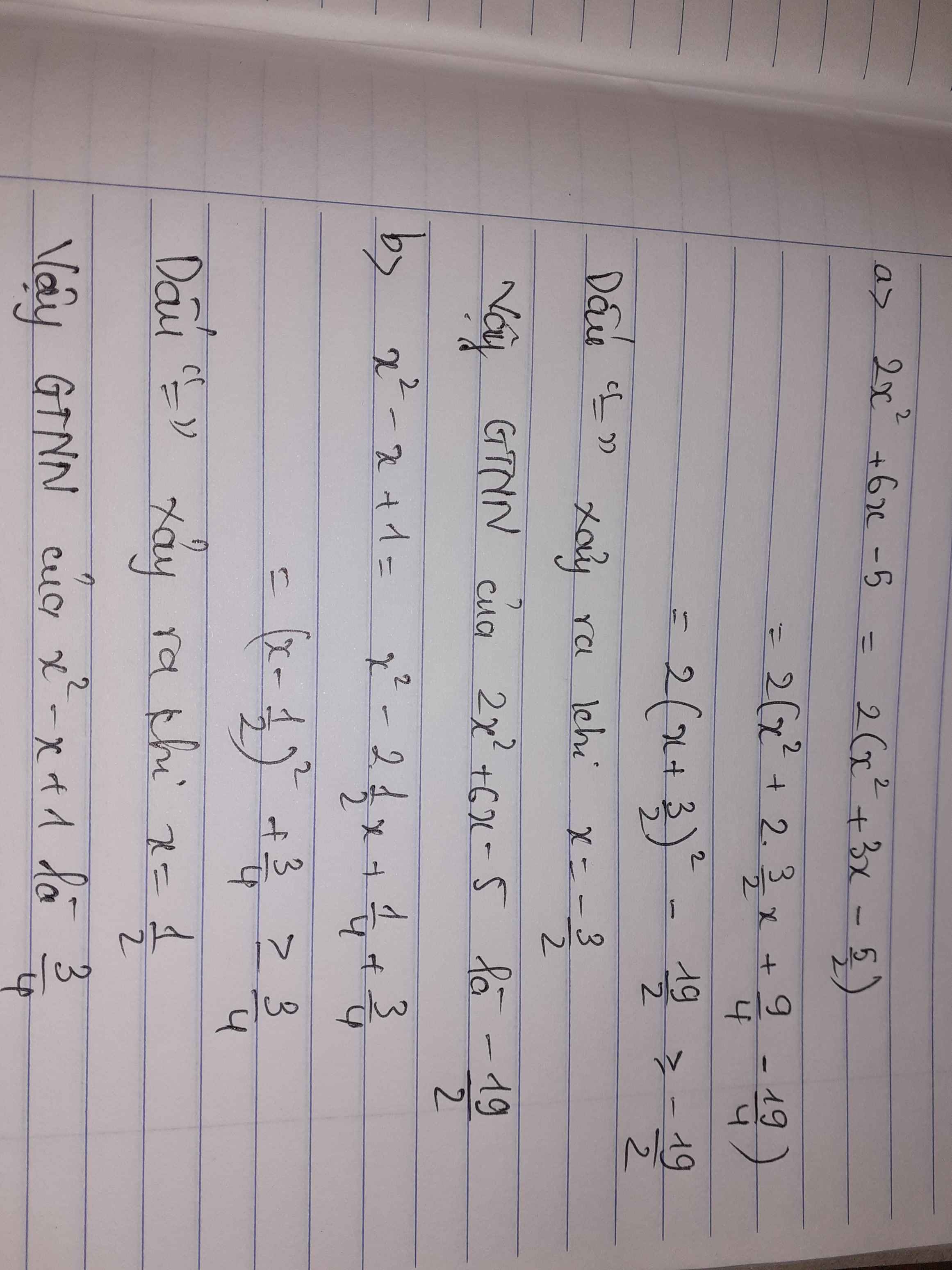có I = (2x2 - 6x +3) / (x2 - 3x + 2 ), tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của I

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Bài 2: Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất, giá trị lớn nhất (nếu có) của:
a) A = x2 - 4x + 1
b) B = -x2 - 8x + 5
c) C = 2x2 - 8x +19
d) D = -3x2 - 6x +1
a) \(A=x^2-4x+1=\left(x-2\right)^2-3\ge-3\)
\(minA=-3\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
b) \(B=-x^2-8x+5=-\left(x+4\right)^2+21\le21\)
\(maxB=21\Leftrightarrow x=-4\)
c) \(C=2x^2-8x+19=2\left(x-2\right)^2+11\ge11\)
\(minC=11\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
d) \(D=-3x^2-6x+1=-3\left(x+1\right)^2+4\le4\)
\(maxD=4\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
a) A = (x-2)^2 - 3 >= -3
--> A nhỏ nhất bằng -3
<=> x = 2
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
b) B = -(x+4)^2 + 21 <= 21
--> B lớn nhất bằng 21
<=> x = -4
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất : a) 2x2+6x-5
b) x2-x+1
\(2x^2+6x-5=2\left(x+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2-\dfrac{19}{2}\ge-\dfrac{19}{2}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(x^2-x+1=\left(x^2-x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)+\dfrac{3}{4}=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (1)
1) tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của
D= 4x-x2+3
E=2x-2x2-5
F=-x2-4x+20
2) chứng minh biểu thức không phụ vào biến
A= (2x+3)(4x2-6x+9)-2(4x3-1)
B=(x+3)3-(x+9)(x2+27)
1. Đề bài sai, các biểu thức này chỉ có giá trị lớn nhất, không có giá trị nhỏ nhất
2.
\(A=\left(2x\right)^3-3^3-\left(8x^3+2\right)\)
\(=8x^3-27-8x^3-2\)
\(=-29\)
\(B=x^3+9x^2+27x+27-\left(x^3+9x^2+27x+243\right)\)
\(=27-243=-216\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
sửa đề lại thành tìm Max nhé1, vì mấy ý này ko có min
\(1,=>D=-\left(x^2-4x-3\right)=-\left(x^2-2.2x+4-7\right)\)
\(=-[\left(x-2\right)^2-7]=-\left(x-2\right)^2+7\le7\)
dấu"=" xảy ra<=>x=2
2, \(E=-2\left(x^2-x+\dfrac{5}{2}\right)=-2[x^2-2.\dfrac{1}{2}x+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{9}{4}]\)
\(=-2[\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{9}{4}]\le-\dfrac{9}{2}\) dấu"=" xảy ra<=>x=1/2
3, \(F=-\left(x^2+4x-20\right)=-\left(x^2+2.2x+4-24\right)\)
\(=-[\left(x+2\right)^2-24]\le24\) dấu"=" xảy ra<=>x=-2
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(D=-x^2+4x+3\)
\(=-\left(x^2-4x-3\right)\)
\(=-\left(x^2-4x+4-7\right)\)
\(=-\left(x-2\right)^2+7\le7\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=2
c) Ta có: \(F=-x^2-4x+20\)
\(=-\left(x^2+4x-20\right)\)
\(=-\left(x^2+4x+4-24\right)\)
\(=-\left(x+2\right)^2+24\le24\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=-2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Bài 1: Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của các biểu thứca ) A x2 – 2x+5b) B x2 –x +1c) C ( x -1). ( x +2). ( x+3). ( x+6)d) D x2 + 5y2 – 2xy+ 4y+3Bài 2: Tìm giá trị lớn nhất của các biểu thức sau:a) A -x2 – 4x – 2 b) B -2x2 – 3x +5c) C ( 2- x). ( x +4)d) D -8x2 + 4xy - y2 +3Bài 3 : Chứng minh rằng các giá trị của các biểu thức sau luôn dương với mọi giá trị của biếna) A 25x – 20x+7b) B 9x2 – 6xy + 2y2 +1c) E x2 – 2x + y2 + 4y+6d) D x2 – 2x +2Giúp mình nha. Cần gấp ạ Chi tiết nha
Đọc tiếp
Bài 1: Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của các biểu thức
a ) A= x2 – 2x+5
b) B= x2 –x +1
c) C= ( x -1). ( x +2). ( x+3). ( x+6)
d) D= x2 + 5y2 – 2xy+ 4y+3
Bài 2: Tìm giá trị lớn nhất của các biểu thức sau:
a) A= -x2 – 4x – 2
b) B= -2x2 – 3x +5
c) C= ( 2- x). ( x +4)
d) D= -8x2 + 4xy - y2 +3
Bài 3 : Chứng minh rằng các giá trị của các biểu thức sau luôn dương với mọi giá trị của biến
a) A= 25x – 20x+7
b) B= 9x2 – 6xy + 2y2 +1
c) E= x2 – 2x + y2 + 4y+6
d) D= x2 – 2x +2
Giúp mình nha. Cần gấp ạ <Chi tiết nha>
Bài 3:
a) Ta có: \(A=25x^2-20x+7\)
\(=\left(5x\right)^2-2\cdot5x\cdot2+4+3\)
\(=\left(5x-2\right)^2+3>0\forall x\)(đpcm)
d) Ta có: \(D=x^2-2x+2\)
\(=x^2-2x+1+1\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)^2+1>0\forall x\)(đpcm)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(A=x^2-2x+5\)
\(=x^2-2x+1+4\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)^2+4\ge4\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=1
b) Ta có: \(B=x^2-x+1\)
\(=x^2-2\cdot x\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
BÀI 11:Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức:
a. A = x2 – 6x + 11
b. B = 2x2 – 20x + 101
c. C = x2 – 4xy + 5y2 + 10x – 22y + 28
\(A=\left(x^2-6x+9\right)+2=\left(x-3\right)^2+2\ge2\\ A_{min}=2\Leftrightarrow x=3\\ B=2\left(x^2-10x+25\right)+51=2\left(x-5\right)^2+51\ge51\\ B_{min}=51\Leftrightarrow x=5\\ C=\left[\left(x^2-4xy+4y^2\right)+10\left(x-2y\right)+25\right]+\left(y^2-2y+1\right)+2\\ C=\left(x-2y+5\right)^2+\left(y-1\right)^2+2\ge2\\ C_{min}=2\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2y+5=0\\y-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2y-5=2-5=-3\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a) \(A=\left(x^2-6x+9\right)+2=\left(x-3\right)^2+2\ge2\)
\(minA=2\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
b) \(B=2\left(x^2-10x+25\right)+51=2\left(x-5\right)^2+51\ge51\)
\(minB=51\Leftrightarrow x=5\)
c) \(C=\left[x^2-2x\left(2y-5\right)+\left(2y-5\right)^2\right]+\left(y^2-2y+1\right)+2=\left(x-2y+5\right)^2+\left(y-1\right)^2+2\ge2\)
\(minC=2\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1: Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức
a, M= x2-10x+3
b, N= x2-x+2
c, P=3x2-12x
Bài 2: Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức
a, M= 2x2-4x+3
b, N= x2-4x+5+y2+2y2
MONG MN GIÚP ĐỠ :3
Bài 1:
a: \(M=x^2-10x+3\)
\(=x^2-10x+25-22\)
\(=\left(x^2-10x+25\right)-22\)
\(=\left(x-5\right)^2-22>=-22\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x-5=0
=>x=5
b: \(N=x^2-x+2\)
\(=x^2-x+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{7}{4}\)
\(=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{7}{4}>=\dfrac{7}{4}\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x-1/2=0
=>x=1/2
c: \(P=3x^2-12x\)
\(=3\left(x^2-4x\right)\)
\(=3\left(x^2-4x+4-4\right)\)
\(=3\left(x-2\right)^2-12>=-12\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x-2=0
=>x=2
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của đa thức:
a) P=x2-2x+5
b)Q=2x2-6x
c) M=x2+y2-x+6y+10
a) \(P=x^2-2x+5\)
\(=x^2-2x+1+4\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)^2+4\ge4\)
\(MinP=4\Leftrightarrow x-1=0\Rightarrow x=1\)
b) \(Q=2x^2-6x\)
\(=2\left(x^2-3x\right)\)
\(=2\left(x^2-2.x.\frac{3}{2}+\frac{9}{4}-\frac{9}{4}\right)\)
\(=2\left(\left(x-\frac{3}{2}\right)^2-\frac{9}{4}\right)\)
\(=-\frac{9}{2}-2\left(x-\frac{3}{2}\right)^2\le\frac{-9}{2}\)
\(MinQ=\frac{-9}{2}\Leftrightarrow x-\frac{3}{2}=0\Rightarrow x=\frac{3}{2}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
M=x^2+y^2-x+6y+10
M=(x^2-x+1/4)+(y^2+6y+9)+3/4
M=(x-1/2)^2+(y+3)^2+3/4
\(minM=\frac{3}{4}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{2}\\y=-3\end{cases}}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của các biểu thức sau :
a,M=x2-3x+10
b,N=2x2+5y2+4xy+8x-4y-100
a) \(M=x^2-3x+10\)
\(M=x^2-2\cdot\dfrac{3}{2}\cdot x+\dfrac{9}{4}+\dfrac{31}{4}\)
\(M=\left(x^2-2\cdot\dfrac{3}{2}\cdot x+\dfrac{9}{4}\right)+\dfrac{31}{4}\)
\(M=\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{31}{4}\)
Mà: \(\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2\ge0\) nên: \(M=\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{31}{4}\ge\dfrac{31}{4}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra
\(\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{31}{4}=\dfrac{31}{4}\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-\dfrac{3}{2}=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
Vậy: \(M_{min}=\dfrac{31}{4}\) với \(x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
b) \(N=2x^2+5y^2+4xy+8x-4y-100\)
\(N=x^2+x^2+4y^2+y^2+4xy+8x-4y-120+16+4\)
\(N=\left(x^2+4xy+4y^2\right)+\left(x^2+8x+16\right)+\left(y^2-4y+4\right)-120\)
\(N=\left(x+2y\right)^2+\left(x+4\right)^2+\left(y-2\right)^2-120\)
Mà:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x+2y\right)^2\ge0\\\left(x+4\right)^2\ge0\\\left(y-2\right)^2\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\) nên \(N=\left(x+2y\right)^2+\left(x+4\right)^2+\left(y-2\right)^2-120\ge120\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x+2y\right)^2=0\\\left(x+4\right)^2=0\\\left(y-2\right)^2=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-4+2y=0\\x=-4\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=2\\x=-4\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-4\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(N_{min}=120\) khi \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-4\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (1)
a
\(M=x^2-3x+10=x^2-2.\dfrac{3}{2}.x+\dfrac{9}{4}+\dfrac{31}{4}\\ =\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{31}{4}\ge\dfrac{31}{4}\)
Min M \(=\dfrac{31}{4}\) khi và chỉ khi \(x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
b
\(N=2x^2+5y^2+4xy+8x-4y-100\\ =x^2+8x+16+y^2-4y+4+x^2+4xy+4y^2-120\\ =\left(x+4\right)^2+\left(y-2\right)^2+\left(x+2y\right)^2-120\ge-120\)
Min N \(=-120\) khi và chỉ khi \(x=-4\) và \(y=2\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Với những giá trị nào của x thì a) x3-x2+3x-30b) x3+x2+9x+90c) 4x3-14x2+6x-210d) x2(2x2+3)+2x2-3
Đọc tiếp
Với những giá trị nào của x thì a) x3-x2+3x-3>0b) x3+x2+9x+9<0c) 4x3-14x2+6x-21<0d) x2(2x2+3)+2x2>-3
a) \(x^3-x^2+3x-3>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)+3\left(x-1\right)>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+3\right)\left(x-1\right)>0\)
Mà: \(x^2+3>0\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>1\)
b) \(x^3+x^2+9x+9< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+1\right)+9\left(x+1\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+9\right)\left(x+1\right)< 0\)
Mà: \(x^2+9>0\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+1< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< -1\)
d) \(4x^3-14x^2+6x-21< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2\left(2x-7\right)+3\left(2x-7\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x^2+3\right)\left(2x-7\right)< 0\)
Mà: \(2x^2+3>0\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-7< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x< 7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< \dfrac{7}{2}\)
d) \(x^2\left(2x^2+3\right)+2x^2>-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^4+3x^2+2x^2+3>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^4+5x^2+3>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+1\right)\left(2x^2+3\right)>0\)
Mà:
\(x^2+1>0\forall x\)
\(2x^2+3>0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in R\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
a: =>x^2(x-1)+3(x-1)>0
=>(x-1)(x^2+3)>0
=>x-1>0
=>x>1
b: =>x^2(x+1)+9(x+1)<0
=>(x+1)(x^2+9)<0
=>x+1<0
=>x<-1
c: 4x^3-14x^2+6x-21<0
=>2x^2(2x-7)+3(2x-7)<0
=>2x-7<0
=>x<7/2
d: =>x^2(2x^2+3)+2x^2+3>0
=>(2x^2+3)(x^2+1)>0(luôn đúng)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Tìm giá trị lớn nhất (hoặc nhỏ nhất) của các biểu thức sau:
a. A = x2 – 6x + 11
b. B = 2x2 + 10x – 1
c. C = 5x – x2
A = x2 - 6x + 11
Nhập phương trình vào máy tính lặp 3 lần dấu =
GTNN của A = 3
B = 2x2 + 10x - 1
Nhập phương trình vào máy tính lặp 3 lần dấu =
GTNN của B = \(-\frac{5}{2}\)
C = 5x - x2
=> C = -x2 + 5x
Nhập phương trình vào máy tính lặp 3 lần dấu =
GTLN của C = \(\frac{5}{2}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)